Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
A fasting plasma glucose test is taken after at least eight hours of fasting and is therefore usually taken in the morning.
The NICE guidelines regard a fasting plasma glucose result of 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l as putting someone at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, particularly when accompanied by other risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
The Best Healthcare Options To Prevent Diabetes
Health care is expensive. Canada spent an estimated $253.5 billion in 2018, and as the cost of health care increases, so does the cost to you. Pre-existing medical conditions, family history, and BMI are all factors that increase the cost of health care. These factors also increase your risk of diabetes, so you must be covered.
Of course, as a Canadian, you are entitled to some free and subsidized health care, which is great. But many people opt for private healthcare and for diabetes prevention this can be very useful. If you’re shopping around for private healthcare, it’s important to choose the right package.
Basic health insurance will usually cover health care, medical services, and prescriptions, but they tend to lack customizations. If you opt for a premium/guaranteed health insurance you have the bonus of a custom plan based on your needs if you are worried about your risk of diabetes this is like gold dust.
Private healthcare plans can cover the cost of many expenses related to diabetes such as blood tests, blood sugar monitors, specialist referrals, hospital stays, and much more! The most important thing to note about private health care is that it covers costs for preventative care, not just treatment for diseases.
There are many different options available, so make sure you search for the best quotes.
How Does Blood Sugar Level Work
With a lack of nutrients and food that contain glucose, the blood sugar level will begin to decline. This is known as hypoglycemia.
After blood sugar becomes low, the pancreas releases a peptide hormone called glucagon. When this happens, the glucose that is stored in the body for energy is instructed to release due to the liver. This causes the glucose to turn into glycogen, known as the glycogenesis process. This is what can help a body to regain energy as the readily stored glycogen, in the liver and muscles, will release into the body.
On the other hand, the blood sugar can also rise and become too high which is known as hyperglycemia.
When the body does not produce enough of the insulin hormone, blood sugar levels begin to increase. This is because glucose relies on the insulin hormone to help it absorb into the bloodstream. Usually, this occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin, known as type 1 diabetes, or does not respond to insulin correctly, known as type 2 diabetes.
Eating too many processed foods can also cause your blood sugar level to rise. If there is not enough insulin present in the body, too much bad food can cause your blood sugar level to build up.
