A Few Different Things Can Cause A Deficiency In Insulin
1. Sickness Stress hormones are produced in response to illness, infection, and dehydration, and stress hormones work against the action of insulin. When you are sick, your insulin doesnt work as well because its being impeded by the stress hormones.
When you are sick, you need to stay hydrated and may need as much as double your usual amount of insulin.
2. No insulin Forgetting to take insulin, especially basal insulin, will get you in trouble with ketones. Chronically missing or skipping mealtime insulin will also cause high blood sugar and lead to ketone development.
3. Spoiled insulin Insulin can spoil if it is exposed to temperature extremes or if it is too old. Know how long you can use your insulin once the pen or vial is opened, and discard it when it is at the end of its useful lifespan. Its also possible that you can become insulin deficient when your insulin is sitting in the tissues and not absorbing into the body where it can be used, so be methodical about rotating your sites.
What can cause this interruption? There are many points in the pipeline where things can go awry:
- Mal-absorption of insulin from the infusion site
- Tubing or infusion set clogs
- Leaking during a bolus improper connection between set and cannula OR a site that leaks around the cannula
- Spoiled insulin
- A leak where the cartridge connects to the tubing
- A dislodged cannula
There are 3 things you need to do
Do You Have To Fast For An A1c Blood Test
Unlike the fasting plasma glucose and the OGTT tests, there is no need to fast before having the A1C test. If A1C test results indicate a person has or might have diabetes, a healthcare provider might suggest one of these tests to confirm the results. Another test, the random plasma glucose test, which does not require fasting, can also be used. If the results are borderline or if the results of the different tests do not match, a doctor might suggest repeating the test in several weeks or months.
My Perspective On A1c As A Person Living With Diabetes
I have a very ambivalent relationship with my A1c myself. Ive been living with type 1 diabetes for over 20 years, and my A1c is not something I think about in my daily life. However, every three months when I see my endo, I get a little anxious because receiving your A1c can feel a lot like getting your diabetes report card.
And, quite honestly, thats really silly. My A1c number doesnt reflect whats been going on in my life for the last three months. It doesnt tell me how much effort Ive put into managing my diabetes and it does not define me as a person. Its a good source of information, nothing more.
Still, we tend to look at it and judge, good or bad, how weve done with our diabetes management. But we really shouldnt!
That doesnt mean that I think we shouldnt get our A1c checked. I absolutely think we should, but we also need to understand what it means as well as why we should look beyond the A1c number. I hope this guide has given you the knowledge and tools to do so!
If you liked this guide on how to lower your A1c, please sign up for our newsletter in the form below. We send out a weekly newsletter with the latest posts and recipes from Diabetes Strong.
Suggested next posts:
If you found this guide to lowering your A1c useful, please sign up for our newsletter using the form below. We send out a weekly newsletter with the latest posts and recipes from Diabetes Strong.
Also Check: Diet For Hyperglycemia Without Diabetes
What Blood Sugar Levels Are Healthy
