Ways To Include Good Quality Carbohydrates In Your Diet:
- Choose wholegrain breads and cereals.
- Have fruit whole, rather than as a juice. Eating an apple with the skin on, for example, will provide more fibre than drinking a glass of apple juice.
- Ring the changes with quinoa and bulgur wheat as an alternative to pasta.
- Try seeds, nuts and pulses as lower carb sources of fibre;
- Choose unsweetened milk and yogurts
How To Calculate Net Carbs
Whether to count net or total carbs is a controversial topic within the low-carb community.
For starters, the term net carbs isnt officially recognized or agreed upon by nutrition experts. In addition, due to conflicting and outdated information, figuring out how to calculate net carbs can be confusing.
In fact, the net carb claims on packaged foods may not reflect the number of carbs your body actually absorbs.
Luckily, knowing how your body processes different types of carbs may help you achieve your target blood sugar, weight loss and health goals.
This article looks at the science behind net carbs, provides simple calculations for determining your intake and discusses the pros and cons of counting net carbs.
Whats The Difference Between Mmol/l And Mg/dl
Both sets of units are used to measure blood sugar levels and both give a measurement of the concentration of glucose in the blood, albeit in slightly different ways.
mmol/L gives the molarity, which is the number of molecules of a substance within a specified volumen, in this case within 1 litre. mg/dL gives the concentration by the ratio of weight to volumen, in this case milligrams per decilitre.
mmol/L is the most common measurement used in the UK with mg/dL predominantly used in the USA and continental Europe.
- mg/dL Unit for measuring concentration of glucose in the blood in the USA milligrams per decilitre. : Milligrams per 100 millilitres
Blood glucose typically varies from 4 mmol/L to 6 mmol/L for people without diabetes.
Blood sugar needs to be tightly controlled in the human body to minimise the risk of complications developing.
- Formula to calculate mmol/l from mg/dl: mmol/l = mg/dl / 18
- Formula to calculate mg/dl from mmol/l: mg/dl = 18 × mmol/l
You May Like: How To Treat Low Blood Sugar
What’s The Deal With Net Carbs On Keto Learn How To Calculate Net Carbs The Difference Between Total Carbs Vs Net Carbs How To Read Them On Labels The Carb Impact Of Sweeteners And More
Despite all the popular terminology surrounding the keto diet, net carbs remains elusive. Many nutrition labels dont clearly label them, but theyre important to keep in mind if youre tracking carb intake. This begs the question: What are net carbs, are total carbs vs net carbs the same thing, and why should you know how to calculate them ?
This article does the deep diving for you. Youll learn how to figure net carbs, the difference between total carbs vs net carbs, how sugar alcohols impact carb counts, and a handy net carb calculator to determine the ideal amount you should have each day.
Looking for the net carb calculator? Jump to the net carb calculator!
Carbs And Blood Sugar
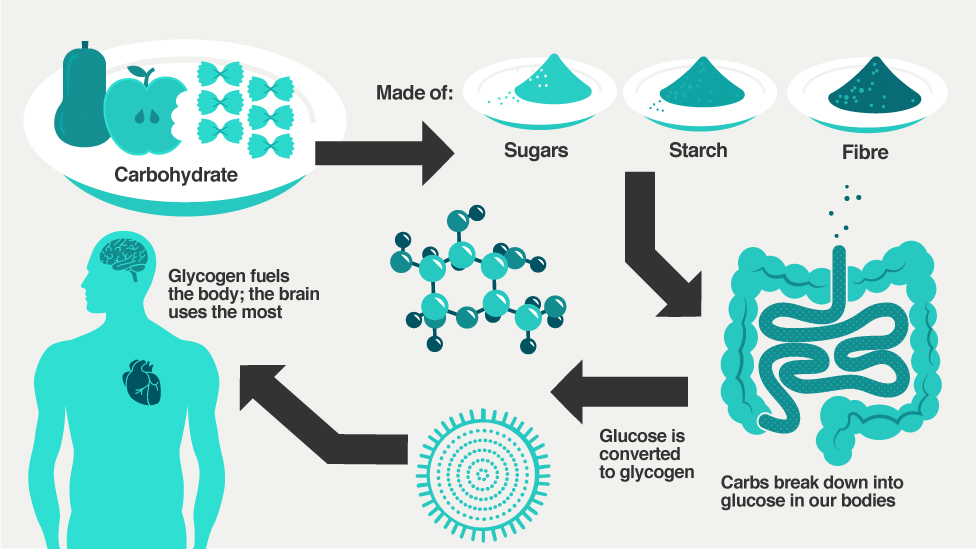
Keeping your blood sugar levels on track means watching what you eat, plus taking medicines like insulin if you need to. Your doctor may also have mentioned that you should keep track of how many carbohydrates you eat. But what exactly are carbohydrates and how do they affect your blood sugar?
