What Are Good Numbers For A Type 2 Diabetes
Know Your Numbers: Blood Pressure People with diabetes are much more likely to develop heart disease, so monitoring heart disease risk factors is a vital part of diabetes self-management. People with diabetes should keep their blood pressure below 140/80 mmHg. Taking blood pressure medications as directed, reaching or maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding foods high in sodium can help keep blood pressure under control.
How Can High Blood Sugar Levels In The Morning Be Controlled
Once you and your doctor determine how your blood sugar levels are behaving at night, he or she can advise you about the changes you need to make to better control them. Options that your doctor may discuss depend on the cause of the morning high blood sugars.
For dawn phenomenon:
- Changing the timing or type of your diabetes medications
- Eating a lighter breakfast
- Increasing your morning dose of diabetes medication
- If you take insulin, switching to an insulin pump and programming it to release additional insulin in the morning
For Somogyi effect:
You May Like: What Raises Your Blood Sugar
Why Is Dehydration The Key Issue In Honk
Many people think that you can go into a diabetic coma if you dont take care of your diabetes. However, that is only partially true. People who dont take care of their diabetes are at risk for HONK, but you only go into a diabetic coma if you are dehydrated. If you are diabetic and become very dehydrated, you can go into a diabetic coma from high blood sugar even when you take good care of diabetes.
Just because you went into a diabetic coma from high blood sugar doesnt mean you have poorly controlled diabetes. This is a simple fact that even many healthcare providers fail to understand. That is because we have been led to believe that bad things only happen to people with diabetes when they dont take care of themselves. It may be true regarding long-term consequences of diabetes, but its not true for a diabetic coma from high blood sugar. As I will explain shortly, it can happen to anyone with diabetes.
You May Like: What Is The Highest Your Blood Sugar Can Go
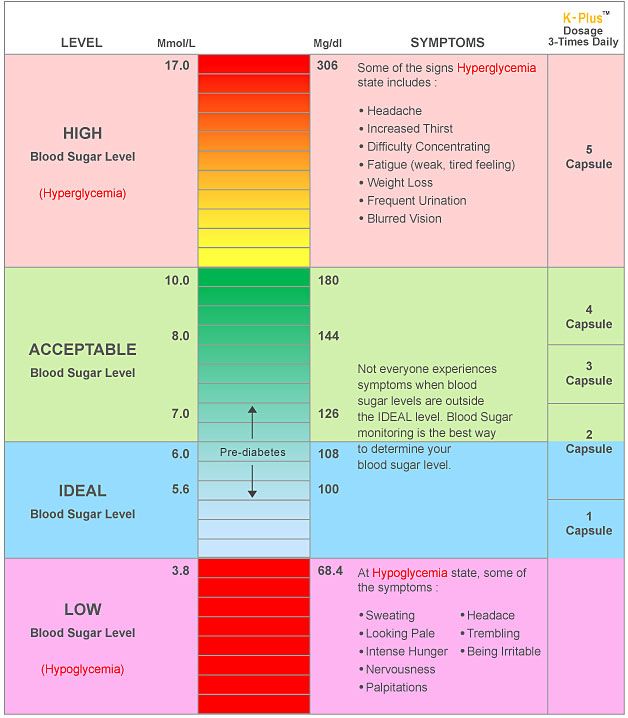
Types Of High Blood Sugar
There are two different main types of high blood sugar or hypoglycemia. Fasting hyperglycemia is measured when the patient has not eaten for at least eight hours.
Patients with a blood glucose level higher than 130 milligrams per deciliter are considered to have fasting hyperglycemia.
Postprandial hyperglycemia, or reactive hyperglycemia, occurs after eating. In patients with postprandial hyperglycemia, the liver does not stop producing sugar as it normally would after a meal, and it stores the extra sugar.
A blood glucose level over 180 mg/dL, taken one to two hours after eating, is considered reactive hyperglycemia.
How To Stabilize Your Blood Sugar Overnight
The most important thing you can do to stabilize your blood sugar is monitor your glucose levels at bedtime, during the night, and when you wake up to look for patterns. This will help you determine whats going on in your body and how you can fix it. While there are many strategies people use to stabilize blood sugar at night, every person is different youll have to look for trends in your body, experiment with ways to lower glucose levels over a period of time, and learn what works best for your body.
-
Check your blood sugar before bed. If its already high, your blood sugar levels may remain high throughout the night. To address this, youll want to start by adjusting when you eat your evening meal and what it consists of, and how much mealtime insulin you take to cover it.
-
Avoid eating lots of food close to bedtime. For diaTribe writer Adam Brown, the key to staying in range overnight is low-carb, early dinners, with no snacking after dinner.