Weve established what normal blood sugar looks like, more or less. But normal levels can be challenging for people with diabetes to achieve. At what point does high blood sugar get dangerous?
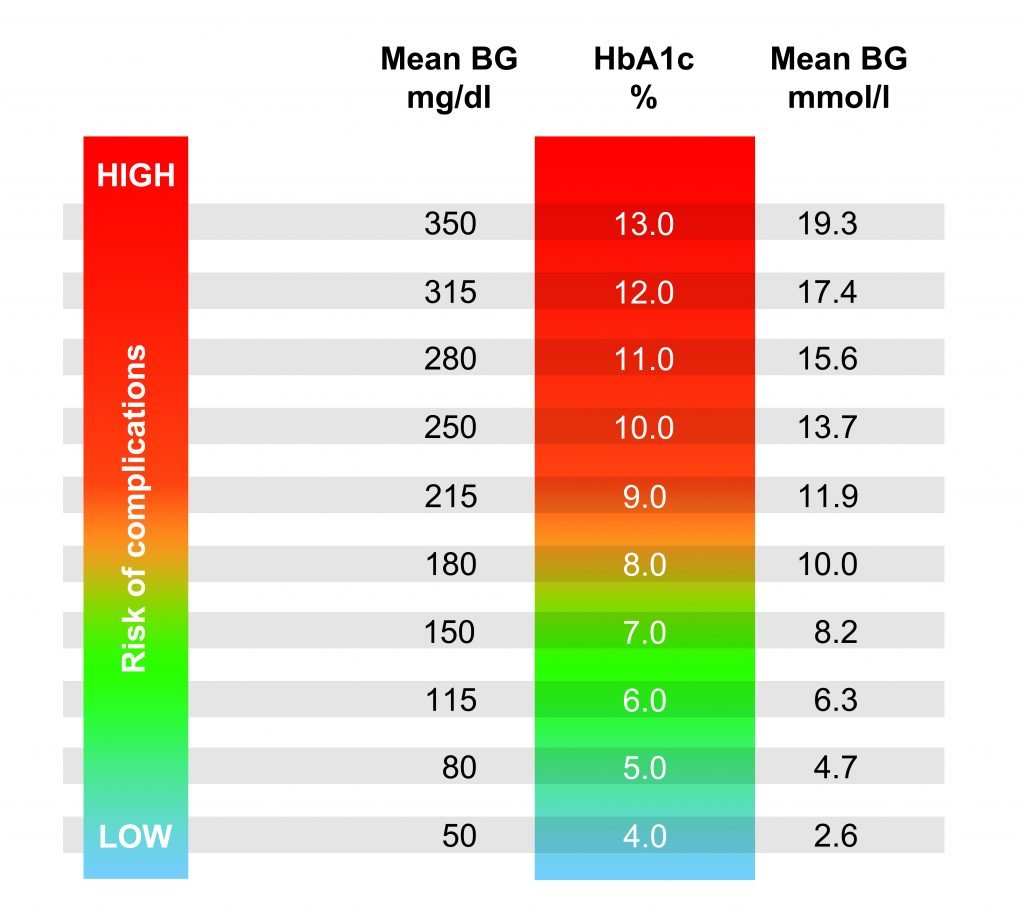
This is an area of some debate. The long-term studies show that the risk of complications drop off dramatically when an HbA1c is lower than 7%, which is an estimated average blood glucose of 154 mg/dL or 8.6 mmol/L. The risks continue to drop until its below 6%, an average blood sugar of 126 mg/dL or 7 mmol/L. There are many people with diabetes who strive for even lower targets, but there is not much research outlining the benefits of that approach yet.
Its important to note that studies of A1c and the rate of complications are only looking at averages. In reality, there seems to be a huge difference in the risk of complications based on genetics and perhaps other unknown factors. There are many people who have lived for many decades with type 1 diabetes, running high blood sugars almost continuously, and have no complications. There are others who have had well-controlled blood sugars that still get complications.
For most people, its safe to say that striving for an HbA1c of below 7% and probably below 6.5% is a realistic goal for staying healthy.
This chart from the American Diabetes Association lists some of the other factors that may indicate when a patient should target a lower or higher blood sugar level:
Normal And Diabetic Blood Sugar Ranges
For the majority of healthy individuals, normal blood sugar levels are as follows:
- Between 4.0 to 5.4 mmol/L when fasting
- Up to 7.8 mmol/L 2 hours after eating
For people with diabetes, blood sugar level targets are as follows:
- Before meals : 4 to 7 mmol/L for people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- After meals : under 9 mmol/L for people with type 1 diabetes and under 8.5mmol/L for people with type 2 diabetes
You May Like: Are Bananas Bad For Blood Sugar
Testing For Pre Diabetes
Doctors generally use one of two different blood tests to diagnose diabetes and prediabetes. One is called the fasting plasma glucose test in which a person’s blood glucose level is measured first thing in the morning before breakfast. The normal fasting blood glucose level is below 100 mg/dl. A person with prediabetes has a fasting blood glucose level between 100 and 125 mg/dl. If the fasting blood glucose level is to 126 mg/dl or above, a person is considered to have diabetes.
The second test used in the diagnosis of diabetes is the oral glucose tolerance test , although this test is no longer commonly used as in the past. This test may be used to diagnosegestational diabetes inpregnant women. In this test, a person’s blood glucose is measured in the morning after fasting overnight and again two hours after drinking a glucose-rich beverage. The normal value for blood glucose is below 140 mg/dl two hours after the drink. In prediabetes, the two-hour blood glucose is 140 to 199 mg/dl. If the two-hour blood glucose rises to 200 mg/dl or above, a person has diabetes.
Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
If your test results show you have prediabetes, ask your doctor or nurse if there is a lifestyle change program offered through the CDC-led National Diabetes Prevention Program in your community. You can also search for an online or in-person program. Having prediabetes puts you at greater risk for developing type 2 diabetes, but participating in the program can lower your risk by as much as 58% .
