What Level Of Blood Sugar Is Dangerous
Knowing what level of blood sugar is dangerous is crucial for people with diabetes and those without. High levels of blood sugar are very serious and can lead to coma. The University of Michigan suggests that individuals with a blood sugar level of 300 mg/dL or higher should call their physician. Other symptoms include confusion, nausea, and dizziness. The best way to prevent this problem is to eat nutritious foods and get regular blood sugar checks.
A low blood sugar level is known as hypoglycemia, which is a condition when blood glucose falls below the recommended range. This is dangerous and should be treated immediately. If a person has a history of low blood sugar, they are at an increased risk of this condition. In the event that their blood sugar is dangerously low, they should seek medical attention immediately. The first step is to monitor their blood glucose levels. If they are low, they should check their urine, but not their bodies.
If your blood sugar is too high, it can cause fluid imbalance in the body and lead to dehydration. Treatment for this condition requires intravenous insulin and IV fluids to correct dehydration. A level of 300 mg/dL is dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible. Your doctor can give you reassurance and give you a personalized treatment plan that will work for your needs. If you are concerned, call your doctor right away.
Blood Sugar And Diabetes Risk
Low blood sugar is called hypoglycemia. It is defined as a blood glucose level lower than 70 mg/dL . It can help diagnose diabetes or prediabetes .
Blood tests can measure glucose levels either while your stomach is empty or after eating . The tests cannot diagnose diabetes on their own, but they can provide the evidence needed to warrant further testing if diabetes is suspected.
| Category | |
|---|---|
| Over 125 mg/dL | Over 200 mg/dL |
Hypoglycemia is common in older adults with diabetes. This may be due to other health concerns, such as other chronic illnesses, malnutrition, or multiple medications. The risk of diabetes complications increases with age.
Hypoglycemia can also result from taking too much diabetes medication. Overtreatment is common in older adults.
How To Raise Blood Sugar When Needed
Hypoglycemia, where your blood glucose is lower than 70 mg/dL, is a common problem for people with type 1 diabetes. Its important to know how to handle it when it happens. Hypoglycemia can be caused by a number of things, such as taking too much insulin, waiting too long before eating or not eating enough, and exercising a lot more than usual.
Resolving it might be as simple as eating something that can raise your blood glucose. But in severe cases, where your blood glucose dips below 55 mg/dL, this might not be enough.
If youre at risk of this, your health care provider might prescribe an injectable medication called glucagon to use in an emergency. You can use it yourself, or someone else can use it on you if youre not able to. You will then need to seek after the injection to make sure that your glucose levels make it back up to a safe level.
Also Check: Do I Have Low Blood Sugar Test
What To Do When Your Blood Sugar Is High Or Low
High blood sugar can harm you. If your blood sugar is high, you need to know how to bring it down. Here are some questions to ask yourself if your blood sugar is high.
- Are you eating too much or too little? Have you been following your diabetes meal plan?
- Are you taking your diabetes medicines correctly?
- Has your provider changed your medicines?
- Is your insulin expired? Check the date on your insulin.
- Has your insulin been exposed to very high or very low temperatures?
- If you take insulin, have you been taking the correct dose? Are you changing your syringes or pen needles?
- Are you afraid of having low blood sugar? Is that causing you to eat too much or take too little insulin or other diabetes medicine?
- Have you injected insulin into a firm, numb, bumpy, or overused area? Have you been rotating sites?
- Have you been less or more active than usual?
- Do you have a cold, flu, or another illness?
- Have you had more stress than usual?
- Have you been checking your blood sugar every day?
- Have you gained or lost weight?
Low Blood Sugar Level Causes
Most low blood sugar level causes are preventable and are caused due to a persons lifestyle and diet habits. Low blood sugar is common among diabetic patients who take medications to increase insulin levels.
All of the above causes are risk factors that may or may not be able to be inhibited. They are important to be aware of and act accordingly to keep yourself from getting a too high or too low blood sugar level.
If a person has medical, lifestyle or diet habits that cause irregular blood sugar levels, symptoms will begin to develop along with the drop or spike in blood sugar, and are as follows:
Read Also: What’s The Best Blood Sugar Monitor
How Can You Prevent Low Blood Sugar
The best way to prevent glucose levels that are too low is to practice careful diabetes management, checking your glucose often , and learning to recognize its early symptoms. Pay attention to the helpful arrows on your blood glucose meter or CGM if the arrow is pointing down, youll want to monitor your blood sugar to make sure you dont go low.