For those with a normal blood sugar level, this will be due to eating the right foods and your body being able to produce and respond to insulin.
You may be wondering what exactly causes an imbalance in blood sugar levels, so here is a roundup:
Read Also: How To Get Off Sugar And Carbs
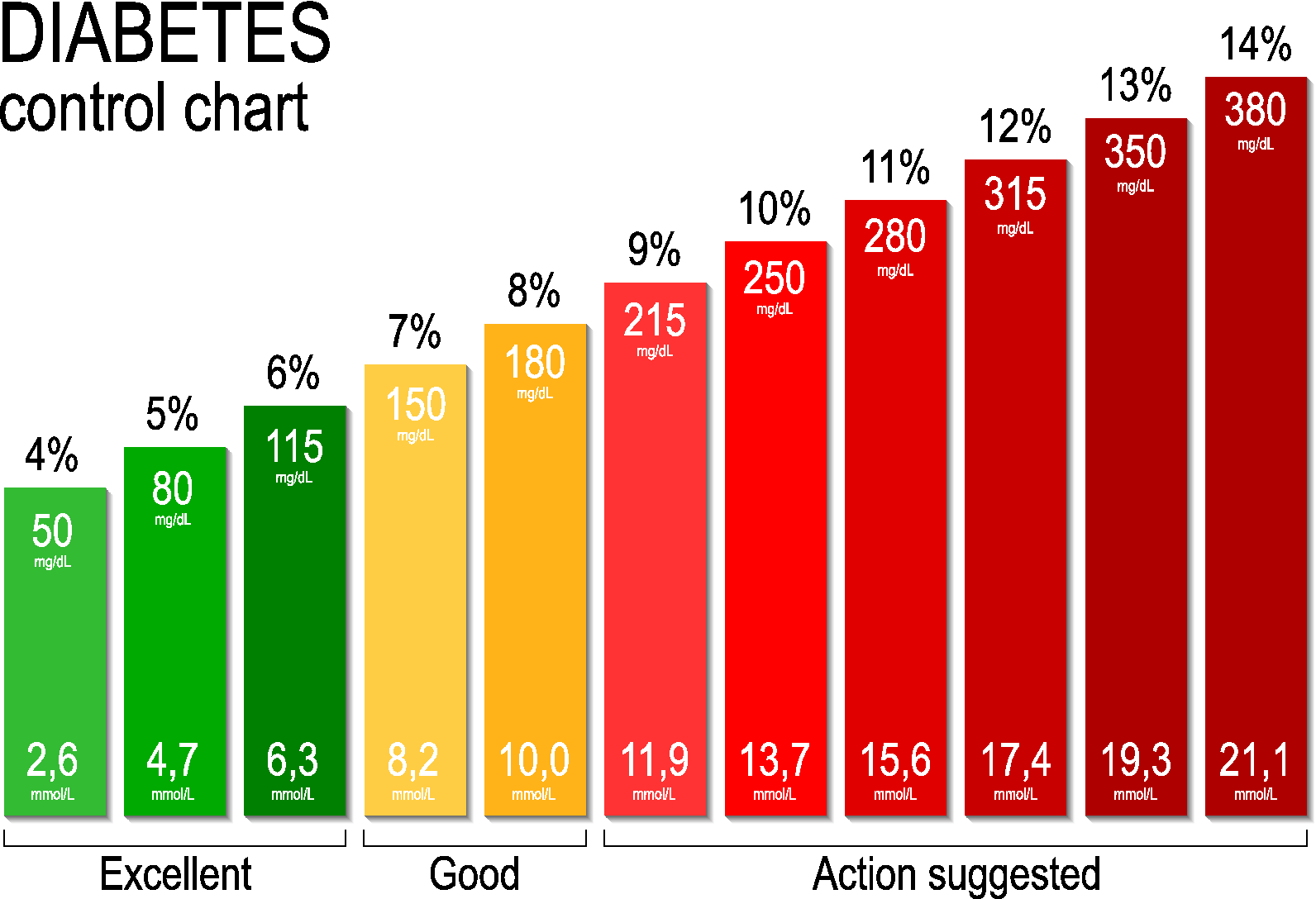
Blood Sugar Chart: Summary
The fasting blood sugar, 2-hour post-meal blood sugar, and HbA1C tests are important ways to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes, as well as indicate how well a persons diabetes is being managed. If you think you have diabetes, its important to not try and diagnose yourself by doing a finger-stick with a home blood glucose meter. There are strict standards and procedures that laboratories use for diagnosing diabetes therefore, you should get tested at your doctors office or at a laboratory.
Its also important to talk with your doctor to make sure you understand a) how often you should have certain tests, such as a fasting blood glucose or HbA1C test b) what your results mean and c) what your blood sugar and HbA1C targets are.
If you have not been previously diagnosed with prediabetes or diabetes but your results are above normal, your doctor may recommend other tests and should discuss a plan of treatment with you. Treatment may include lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, a healthy eating plan, and regular physical activity. You may need to start taking diabetes medications, including insulin. If you are diagnosed with diabetes, its recommended that you learn how to check your blood sugars with a meter so that you and your healthcare team can determine how your treatment plan is working for you.
How To Choose A Blood Glucose Meter
There are many blood sugar meters to choose from, so start by thinking about what’s most important to you. Ask yourself a few questions.
- Are you concerned about accuracy? Make sure you’re using a meter and test strips that provide accurate results. Roche quality control processes ensure consistent accuracy. Find out more about our accuracy commitment.
- Do you use blood glucose results to dose insulin? The Accu-Chek Guide meter sends results directly to a smartphone app that includes an insulin calculator.5
- Do you feel like you’re always short on time? A system that syncs your data wirelessly, without manually entering results, can save time with every test. You may also want to consider a blood glucose meter that gives results quickly, makes it easier to handle test strips, doesn’t require coding, or simplifies lancing or dosing.
- Would you like to reduce the pain of testing? Choose a system with a lancing device specifically designed for comfort, such as the Accu-Chek FastClix lancing device. Precision-guided technology minimizes the lancet’s painful side to side motion and thin-gauge, bevel-cut lancets help ensure smoother entry. Plus, 11 customizable depth settings make it easier to get the right amount of blood the first time.