Recommended Reading: Is There Sugar In Pedialyte
Factors That Increase Your Risk Of Prediabetes
While mainstream media often depicts type 2 diabetes as the result of being overweight, not exercising, and eating unhealthy food, it is significantly more complex.
There are actually two pathways that lead to prediabetes and type 2 diabetes.
The first is basic insulin resistance, which means your body needs more and more insulin in order to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. At a certain point, the pancreas cant keep up with the demand, and blood sugars begin to rise.
The second is a genetic disposition that results in the gradual dysfunction and destruction of your pancreas beta-cells. Beta-cells play the leading role in insulin production, and many people with type 2 diabetes struggle to actually produce normal amounts of insulin.
Determining which group you are in isnt easy, or even possible for the average patient.
For patients in this second group, reversing diabetes isnt likely possible, but that doesnt mean you cant take steps towards improving your health isnt worthwhile.
The most important factors that increase your risk of prediabetes are:
Measuring Fasting Blood Glucose Level Of 126
QUESTION: I am 62 year old have High Blood Pressure, controlled by tablet. Time to time i check my blood sugar,it was ok,but i checked yesterday it was 126 fasting. i am not a smoker,drinker,not even overweight.Please advise how i can control.ANSWER: Hi Sunil, It is very good that you are checking your blood glucose from time in time, and everyone has to do this, especially those, who are above the age of 50, and are suffering of High blood pressure as you are.
Recommended Reading: Smirnoff Ice Nutrition Sugar
High Blood Sugar: Hidden Dangers
In the short term, high blood sugar levels can zap your energy, cause excessive thirst and urination, and blur your vision. High blood sugar levels can also lead to dehydration, dry and itchy skin, and infections. Minimizing the time spent above your target blood sugar range can help you feel your best and will help prevent complications and injury to your body.
Over time, high blood sugar affects many parts of the body. Chronic high blood sugar can start to cause noticeable changes, including:
- Memory problems
- Vision problems like blurriness, diabetic retinopathy, and blindness
- Gum disease that leads to tooth loss, which can make eating healthy foods difficult due to problems chewing
- Heart attack and stroke due to increased plaque build-up in the vessels and other vascular issues
- Kidney disease, which can lead to the need for dialysis or a kidney transplant
- Nerve damage that can cause decreased sensation in the feet and legs which increases the risk for wounds to turn into serious infections and even amputation
Nerve damage from high blood sugar can also cause a variety of symptoms including:
- Pain and tingling in the feet and hands
- Difficulty emptying your bladder
- Problems during the digestion process after eating, which can cause food to sit in the stomach too long and lead to nausea, vomiting, and erratic blood sugar levels
Checking your blood sugar frequently and taking immediate action when it is above range can reduce your risk of complications.
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
A fasting plasma glucose test is taken after at least eight hours of fasting and is therefore usually taken in the morning.
The NICE guidelines regard a fasting plasma glucose result of 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l as putting someone at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, particularly when accompanied by other risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Don’t Miss: What Helps Bring Your Sugar Down
Glipizide Contraindications & Warnings
Glipizide is a great medication for treating Type 2 diabetes, but it isnt right for everyone. Here are some contraindications and warnings about glipizide to be aware of:
- Abuse and dependence: Glipizide isnt a habit-forming drug, but it is important to talk with your healthcare provider about any concerns you may have while taking it.
- Overdose: The maximum daily dose of glipizide for adults is 40 mg for regular tablets and 20 mg for extended-release tablets. That dose may be lower for people with certain health conditions. Overdosing on glipizide can potentially cause life-threatening hypoglycemia and symptoms like seizures, tremors, confusion, and blurred vision. The maximum daily dose of glipizide shouldnt be exceeded unless approved by a medical professional. If you or someone you know has overdosed on glipizide, seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222.
- Restrictions: The risks and benefits of glipizide while pregnant or breastfeeding should be discussed with your doctor. Glipizide shouldnt be taken by pregnant women who are near-term. It also shouldnt be taken by people who have an allergy to the medication or diabetic ketoacidosis. It should be used with caution in people who have:
- A G6PD deficiency
Donât Miss: What Should Blood Sugar Be At Bedtime For Non Diabetic
What Is Normal Blood Sugar Level

The blood sugar concentration or blood glucose level is the amount of glucose present in the blood of a human or an animal. The body naturally tightly regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis.