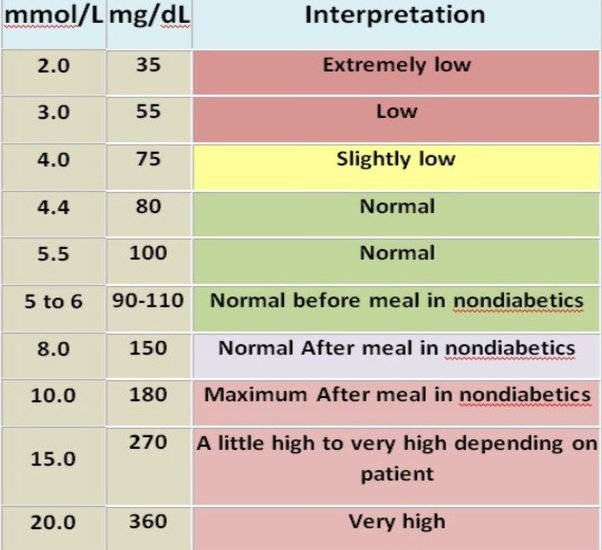
What Are Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose level, is the level of sugar/glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a simple version of sugar which comes from the food we eat. Therefore, the more food you consume with high sugar levels over a period of time, will typically increase your blood sugar level.
Glucose comes from the foods we eat and its sugar content. When a person consumes a food with high sugar content, that is turned into glucose. The glucose is then absorbed into the bloodstream with the support of insulin. This is then distributed between the bodys cells and used as energy.
Foods high in glucose include most carbohydrates and a handful of proteins and fats. Most foods contain glucose as it is simply a natural sugar that occurs in most dietary forms. However, it is carbohydrates that contain the most sugar and 100% of it turns into glucose, through the process mentioned above, once consumed. The concentration of glucose present in the blood will determine your blood sugar level.
Here is a quick video explaining Blood sugar levels chart :
Your blood sugar level can either be low, normal or high. Depending on what you eat and health conditions, it will vary from person to person. Here is a breakdown of how your blood sugar works and how low or high blood sugar levels happens:
Read Also: Is 240 Blood Sugar Too High
Normal Blood Sugar Before And After Meals
Normal blood sugar levels vary from person to person. That’s why when we talk about ‘normal’ blood glucose levels, we refer to a range of values that are considered healthy for most individuals. According to the World Health Organization ), a normal range for fasting blood sugar is between 70 and 100 milligrams per deciliter .
For most people, eating a meal or drinking a sugary drink will lead to a temporary increase in the blood glucose levels. As stated by the American Diabetes Association , the blood sugar two hours after eating should not exceed 140 milligrams per deciliter. However, people with certain metabolic conditions, such as prediabetes or diabetes, typically have lower blood sugar than those guidelines suggest. Researchers from the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology continuously measured people’s blood glucose and found that most individuals averaged around 82 mg/DL during the night and around 93 mg/DL during the day, and spiked to a maximum of 132 mg/DL an hour after a meal.
What Causes Blood Sugar To Be High
Many things can cause high blood sugar , including being sick, being stressed, eating more than planned, and not giving yourself enough insulin. Over time, high blood sugar can lead to long-term, serious health problems. Symptoms of high blood sugar include:
- Feeling very tired.
- Having blurry vision.
- Needing to urinate more often.
If you get sick, your blood sugar can be hard to manage. You may not be able to eat or drink as much as usual, which can affect blood sugar levels. If youre ill and your blood sugar is 240 mg/dL or above, use an over-the-counter ketone test kit to check your urine for ketones and call your doctor if your ketones are high. High ketones can be an early sign of diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately.
You May Like: Does High Blood Sugar Affect Kidneys
What Else Can I Do To Help Manage My Blood Sugar Levels
Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular physical activity can all help. Other tips include:
- Keep track of your blood sugar levels to see what makes them go up or down.
- Eat at regular times, and dont skip meals.
- Choose foods lower in calories, saturated fat, trans fat, sugar, and salt.
- Track your food, drink, and physical activity.
- Drink water instead of juice or soda.
- Limit alcoholic drinks.
- For a sweet treat, choose fruit.
- Control your food portions .
What Is A Normal Blood Sugar Level
Achieving a normal blood sugar or glucose level is a bit of a misnomer. Often, the word normal is used to reference what someones blood sugars might be if they didnt have diabetes.
However, this terminology is flawed because even people without diabetes do see blood sugar spikes, especially after eating and when consuming something with high amounts of sugar, or a complex carbohydrate like pizza or pasta.