-
Consider eating less food at night and taking more basal insulin to cover your evening meal.
Check your blood sugar during the night, between midnight and 3am. If you were in range before bed but have high glucose levels between midnight and 3am, you may need to adjust your basal insulin dosage and timing. If you are low during that time, you may experience a rebound high blood sugar later on this is usually associated with overcorrecting the low.
Also Check: How Do You Cut Out Sugar In Your Diet
How Do You Treat Hypoglycemia
Low blood sugar levels happen when theres too little glucose left in the bloodstream to continue supplying fuel to your organs, muscles, and tissues. It most often occurs when you dont eat enough food, especially carb-containing foods, given your blood-sugar-lowering medications and physical activity levels, ONeill says. Levels can decrease gradually or suddenly.
When the amount of glucose in the bloodstream drops to too-low levels, the body reacts by releasing epinephrine, also called adrenaline or the fight or flight hormone. Epinephrine revs your heart rate and can cause sweating, shaking, anxiety, and irritability. If not enough glucose is able to reach the brain, the result may be difficulty concentrating, confused thinking, and slurred speech. In extreme cases, a lack of glucose within the brain can lead to seizures, coma, and even death, she says.
People with low glucose levels can use the ADAs 15-15 Rule, which advises people consume 15 g of carbs, wait 15 minutes, and check their levels again. If the number is still low, repeat until reaching at least 70 mg/dL.
You can find 15 g of carbs in:
- 1 slice of bread
- 1 small piece of fresh fruit
- cup of yogurt
- Three to four hard candies
- Glucose tablets as indicated on the label
- Glucose gel as indicated on the label
Once your glucose levels are back to normal, the ADA suggests going ahead and eating your next scheduled meal or snack, which will help prevent levels from dropping again.
About High Blood Sugar
High glucose levels occur when the body doesn’t have enough insulin or can’t properly use the insulin it has to shuttle glucose from the bloodstream to the bodys muscles, organs, and tissues for fuel, ONeill says. As a result, the amount of sugar in the blood builds up.
Hyperglycemia typically happens when you consume more carbohydrates or bigger portions of food than usual if you don’t take enough insulin or other diabetes medication as prescribed and if you decrease your levels of physical activity, she says. Heightened stress levels can also increase blood sugar levels. Non-diabetes-related medications that are known to raise blood sugar levels include steroids, beta-blockers, birth control pills, and many mental health medications, she explains.
Signs of high blood sugar include frequent urination, fatigue, dry or itchy skin, feeling thirsty, more frequent infections, and eating more food but not gaining as much weight as usual, says Athena Philis-Tsimikas, MD, the corporate vice president for the Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute in La Jolla, California.
High blood sugar levels can cause these symptoms through various mechanisms, according to the Mayo Clinic. For example, high blood sugar levels damage blood vessels and nerves throughout the body. They can also deprive organs of energy and can cause fluid to accumulate in the eyes. And in an attempt to get your blood sugar to a healthier level, your body will often increase urine output.
Also Check: When I Test My Blood Sugar What Should It Be
High Calorie Foods May Or May Not Cause The Blood Sugar Level To Rise
Many people think that all high-calorie foods raise blood sugar level, but this is not always the case.
In general, foods that cause blood sugar level to rise the most are those that are high in carbohydrates, which are quickly converted into energy, such as rice, bread, fruits and sugar. Next are foods high in protein, such as meats, fish eggs, milk and dairy products, and oily foods. However, even though carbohydrates affect blood sugar levels, if you don’t eat them your diet will be unbalanced and you won’t feel satisfied after your meal, which can lead to excessive consumption of foods rich in protein and fat.
Food containing three major nutrients
| Carbohydrates |
|---|
Why Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
There are many factors that can cause your blood sugar to increase at night. For example: what food you ate during the day, how much and when you exercised, whether you ate snacks before bed, the timing of your insulin doses, and your stress level. You can experience different patterns of high blood sugar at night. You may start with high glucose when you go to bed, start the night in range but go high several hours later, or spend most of the night in range until the hours just before you wake up. By identifying your bodys patterns, you can figure out what is causing your high blood sugar and how to address it.