If blood sugar levels are either increased or decreased by a greater margin than expected this might indicate a medical condition.
Diabetic patients must monitor their levels as bodys inability to properly utilize and / or produce insulin can pose a serious threat to their health.
Don’t Miss: What Vitamin Stops Sugar Cravings
New Diabetes Guidelines: A Closer Look At The Evidence
STEVEN H. WOOLF, M.D., M.P.H., and STEPHEN F. ROTHEMICH, M.D., Medical College of Virginia at Virginia, Commonwealth University, Richmond, Virginia
Am Fam Physician. 1998 Oct 15 58:1287-1290.
In this issue of American Family Physician, Mayfield1 summarizes recent recommendations of the American Diabetes Association , which broaden the diagnostic criteria for diabetes mellitus and advocate routine screening. Under the new guidelines,2 the threshold fasting plasma glucose level for the diagnosis of diabetes has been lowered from 140 mg per dL to 126 mg per dL . Screening is recommended every three years, beginning at age 45 .
Third, and most important, there is no prospective evidence that correcting these mild elevations improves health. The evidence that does exist is for persons with higher glucose levels. In the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial ,7 the landmark study showing that glycemic control prevents microvascular complications, patients began treatment with a mean blood glucose level of 234 mg per dL and lowered it to a mean of 155 mg per dL . Whether normalizing fasting plasma glucose levels in the range of 126 to 140 mg per dL has a meaningful impact on patient outcomes is unknown.
Read the full article.
- Get immediate access, anytime, anywhere.
- Choose a single article, issue, or full-access subscription.
- Earn up to 6 CME credits per issue.
Getting A Second Opinion
You should always feel free to get a second opinion if you have any concerns or doubts about your diagnosis.
If you change doctors, youll want to ask for new tests. Different doctors offices use different laboratories to process samples. The NIDDK says it can be misleading to compare results from different labs. Remember that your doctor will need to repeat any test to confirm your diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: Is Pedialyte Good For Diabetics
Blood Sugar And Diabetes
In a person with diabetes, the story is much more complex. The body has largely or entirely lost the ability to regulate blood glucose levels, and as a result glucose levels are likely to be volatile and to inhabit a much wider range of values:
| Below 70 mg/dLBelow 3.8 mmol/L | Low Blood Sugars . When blood sugars drop below this level, you may start feeling hunger, shakiness, or racing of the heart. Your body is starved for sugar . Read how to detect and treat low blood sugars. |
| 70 mg/dL to 140 mg/dL3.8 mmol/L to 7.7 mmol/L | Normal Blood Sugar. In this range, the body is functioning normally. In someone without diabetes, the vast majority of the time is spent in the lower half of this range. |
| 140 mg/dL to 180 mg/dL7.7 mmol/L to 10 mmol/L | Elevated Blood Sugars. In this range, the body can function relatively normally. However, extended periods of time in this zone put you at risk for long-term complications. |
| Above 180 mg/dLAbove 10 mmol/L | High Blood Sugars. At this range, the kidney is unable to reabsorb all of the glucose in your blood and you begin to spill glucose in your urine. Your body may begin to turn to fat for energy and release ketones in your urine. |
Frequently Asked Questions: Faqs
Can diabetes go away?
Yes! Prediabetes and type 2 diabetes are reversible conditions for most people who commit to a combination of diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
What are the warning signs for prediabetes?
The primary indicator of prediabetes is a hemoglobin A1C level of 5.7% or greater. Other risk factors include being overweight, being 45 years or older, smoking, physical inactivity, or having a family history of prediabetes.
What level of A1C is dangerous?
An A1C level between 5.7 and 6.4% means your blood sugar is higher than normal. An A1C reading of 6.5% indicates diabetes, and an A1C level of 8% or above is a sign of uncontrolled diabetes, meaning you have a higher risk of developing complications such as kidney damage or stroke.
Whats the best way to reverse prediabetes?
The best way is a combination of 1) whatever way works for you and 2) whatever way is sustainable.
Some people can control their blood sugar with modifications to their diet and lifestyle, while others need medication as well. The most important thing is to collaborate with your doctor to find the treatment plan that gets your blood sugar in check and keeps it there so that you dont develop T2D.
Is diabetes curable?
No, but it is reversible. If you catch your prediabetes before it morphs into type 2 diabetes, you can turn back the process and avoid becoming diabetic. Even T2D can be kicked if it is caught before it is allowed to progress. So, take heart. You can do this!
Also Check: Pedialyte For Diabetics