Official Hba1c Ada Recommendation For Someone With Diabetes
The American Diabetes Association recommends an HbA1C of less than 7% for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. A lower goal, such as less than 6.5%, may be appropriate for some people who have had diabetes for a shorter amount of time, for younger people, for those without heart disease, and/or for those with type 2 diabetes treated with lifestyle or metformin only. A higher HbA1C goal, such as less than 8%, may be appropriate for people with a history of severe hypoglycemia, a limited life expectancy, advanced diabetes complications, other illnesses, or for whom a lower HbA1C goal is difficult to achieve. Its important that people with diabetes discuss their target blood sugar goals with their healthcare provider.
HbA1C levels should be checked between two to four times per year in people who have diabetes.
Why Do I Need To Know My Blood Sugar Numbers
Your blood sugar numbers show how well your diabetes is managed. And managing your diabetes means that you have less chance of having serious health problems, such as kidney disease and vision loss.
As you check your blood sugar, you can see what makes your numbers go up and down. For example, you may see that when you are stressed or eat certain foods, your numbers go up. And, you may see that when you take your medicine and are active, your numbers go down. This information lets you know what is working for you and what needs to change.
Low Blood Sugar Level Causes
Most low blood sugar level causes are preventable and are caused due to a persons lifestyle and diet habits. Low blood sugar is common among diabetic patients who take medications to increase insulin levels.
All of the above causes are risk factors that may or may not be able to be inhibited. They are important to be aware of and act accordingly to keep yourself from getting a too high or too low blood sugar level.
If a person has medical, lifestyle or diet habits that cause irregular blood sugar levels, symptoms will begin to develop along with the drop or spike in blood sugar, and are as follows:
Also Check: Can Diabetics Eat Banana
Controlling Blood Glucose Levels
Uncontrolled blood sugar can result in regular episodes of hyperglycemia . This can cause a variety of symptoms including:
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Fatigue
These symptoms are uncomfortable to experience but there are things you can do at home to reduce your blood sugar. In terms of drinks, water is the best as it will help to maintain hydration and dilute excess sugar in the blood. Also, try to add more fiber to your diet to reduce your blood sugar apples, bananas, oranges, and strawberries are all fibrous fruits.
However, uncontrolled blood sugar levels can also lead to more severe, long term disease. Poorly managed diabetes leads to vision loss, kidney problems, nerve damage, heart attack, and stroke. Therefore, if your blood sugar level reaches 16.7mmol/L, this could be dangerous and you need to seek immediate medical attention.
Who Should Seek Screening
should undergo a prediabetes screening:
- an age of 45 years or over
- obesity or overweight, or a body mass index over 25
- a waist circumference larger than 40 inches in males or over 35 inches in females
- a close relative with diabetes
- a condition that increases insulin resistance, including PCOS, acanthosis nigricans, and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- an ethnic background that places an individual at high risk of diabetes, including people who are African-American, Asian-American, Latino, Native American, or a Pacific Islander
- a history of gestational diabetes, or diabetes as a result of pregnancy
- having given birth to an infant weighing over 9 pounds
- having a disease that harden the arteries
- recent treatment with glucocorticoids or atypical antipsychotic medications
If a doctor identifies any of these risk factors, they may recommend that the person has a screening for blood glucose levels.
Medical professionals advise repeating screening tests every 1 to 3 years if a person has these risk factors.
The NIDDK has an official resource to check diabetes risk. Click here to take the test.
However, anyone who is concerned that they may have borderline diabetes should visit the doctor for testing and a proper diagnosis.
Prediabetes is reversible, but it is often easier to prevent than treat. Lifestyle factors are the primary causes of prediabetes, and making changes in some aspects of life can significantly reduce risk factors.
about what to eat with prediabetes.