The foods we eat contain nutrients that provide energy and other things the body needs, and one of these is carbohydrates. The two main forms of carbohydrates are:
The body breaks down or converts most carbohydrates into the sugar glucose. Glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream, and with the help of a hormone called insulin it travels into the cells of the body where it can be used for energy.
People with diabetes have problems with insulin that can cause blood sugar levels to rise. For people with type 1 diabetes, the pancreas loses the ability to make insulin. For people with type 2 diabetes, the body can’t respond normally to the insulin that is made.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Normal Blood Sugar Range For Adults
Examples Of Sugar Alcohols Include:
- Sorbitol
- Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysates
Heres what you need to know:
Because sugar alcohols are harder for the body to digest, the effect on blood sugar levels is less than sugar. Sugar alcohols have about half the amount of calories compared with sugar and other types of carbohydrates. When counting carbohydrates for products made with sugar alcohols, subtract half of the grams of sugar alcohol listed on the food label from the total grams of carbohydrate.
Remember that because sugar alcohols are harder for your body to digest, eating too many sugar alcohols may cause digestive complaints like gas, cramping and diarrhea. So while it is safe to eat products with sugar alcohols, it is best to limit the amount.
Now lets practice counting carbohydrates using the sample food label shown here:
- Locate the total carbohydrate in one serving. You will see that the total carbohydrate is 29 grams.
- The amount of sugar alcohol is 18 grams per serving.
- Calculate half the grams of sugar alcohol .
- Subtract only half of the grams of sugar alcohol from the total carbohydrate Count this product as 20 grams of carbohydrate .
View a printer-friendly Guide to Sweeteners.
They Promote Digestive Health
Unlike sugars and starches, dietary fiber is not broken down into glucose.
Instead, this type of carbohydrate passes through the body undigested. It can be categorized into two main types of fiber: soluble and insoluble.
Soluble fiber is found in oats, legumes and the inner part of fruits and some vegetables. While passing through the body, it draws in water and forms a gel-like substance. This increases the bulk of your stool and softens it to help make bowel movements easier.
In a review of four controlled studies, soluble fiber was found to improve stool consistency and increase the frequency of bowel movements in those with constipation. Furthermore, it reduced straining and pain associated with bowel movements .
On the other hand, insoluble fiber helps alleviate constipation by adding bulk to your stools and making things move a little quicker through the digestive tract. This type of fiber is found in whole grains and the skins and seeds of fruits and vegetables.
Getting enough insoluble fiber may also protect against digestive tract diseases.
One observational study including over 40,000 men found that a higher intake of insoluble fiber was associated with a 37% lower risk of diverticular disease, a disease in which pouches develop in the intestine (
9 ).
As viscous soluble fiber passes through the small intestine, it binds to bile acids and prevents them from being reabsorbed. To make more bile acids, the liver uses cholesterol that would otherwise be in the blood.
Also Check: Is Honey Better Than Sugar
How Do You Use The Food Label To Count Carbohydrates
Looking at a food label, find the serving size and the total carbohydrate in that one serving. Note: Total carbohydrate includes sugar, starch, and fiber. Use the grams of total carbohydrate when carbohydrate counting.
To calculate the number of carbohydrate choices in that particular serving, simply divide the amount of total carbohydrate by 15.
Refer to the following information to assist with calculating carbohydrate choices:
- Grams of Carbohydrate 0-5
Carbohydrate Digestion And Absorption
*This content has been reviewed by Dr. David Kitts
Dietary carbohydrates include starches, sugars, and fibre.