Common causes of a glucose increase at night include:
Also Check: Does Truvia Affect Blood Sugar
What Is High Blood Sugar
Elevated blood sugar levels are known as hyperglycemia. Blood sugar levels are measured using a small sample of blood that is tested in a lab. Blood sugar can also be tested using at home devices such as a handheld glucometer. Levels that indicate hyperglycemia are indicative of prediabetes and both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
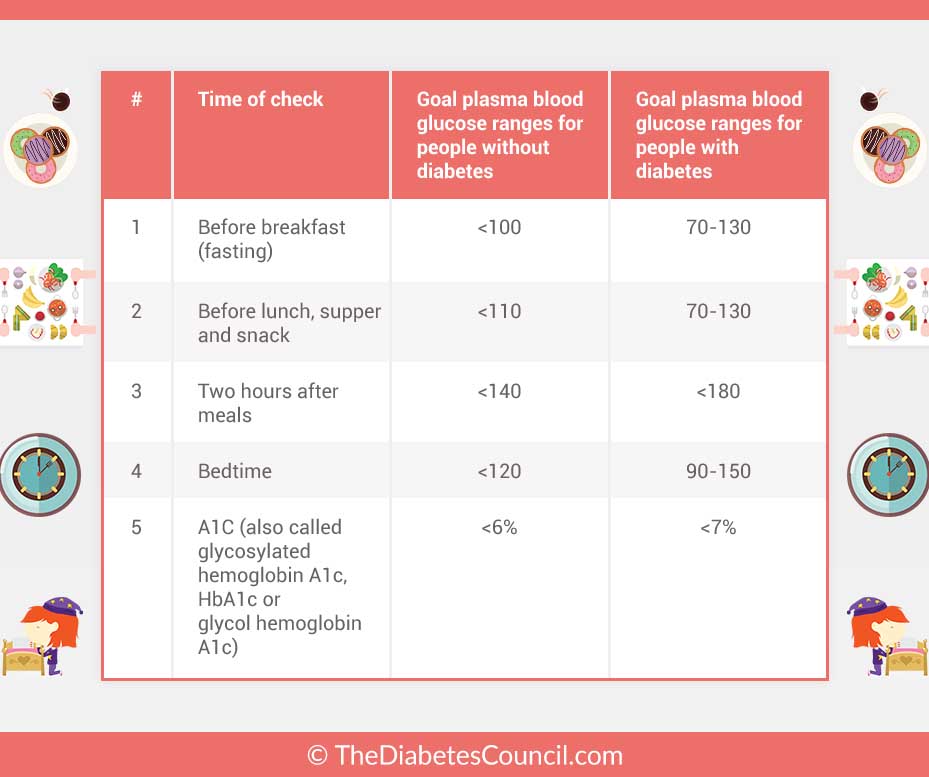
Normal ranges of blood sugar will vary depending on the test being done. In general, a normal fasting glucose level will be between 70-100 mg/dL. After a meal, these levels are expected to rise slightly around 1 to 2 hours after the beginning of a meal, but should be less than 180 ml/dL.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is important not only for metabolic health, but heart health too. Over time, high blood sugar can damage blood vessels and the nerves that control your heart. People with diabetes are also more likely to have other conditions that raise the risk for heart disease:
- High blood pressure increases the force of blood through your arteries and can damage artery walls. Having both high blood pressure and diabetes can greatly increase your risk for heart disease.
- Too much LDL cholesterol in your bloodstream can form plaque on damaged artery walls.
Read Also: Sugar Tablet Before Or After Food
High Blood Sugar: Causes Complications And How To Lower Blood Sugar
Your body breaks down glucose for energy using the insulin produced by the pancreas. This is required for our bodies to function. Illness can have an impact on the way our pancreas functions. Read this to learn how high blood sugar can affect your health.
7 minute read
Your body requires energy to function, and this energy comes from food. Specifically, your body breaks down glucose for energy using the insulin produced by the pancreas.
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes cause impairment to this breakdown of sugar in the body, causing blood glucose levels to become irregular. When glucose is not broken down into energy, it can build up in the bloodstream and then becomes a health problem.
Your pancreas produces insulin, which breaks down glucose. With type 1 diabetes, the cells that produce insulin are mistakenly attacked by your immune system. As a result of this autoimmune condition, blood sugar levels can become dangerously high without intervention.
Type 2 diabetes occurs when your body no longer responds to insulin as well as it should and then also causes glucose to accumulate in the blood.
Dont Miss: How To Come Sugar Disease
Recommended Reading: How To Kill Black Sugar Ants
What Are The Symptoms Of Hyperglycemia
Its especially important to know the early signs of hyperglycemia if you have type 1 diabetes. If hyperglycemia is left untreated in people with type 1 diabetes, it can develop into ketoacidosis, where ketones, which are toxic acids, build up in the blood. This condition is an emergency situation that can lead to coma or death.
Early symptoms of hyperglycemia include:
- High blood sugar.
- Unusual fruity smell on the breath.
- Deep labored breathing or hyperventilation.
- Rapid heartbeat.