- Will you track results in the blood sugar meter, with an app or on a computer? Most blood sugar monitors have built-in memories, and many can beam or transfer data directly to your computer or an app on your smartphone, such as the mySugr app.
Don’t Miss: What Fruit Contains The Most Sugar
Low Blood Sugar Level Causes
Most low blood sugar level causes are preventable and are caused due to a persons lifestyle and diet habits. Low blood sugar is common among diabetic patients who take medications to increase insulin levels.
All of the above causes are risk factors that may or may not be able to be inhibited. They are important to be aware of and act accordingly to keep yourself from getting a too high or too low blood sugar level.
If a person has medical, lifestyle or diet habits that cause irregular blood sugar levels, symptoms will begin to develop along with the drop or spike in blood sugar, and are as follows:
Blood Sugar Levels After Eating
Blood sugar fluctuates throughout the day, but the biggest changes happen around mealtimes. Before eating, a healthy sugar level is between 3.9-5.5mmol/L. Around 1-2 hours after eating, expect blood sugar to rise to 5-10mmol/L.
If your blood sugar doesn’t stick within these ranges, the body may have stopped regulating blood sugar effectively which can lead to prediabetes and diabetes.
Also Check: Which Cells Produce Hormones To Regulate Blood Sugar
Blood Sugar Levels Of Children With Diabetes:
Summary
In diabetic children, the healthy blood sugar levels are between 70 to 180 mg/dL.
Normal Fasting Blood Sugar For Person Without Diabetes
A normal fasting blood glucose for someone who does not have diabetes ranges from 70 to 99 mg/dl. The American Diabetes Association recommends a routine screening for type 2 diabetes starting at age 45. If the results are normal, the screening should be repeated every 3 years.
If have diabetes risk factors, which include being overweight or obese, having a family history of type 2 diabetes, having a history of gestational diabetes, or being of a certain race/ethnicity , you should be screened for diabetes sooner than age 45.
Children and adolescents who have diabetes symptoms or who are overweight and have a family history of type 2 diabetes, are of African American, Latino, Asian American, Native American or Pacific Islander descent, who have signs of prediabetes or a mother who had gestational diabetes should be tested beginning at age 10 and then every 3 years thereafter.
A fasting blood sugar of 100 to 125 mg/dl is indicative of prediabetes, which is a condition where blood sugar levels are above normal but not high enough to be considered diabetes. Prediabetes is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, heart disease and stroke. Its managed by lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication.
Recommended Reading: Is There Sugar In Pedialyte
Normal Blood Sugar Levels In Children
Younger than 6 years old mg/dL
| Bedtime | 100-140 |
Adults who are 20 years or older will have blood sugar levels that range between less than 100-180 mg/dL over the course of a day. When you wake up in the morning, your fasting blood sugar should be at its lowest because you havent consumed food for about eight hours. If youre an adult and struggling with glucose control, your healthcare provider can help you develop a treatment plan to manage your blood sugar better.
Blood glucose levels outside the ranges listed above are categorized as either high or low blood sugar. Blood sugar levels are considered high if theyre over 130 mg/dL before a meal or 180 mg/dL within one to two hours after a meal. Many people wont start to experience symptoms from high blood sugar until their levels are at 250 mg/dL or higher. The highest blood sugar level thats considered safe will depend on the person and whether they have diabetes, but will typically be between 160 to 240 mg/dL.
Chart Of Normal Blood Sugar Levels For Adults With Diabetes Age Wise
Our body maintains a level of blood glucose for body metabolism. The normal blood glucose levels in a healthy body are between 90 to 100 mg/dL. But sometimes, these blood glucose levels may go high or low. Such high or low blood glucose levels are signs of health conditions requiring medical attention. This article gives in-depth information about normal blood sugar levels chart for adults with diabetes according to age.
Read Also: How Much Sugar To Add To Hard Cider
Symptoms Of Blood Blood Sugar Levels
Symptoms of blood sugar levels differ depending on if it is high or low. To determine which way the blood sugar have moved, the symptoms for each are typically:
| High Blood Sugar Symptoms | |
| Slow healing wounds | Turning pale |
If symptoms are left untreated, more extreme circumstances can happen such as fainting, weakness, disorientation, vomiting and dehydration. When you notice symptoms, usually more than one at one time, it is advised to see a doctor right away.
It is important to get the right treatment so that you can return to a healthy normal blood sugar level and inhibit it from occurring again.