- Use of Dietary Carbohydrates as Energy. Glucose is the primary energy source of the body. Major dietary sources of glucose include starches and sugars.
- Digestion of Carbohydrates. Dietary carbohydrates are digested to glucose, fructose and/or galactose, and absorbed into the blood in the small intestine.The digestion and absorption of dietary carbohydrates can be influenced by many factors.
- Absorption of Carbohydrates. Absorbed carbohydrate molecules are used immediately for energy or stored in various forms in the muscles, liver or adipose tissue for future use.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Test Your Blood Sugar
Why Do I Need Carbohydrates
When you eat carbs, your body breaks them down into simple sugars, which are absorbed into the bloodstream. As the sugar level rises in your body, the pancreas releases a hormone called insulin. Insulin is needed to move sugar from the blood into the cells, where the sugar can be used as a source of energy.
When it occurs more slowly, as with a whole-grain food, you’ll feel satisfied longer because it takes longer for your body to break down the complex carbohydrates in whole-grains into simple sugars. These types of complex carbohydrates give you energy over a longer period of time.
The carbs in some foods cause the blood sugar level to rise more quickly than others. How fast or slow carbohydrates are turned into blood glucose are measured on the glycemic index. If youre healthy, carbohydrates turn into glucose , which your body uses for energy. But if your blood glucose levels become too high or too low, it could be a sign that your body can have trouble producing the insulin that it needs to stay healthy which can eventually result in diabetes.
Learn To Estimate Food Portions
A very practical technique for counting carbohydrates is the portion conversion method. Portion conversion involves estimating the volume of a serving of food by comparing it to a common object such as your fist, a soft drink can or a milk carton, and then converting the volume into a carbohydrate count based on the typical carbohydrate content for a known amount of that type of food. This approach is particularly useful when having a complex meal , dining out, or eating foods that vary in size .
Heres an example of how it works: You know that one cup of cooked pasta contains about 40 grams of carbohydrate. Next, you estimate that the portion of pasta youre about to eat is 1 1/2 cups by visually comparing the amount of pasta on your plate to a 12-ounce soft drink can. You then do the math to determine that youre about to eat 60 grams of carbohydrate.
Here are some common measuring devices that can be used to mentally calculate portions:
Average adults fist = 1 cupBaseball = 1 cup
Read Also: What Artificial Sweetener Tastes The Most Like Sugar
What Types Of Carbohydrates Turn To Sugar
Related Articles
The three types of carbohydrates are sugar, starch and fiber. During the digestive process, both sugars and starches are turned into the sugars that the body uses for energy. People lack the enzymes needed to digest fiber, so it passes through the digestive tract without turning into to sugar.
Which Foods Contain Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate is found, to varying degrees in a wide variety of food, notably in starchy foods such as rice, pasta and flour .
Sugar is also a form of carbohydrate.
Carbohydrate is generally found in all fruits and vegetables, however, the amounts of carbohydrate can vary substantially.
Carbohydrate is generally found, at least to some degreen, in all fruits and vegetables
However, the amounts of carbohydrate can vary substantially with vegetables such as celery having almost negligible carbohydrate whilst potatoes and citrus fruits typically have a higher amount of carbs.
Fruit and vegetables with relatively high carbohydrate content include:
- Potatoes
- Pears
Recommended Reading: What Should Fasting Blood Sugar Be
Factors Affecting Carbohydrate Digestion
The glycemic index measures how much a particular carbohydrate-containing food increases blood-glucose levels or how quickly carbohydrates are turned into sugar. Foods with a low glycemic index are more slowly digested, so they don’t cause large spikes in blood sugar levels. Foods containing protein and fiber are digested more slowly, and if you combine foods with a high glycemic index with those that have a lower glycemic index, it also slows digestion.
References
Good Carbs Bad Carbs: What You Need To Know
“The Healthy Geezer” answers questions about health and aging in his weekly column.
Question: ;What exactly is the difference between good carbs and bad carbs?
Answer: Here’s the short answer: Good carbs or carbohydrates are good for you. Bad carbs aren’t.