You May Like: How To Reduce Diabetes Instantly
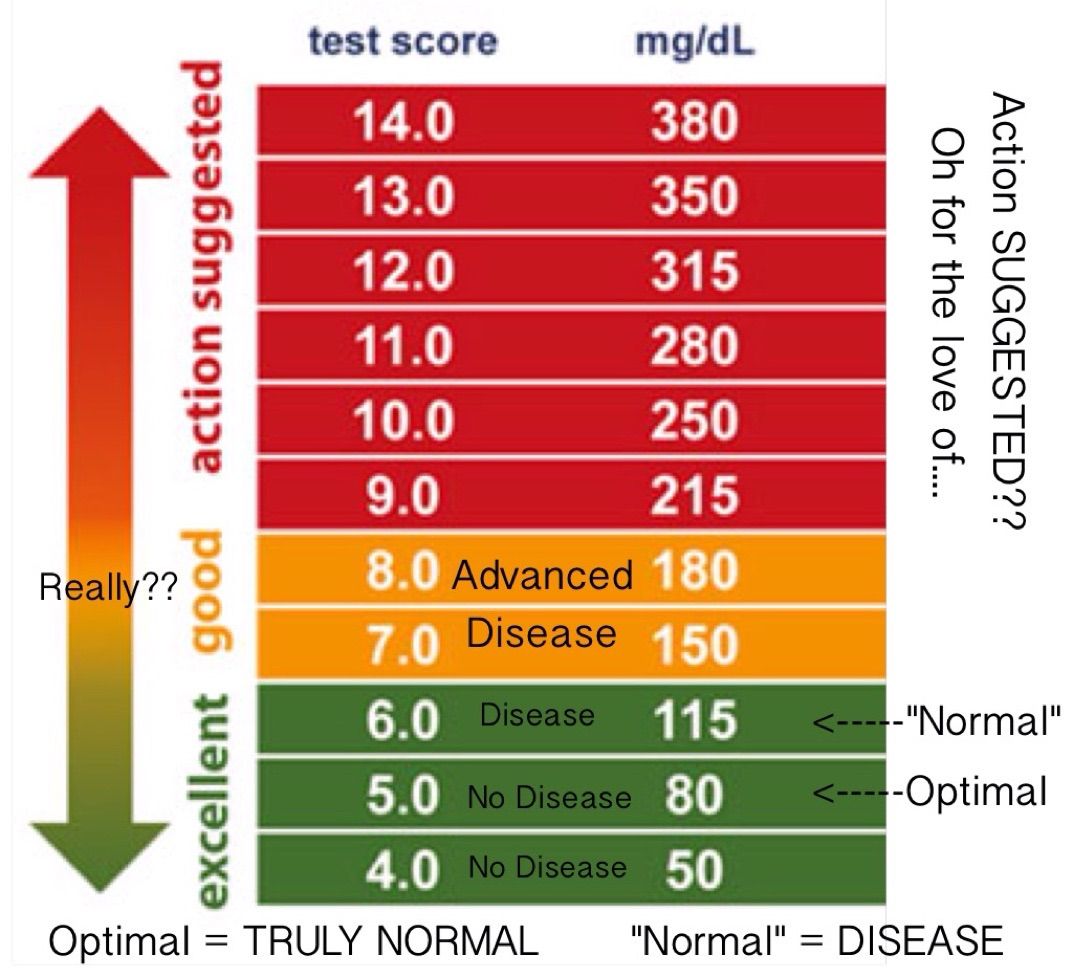
Blood Sugar Level Chart
- Normal reading for nondiabetic person = 7099 mg/dl
- The recommendation for someone who is diabetic = 80130 mg/dl
Two hours after a meal
- Normal reading for nondiabetic person = Below 140 mg/dl
- The recommendation for someone who is diabetic = Below 180 mg/dl
HbA1c
- Normal reading for nondiabetic person = Below 5.7%
- The recommendation for someone who is diabetic = 7% or less
**My Med Memo The measurement mmol is the abbreviation for millimole.
Recommended Reading: Can Type 2 Diabetics Eat Bananas
What Are Normal Blood Glucose Levels In Healthy Individuals
Blood sugar levels can either be normal, high, or low, depending on how much glucose someone has in their bloodstream. Glucose is a simple sugar thats present in the bloodstream at all times. Normal blood glucose levels can be measured when someone fasts, eats, or after theyve eaten. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, who havent eaten for at least eight hours is less than 100 mg/dL. A normal blood glucose level for adults, without diabetes, two hours after eating is 90 to 110 mg/dL.