Moderate Versus Tight Glycemic Control
Glycemic goals within the hospital setting have changed in the last 14 years. The initial target of 80110 mg/dL was based on a 42% relative reduction in intensive care unit mortality in critically ill surgical patients . However, a meta-analysis of over 26 studies, including the largest, Normoglycemia in Intensive Care EvaluationSurvival Using Glucose Algorithm Regulation , showed increased rates of severe hypoglycemia and mortality in tightly versus moderately controlled cohorts . This evidence established new standards: initiate insulin therapy for persistent hyperglycemia greater than 180 mg/dL . Once insulin therapy is initiated, a glucose target of 140180 mg/dL is recommended for most critically ill patients . More stringent goals, such as 110140 mg/dL may be appropriate for select patients, such as cardiac surgery patients , and patients with acute ischemic cardiac or neurological events provided the targets can be achieved without significant hypoglycemia.
A glucose target between 140 and 180 mg/dL is recommended for most patients in noncritical care units . Patients with a prior history of successful tight glycemic control in the outpatient setting who are clinically stable may be maintained with a glucose target below 140 mg/dL . Conversely, higher glucose ranges may be acceptable in terminally ill patients, in patients with severe comorbidities, and in in-patient care settings where frequent glucose monitoring or close nursing supervision is not feasible.
You May Like: How To Get Electrolytes Without Sugar
What Are Blood Sugar Targets
A blood sugar target is the range you try to reach as much as possible. These are typical targets:
- Before a meal: 80 to 130 mg/dL.
- Two hours after the start of a meal: Less than 180 mg/dL.
Your blood sugar targets may be different depending on your age, any additional health problems you have, and other factors. Be sure to talk to your health care team about which targets are best for you.
Why Your Blood Sugar Level May Be Low
If blood sugar drops below 70 mg/dL, it is below normal levels. This can be caused by a variety of factors, such as:
- Not eating enough or missing a meal or snack
- Reducing the amount of carbohydrates you normally eat
- Alcohol consumption especially if youre drinking on an empty stomach
- Taking too much insulin or oral diabetes medication based on carbohydrates or activity levels
- Increased physical activity
- Side effects from medications
If you have diabetes, keep your blood glucose meter and sources of fast-acting glucose close by in case your blood sugar drops. This is especially important for people with hypoglycemia unawareness, which is a condition that causes symptoms of low blood sugar to go unnoticed.
Eating balanced meals and snacks at regular times throughout the day is a big part of maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Check out our article on meal planning for diabetes to better understand the three macronutrients where calories come from and which have the biggest effect on blood sugar.
Meal Planning for Diabetes: How to Optimize Your Diet >
Everyone will respond differently to certain factors, which is why its important to have individualized target glucose levels. To help you reach your target blood glucose goals, work with your healthcare provider to discuss modifications to your diet, physical activity, or medications, and alert them of other factors like a recent illness or stressful event.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Tell When Your Blood Sugar Is Low
Low Blood Sugar And Driving
Having a low blood sugar while driving could be dangerous for you and others.
You can usually still drive if youre at risk of low blood sugar. But youll need to take extra precautions to reduce the chance of this happening while driving.
You also need to tell the Driver & Vehicle Agency and your car insurance company about your condition.
For more information, see:
What Causes High Blood Sugar Levels
Managing diabetes is like a three-way balancing act because you have to watch:
All three need to be balanced. If any one of these is off, blood sugar levels can be too. In general, higher than normal blood glucose levels can be caused by:
- not taking your diabetes medicine when you’re supposed to or not taking the right amounts
- not following the meal plan
- not getting enough exercise
- having an illness, like the flu
- taking other kinds of medicines that affect how your diabetes medicines work
A single high blood sugar reading usually isn’t cause for alarm it happens to everyone with diabetes from time to time. But if you have high blood sugar levels a lot, let your parents and your diabetes health care team know. Insulin or meal plans may need adjusting, or you may have an equipment issue, like an insulin pump that isn’t working right. Whatever the case, make sure you get help so you can get your blood sugar levels back under control.
Read Also: Does Moringa Lower Blood Sugar
How Can I Measure My Blood Sugar Levels
You can measure your blood glucose levels with a glucometer. First, you prick your finger with a small device called a lancet to get a drop of blood. Your blood goes on a test strip which you put into the glucometer. Then, the device tells you your blood sugar levels.
You can also use a continuous glucose monitoring device, which uses a sensor thats placed under your skin to automatically check your levels every few minutes.
You May Like: Are Bed Bugs Attracted To Certain Blood Types
Supporting Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels during the day is a good way to prevent high blood sugar at night. That means exercising regularly, taking the right amount of diabetes medications if you use them, and managing stress levels.
Lack of sleep itself is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, so it is important to maintain a healthy sleep cycle as part of a healthy lifestyle.
Read Also: How To Bring Your Blood Sugar Level Down