Treatment methods vary from the severity of the blood sugar level, whether it is high or low and if the patient has existing medical conditions, such as diabetes. Here are ways in which blood sugar levels can be treated:
What Is Considered A Normal Blood Sugar Level
The normal blood sugar level for a healthy adult should be less than 126 mg/dL or 6 mmol/L before fasting and meals, and below 200mg/dL two hours after meals.
If you are diabetic, then you should consult with your doctor in order for appropriate blood sugar level targets to be set based on the severity of your condition, medications taken and overall health status.
The below information describes what normal blood sugar levels are prior to and after meals and what the recommended HbA1c levels are for those with and without diabetes.
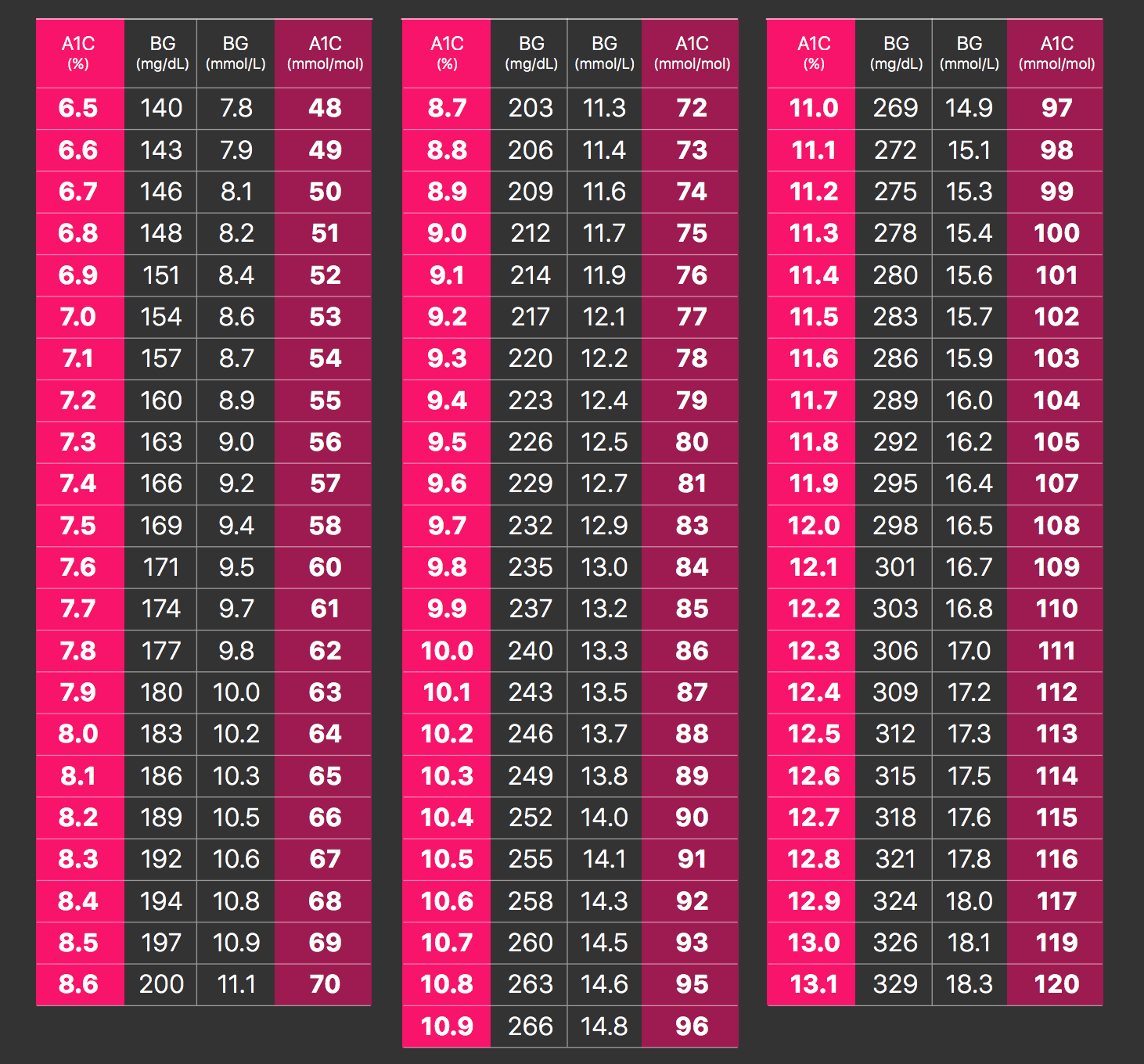
A HbA1c test determines your average level of blood glucose over the past two to three months. Red blood cells have a lifespan of roughly three months, and a HbA1c blood test measures the amount of glucose that has bound to them during this period.