Many factors affect blood sugar levels throughout the day:
- Type of food consumed, how much, and when
- Physical activity
- Menstrual periods
- Alcohol
An ideal blood sugar level for anyone without diabetes or prediabetes, regardless of age, in the morning should be less than 100 mg/dL. Remember, blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day as a result of the factors previously mentioned.
Recommended Reading: Can We Control Sugar Without Medicine
Severe Low Blood Sugar
As your low blood sugar gets worse, you may experience more serious symptoms, including:
- Feeling weak.
- Having difficulty walking or seeing clearly.
- Acting strange or feeling confused.
- Having seizures.
Severe low blood sugar is below 54 mg/dL. Blood sugar this low may make you faint . Often, youll need someone to help you treat severe low blood sugar.
People with diabetes may experience low blood sugar as often as once or twice a week, even when managing their blood sugar closely. Knowing how to identify and treat it is important for your health. Learn how to treat low blood sugar.
Frequently Asked Questions: Faqs
Can diabetes go away?
Yes! Prediabetes and type 2 diabetes are reversible conditions for most people who commit to a combination of diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
What are the warning signs for prediabetes?
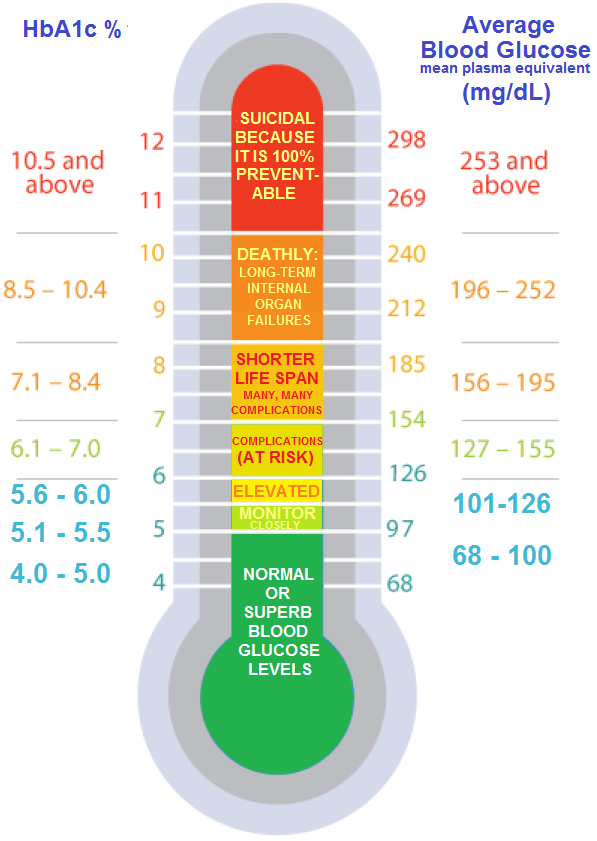
The primary indicator of prediabetes is a hemoglobin A1C level of 5.7% or greater. Other risk factors include being overweight, being 45 years or older, smoking, physical inactivity, or having a family history of prediabetes.
What level of A1C is dangerous?
An A1C level between 5.7 and 6.4% means your blood sugar is higher than normal. An A1C reading of 6.5% indicates diabetes, and an A1C level of 8% or above is a sign of uncontrolled diabetes, meaning you have a higher risk of developing complications such as kidney damage or stroke.
Whats the best way to reverse prediabetes?
The best way is a combination of 1) whatever way works for you and 2) whatever way is sustainable.
Some people can control their blood sugar with modifications to their diet and lifestyle, while others need medication as well. The most important thing is to collaborate with your doctor to find the treatment plan that gets your blood sugar in check and keeps it there so that you dont develop T2D.
Is diabetes curable?