Carbohydrates that come from white bread, white rice, pastry, sugary sodas and other highly processed foods can make you fat. If you eat a lot of these so-called bad carbs, they will increase your risk for disease.
On the other hand, the good carbs, including whole grains, beans, fruits and vegetables, keep you healthy by providing you with vitamins, minerals, fiber and many other nutrients. That’s why a healthy diet should include good carbs.
Carbohydrates are the most important source of energy for your body. Your digestive system converts carbohydrates into blood sugar . Your body uses the glucose and stores any extra sugar for when you need it.
Carbohydrates were once grouped into two main categories simple and complex. Simple carbohydrates included sugars such as fruit sugar , corn or grape sugar and table sugar . Complex carbohydrates included everything made of three or more linked sugars. Complex carbohydrates were thought to be the healthiest to eat. Now there are questions about that assumption.
However, other studies have found that the glycemic index has little effect on health or weight. As a result, more research on the glycemic index is needed.
2. Use whole grain breads for lunch or snacks.
Don’t Miss: What Happens To Your Body When You Cut Out Sugar
Convert Carbs To Grams Of Sugar
I know that digestible carbs end up as sugar in the blood stream. what i dont know is how to convert the amounts. if you eat 10 grams of carbs, how many grams of sugar does that end up being in the blood?. Subtract half the grams of sugar alcohols from the total carbohydrate count, since sugar alcohols affect blood glucose half as much as ordinary carbohydrates. for example, a food item containing 17 g total carbohydrate and 8 g of sugar alcohols should be counted as 13 g carbohydrate .. When people eat a food containing carbohydrates, the digestive system breaks down the digestible ones into sugar, which enters the blood. as blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that prompts cells to absorb blood sugar for energy or storage..
1 kilogram is equal to 7716.1791764707 calories, or 1000 grams. note that rounding errors may occur, so always check the results. use this page to learn how to convert between calories and grams.. Measuring your ingredients by weight can help make your ingredient amounts are accurate. its especially true in bakingthink how much flour you can fit in a measuring cup depending on how much you pack it.. How to convert grams of sugars into teaspoons to one teaspoon. to be precise, 4.2 grams equals a visualize how many teaspoons of sugar are. americans eat over 355 extra calories a day from added sugar, says the american heart association. one gram of sugar contains 3.87 calories
Why Is Sugar Bad For You
Added, refined sugars in readily available processed foods are a health risk, not fruit, vegetables, and grains.
Its fair to say that when we mention carbohydrates, most people think of sugar. Although they may be partly correct, as this article shows, not all carbohydrates are bad. In fact, some are essential for the health of many of our body systems.
When we talk of bad sugar, we are mostly referring added sugar or free sugars that are used by manufacturers to flavour foods: these are the ones we need to become more conscious of when selecting foods to eat.
Sugars which occur naturally, like those in fruit, vegetables, and milk, are not harmful like free sugars, and we dont need to reduce our intake of them. Nowadays, most individuals consume more added sugar than the recommended amounts.
For example, its easy to exceed the daily recommended limit for added sugars: a soft drink with lunch, a chocolate bar for your afternoon snack When you add it all up, its easy to exceed the limit.
Its these added sugars that can be detrimental to our health, especially when you look at the science. Studies highlight significant links between diets high in refined sugars and obesity, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.
Diets high in sugar put stress on the bodys mechanism for regulating blood glucose levels. This is managed by insulin, a hormone that signals to the liver, muscles, and fat cells that its time to store sugar as energy.
You May Like: How To Lower Sugar Levels Fast
Factors That Affect Absorption Of Carbohydrates
A number of factors affect carbohydrate digestion and absorption, such as the food matrix and other foods eaten at the same time .;;
Glycemic Index is a scale that uses a numbering system to rank carbohydrate rich foods as high GI, medium GI, and low GI based on the rate that glucose-containing carbohydrates are digested and absorbed, and the rate they increase blood glucose levels . Foods with a high GI are more quickly digested, and cause a larger increase in blood glucose level compared to foods with a low GI. Foods with a low GI are digested more slowly and do not raise blood glucose as high, or as quickly, as high GI foods. Examples of factors that affect carbohydrate absorption are described in the table below:
For more information, additional resources include:;