A blood test to determine Haemoglobin A1c levels is often performed in those who have diabetes. These levels are a reflection of how well diabetes is being controlled.
Read Also: What Is Signs Of High Blood Sugar
Low Blood Sugar Chart And Action Plan
Low blood sugar is also called hypoglycemia. The numbers below represent values in the hypoglycemic range and require action to bring blood sugar levels up into a normal range.
| Alert Level and Treatment Plan | |
| 50 mg/dL or under | Red Flag: Blood sugar is critically low and requires immediate treatment.
If a person is unable to speak and/or is not alert, treat with glucagon via injection or nasal spray. Call emergency medical response if necessary. Do not place food or drink into the mouth. If a person is alert and able to speak clearly, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate such as glucose gel, 4 oz regular soda, or fruit juice. Re-test blood sugar in 15 minutes and repeat as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 51-70 mg/dL | Red Flag: Blood sugar is below normal levels and requires immediate treatment.
Treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 71-90 mg/dL | Yellow Flag: Blood sugar levels should be watched and treated as needed.
If youre having symptoms of low blood sugar, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment or follow with a meal. If it is meal time, move forward with eating the meal. People often fall into this range when they are late for a meal or have been especially active. |
Change Your Life Today And Reduce Your Risk Of Diabetes
Diabetes can be a massive burden on both your health and your wallet. But, maintaining normal blood sugar levels, managing your weight, and staying physically active are great ways to reduce your risk of developing diabetes.
If you are looking to improve your health and monitor your risk factors for disease, getting covered is a great way to relieve the financial pressures of looking after yourself.
Why not contact us today at Insurdinary for a free, personalized, no-obligation quote from some of the best health care providers in Canada!
Read Also: Is There Sugar In Pedialyte
Identify The Persons Blood Sugar Level
The CGM and the glucometer are excellent methods used mostly by doctors and people with diabetes to track their glucose levels throughout the day. When a person checks their blood sugar after fasting or before eating breakfast and any other meals, their average blood sugar level is expected to hit 60-90 mg/dl. If they check it an hour after their meal, their average blood sugar level is expected to reach 100-120 mg/dl.
Type 2 Along With Insulin Or Other Medication Going On
The frequency of tests varies depending on your insulin dosage and any other medicines you are taking.
If you are on intensive insulin medication, you should do tests at fasting, before meals, before bedtime, and sometimes in the night if needed. Those on usual insulin and additional medications dosage should at least perform the tests at fasting and bedtime.
Those not on insulin but oral medications or diet control do not require frequent blood sugar testing at home.
Type 2 diabetes and low risk of low blood sugar
Daily tests are not usually required. If blood sugar goals or A1C levels are not met on a regular basis, the frequency of testing can be increased until the levels are back within normal ranges.
Also Check: What Is Signs Of High Blood Sugar
Causes Of Blood Sugar Levels
Whilst the liver and muscles produce some glucose, most comes from the foods we eat. Food and drinks that are high in carbohydrates are most impactful on blood sugar level. What we eat provides us most of the nutrients our body needs and sometimes, does not need. That is not to say that food is a major cause of blood sugar level increasing or decreasing too dramatically.
Typically, if a person has health conditions or poor nutrition, this will lead to a spike or decline in blood sugar level. The causes differ from high to low blood sugar levels and are as follows:
Why Your Blood Sugar Level May Be High
Based on the ADA guidelines above, if your blood sugar is above 180 mg/dL two hours after a meal, it is considered above the normal range. What might cause your glucose or blood sugar to rise? Consider the following factors:
- Consuming more carbohydrates or a larger meal than usual
- Not taking enough insulin or oral diabetes medication based on carbohydrates or activity levels
- Reduced physical activity
- Side effects from medications like steroids or antipsychotics
You May Like: What Causes High Glucose Levels