No, but it is reversible. If you catch your prediabetes before it morphs into type 2 diabetes, you can turn back the process and avoid becoming diabetic. Even T2D can be kicked if it is caught before it is allowed to progress. So, take heart. You can do this!
Recommended Reading: How To Reduce Sugar Level Immediately
What Blood Sugar Level Is Prediabetic
Exercise, Fitness & Nutrition Expert | Lark Health
Prediabetes is a condition with increased blood sugar, but how is it measured? Exactly what sugar level range is considered prediabetic, and how is that different from diabetes? Here is what you need to know about blood sugar levels in prediabetes, and what you can do about yours.
If you have been told that you have prediabetes, or you think that you might have it or be at risk for it, you can take your awareness in a positive way. While nobody actually wants to think about having a chronic health condition, being aware of prediabetes can be seen as a fork in the road of life.
On one branch of the fork in the road, prediabetes can lead to type 2 diabetes. Most people who get prediabetes take this branch, and end up with diabetes. However, you can choose to take the other branch in the road because in most cases, prediabetes is reversible.
Are you at risk for type 2 diabetes? Lark Diabetes Prevention Program is a personalized program to help you lower your risk by making healthy lifestyle changes, such as losing weight and increasing physical activity. Your personal Lark coach is available to support you 24/7 on your smartphone. Lark can help you make small changes that fit into your lifestyle and have big results for your health!
How Can You Find Out If You Have Normal Blood Sugar Levels
There are a few different ways that you can test or keep track of your average blood sugar level. Some popular glucose monitoring methods include a continuous glucose monitor , an A1C test, a glucose meter, doing a fasting blood glucose test, or an oral glucose tolerance test. You can also get your ketones tested, which usually appear in the urine of Type 1 diabetes patients.
Your healthcare provider will analyze your test results, and let you know the best course of action if theyâre not in the normal range. This may include diabetes medications like metformin or lifestyle changes.
Read Also: How To Control High Sugar Level Immediately
Normal Hba1c For Person Without Diabetes
For someone who does not have diabetes, a normal HbA1C level is below 5.7%. An A1C between 5.7% to 6.4% is indicative of prediabetes.
Its recommended that adults over the age of 45 or adults under 45 who are overweight and have one or more risk factors for diabetes have a baseline A1C checked. If the result is normal, the A1C should be checked every 3 years. If the result indicates prediabetes, the A1C should be checked every 1 to 2 years.
High Blood Sugar Levels
Different targets have been set by various health organizations, but the American Diabetes Association has stated that fasting blood sugar should be between 80-130mg/dL, and two hours after a meal it should be less than 180mg/dL.
Some people experience high blood sugar in the mornings for several common reasons, like the Dawn Phenomenon. Fasting blood sugar is important to note, as it can give an idea of where your blood sugar naturally settles after a period without intervention.
Blood sugar rises after a meal, and then comes back down . Postprandial blood sugar is where it lands at the end of the trend line, which is generally two hours after the meal. If blood sugar is 180 mg/dL two hours after a meal, it could mean mis-calculating carb intake. Knowing the range your doctor has identified as a healthy rise is important in being aware of your bodys processes. Any number above your specific ranges is considered to be high.
Glucose is needed by your body, but when it rises too high over an extended period of time, it can have lasting detrimental effects. Its important that you regularly monitor your blood sugar levels so that youre aware of how your body is responding to your diabetes care plan.
You May Like: Sugar In Low Blood Pressure
Diabetes Is Diagnosed By Any One Of The Following:
Sometimes you may have symptoms of fatigue, excessive urination or thirst, or unplanned weight loss. However, often people have no symptoms of high blood glucose and find a diabetes diagnosis surprising.
Diabetes By The Numbers
Staying healthy with type 2 diabetes is a numbers game. Get the scoop on the health indicators you should be measuring and why.
Thinkstock
When you have type 2 diabetes, youve got to know your numbers. Its not just about blood sugar. To successfully manage diabetes, there are several measurements that you should take, or have taken, on a regular basis. Keeping track of the following numbers can help you live well with type 2 diabetes and lower your risk of complications.
Blood sugar levels. This is probably the type 2 diabetes measure youre most familiar with. Testing your blood sugar regularly allows you to see how certain foods, exercise, and other activities affect your blood sugar levels on a day-to-day basis. Many people with type 2 diabetes need to test once or twice a day to make sure blood sugar levels are in target range. If your blood sugar is very well controlled, you may only need to check a few times a week, according to the National Institutes of Health.
The American Diabetes Association recommends aiming for a blood sugar level between 70 to 130 mg/dl before meals and less than 180 mg/dl one to two hours after a meal. To keep your blood sugar within this range, follow a healthy, well-rounded diet and eat meals and snacks on a consistent schedule. If your blood sugar is not well controlled, talk to your doctor about adjusting your diabetes management plan.
Recommended Reading: Sugar Tablets Side Effects
Symptoms Of Blood Blood Sugar Levels
Symptoms of blood sugar levels differ depending on if it is high or low. To determine which way the blood sugar have moved, the symptoms for each are typically:
| High Blood Sugar Symptoms | |
| Slow healing wounds | Turning pale |
If symptoms are left untreated, more extreme circumstances can happen such as fainting, weakness, disorientation, vomiting and dehydration. When you notice symptoms, usually more than one at one time, it is advised to see a doctor right away.
It is important to get the right treatment so that you can return to a healthy normal blood sugar level and inhibit it from occurring again.
Treatment methods vary from the severity of the blood sugar level, whether it is high or low and if the patient has existing medical conditions, such as diabetes. Here are ways in which blood sugar levels can be treated:
High Blood Sugar: Hidden Dangers
In the short term, high blood sugar levels can zap your energy, cause excessive thirst and urination, and blur your vision. High blood sugar levels can also lead to dehydration, dry and itchy skin, and infections. Minimizing the time spent above your target blood sugar range can help you feel your best and will help prevent complications and injury to your body.
Over time, high blood sugar affects many parts of the body. Chronic high blood sugar can start to cause noticeable changes, including:
- Memory problems
- Vision problems like blurriness, diabetic retinopathy, and blindness
- Gum disease that leads to tooth loss, which can make eating healthy foods difficult due to problems chewing
- Heart attack and stroke due to increased plaque build-up in the vessels and other vascular issues
- Kidney disease, which can lead to the need for dialysis or a kidney transplant
- Nerve damage that can cause decreased sensation in the feet and legs which increases the risk for wounds to turn into serious infections and even amputation
Nerve damage from high blood sugar can also cause a variety of symptoms including:
- Pain and tingling in the feet and hands
- Difficulty emptying your bladder
- Problems during the digestion process after eating, which can cause food to sit in the stomach too long and lead to nausea, vomiting, and erratic blood sugar levels
Checking your blood sugar frequently and taking immediate action when it is above range can reduce your risk of complications.
Recommended Reading: Reduce Sugar Level Immediately
How Food Affects Blood Sugar
When you eat food, your body breaks it down into essential parts:
- Carbohydrates
- Fats
- Vitamins and minerals
All parts are necessary in a healthy diet, but the three types of carbohydrates are particularly important when it comes to your blood glucose level. While the general rule is that the more carbohydrates you eat, the higher your blood sugar level, not all three types of carbohydrates convert to blood sugar at the same rate.
The foods that fit into each carb category include:
- Starches, or complex carbohydrates: Starchy vegetables, dried beans, and grains
- Sugars: Fruits, baked goods, beverages, and processed food items like cereals or granola bars
- Fiber: Whole wheat products, chickpeas, lentils, berries, pears, and brussels sprouts
The glycemic index helps you find out which foods can increase or help decrease blood sugar levels. Based on a scale ranging from 0 to 100, high-indexed foods are rapidly digested, absorbed, and metabolized, resulting in marked fluctuations in blood sugar levels, while low-indexed foods produce smaller fluctuations in your blood glucose.
The American Diabetes Association advises adding lean sources of protein and heart-healthy fats to help reduce the overall glycemic impact of a meal or snack.