Even though that persons body will immediately start working to counterbalance that rising glucose level by producing more insulin, their blood sugars may still spike for a brief time even beyond those normal ranges. The same can happen with intense exercise or in high-stress situations if the persons natural glucose metabolizing cannot quickly balance everything out.
For those with diabetes, the fact that our bodies dont make or use insulin correctly means we must manually keep tabs on blood sugar levels and take enough insulin or glucose-lowering medication to balance everything out.
Recommended Reading: Is Sugar Bad For Depression And Anxiety
High Blood Sugar Levels Symptoms
High blood sugar levels, or hyperglycemia can occur if you don’t take enough insulin, you miss a meal, or you exercise too little. High blood sugar levels can also be caused by stress, illness, or some medications.
Signs and symptoms that your blood sugar might be on the high side include:
- Increased urination
It’s important to treat high blood sugar levels quickly to avoid more serious problems. You can avoid high blood sugar levels by taking your insulin or diabetes medications regularly and following your recommended diet as best as possible.
If your blood sugar levels are higher than acceptable, you should monitor levels at frequent intervals and seek advice from your doctor or specialist nurse).
What Is High Blood Sugar
If your blood sugar levels are chronically higher than normal, then this is referred to as hyperglycaemia. This is a common issue for those suffering from diabetes. The condition can also affect pregnant women who have gestational diabetes and occasionally those who are severely ill .
Some of the symptoms of hyperglycaemia include:
- Increased thirst
- Issues with concentration and/or thinking
If severe hyperglycaemia is left untreated the condition can lead to organ and tissue damage as the excess glucose present in the body can make it difficult for the organs and cells to function correctly. The disorder can also impair the immune system response in the healing of wounds and cuts.
Also Check: Is 500 High For Blood Sugar
Hba1c Test For Diabetes Diagnosis
An HbA1c test does not directly measure the level of blood glucose, however, the result of the test is influenced by how high or low your blood glucose levels have tended to be over a period of 2 to 3 months.
Indications of diabetes or prediabetes are given under the following conditions:
- Normal: Below 42 mmol/mol
- Prediabetes: 42 to 47 mmol/mol
- Diabetes: 48 mmol/mol
Other Severe Symptoms Of Hyperglycaemia Include:
- Blood vessel damage
Mild hyperglycaemia, depending on the cause, will not typically require medical treatment. Most people with this condition can lower their blood sugar levels sufficiently through dietary and lifestyle changes.
Those with type 1 diabetes will require the administration of insulin , while those with type 2 diabetes will often use a combination of injectable and oral medications , although some may also require insulin.
Read Also: Is 70 Blood Sugar Normal
How Should Blood Sugar Levels Be Before And After Eating
In healthy individuals, preprandial blood glucose levels , are usually between 80-130 mg/dL. One to two hours after a meal , blood sugars levels are normally below 180 mg/dL.
Blood glucose levels can be affected by the type and amount of food consumed, as well as other different factors like physical activity, medications, co-existing medical conditions, stress, age, an illness, and even menstrual periods or pregnancy.
Blood Sugar Why Does It Matter In Diabetes
Blood sugar is the sugar or glucose in your blood. Having some sugar in your blood is vital because its a significant energy source for your body. A hormone called insulin, produced by the pancreas regulates blood sugar levels.
If you have diabetes, your body either doesnt make enough insulin or cant use the insulin it produces effectively. As a result, it raises your blood sugar levels, which may lead to several serious health problems if left untreated.
High blood sugar can damage your blood vessels and organs and lead to heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and amputation. Thats why controlling your blood sugar level is crucial if you have diabetes.
Recommended Reading: Can Not Eating Make Your Blood Sugar Go Up
Beyond Normal Goals: Whats An Optimal Glucose Level And Why Does It Matter
Exact numbers for what is considered optimal glucose levels to strive for while using CGM to achieve your best health are not definitively established this is a question that is individual-specific and should be discussed with your healthcare provider. With that said, research shows that there is an increased risk of health problems as fasting glucose increases, even if it stays within the normal range, making finding your optimal glucose levels all the more important.
While the International Diabetes Federation and other research studies have shown that a post-meal glucose spike should be less than 140 mg/dL in a nondiabetic individual, this does not determine what value for a post-meal glucose elevation is truly optimal for your health. All that number tells us is that in nondiabetics doing an oral glucose tolerance test, researchers found that these individuals rarely get above a glucose value of 140 mg/dL after meals.
So, while this number may represent a proposed upper limit of whats normal, it may not indicate what will serve you best from a health perspective. Many people may likely do better at lower post-meal glucose levels. Similarly, while the ADA states that a fasting glucose less than 100 mg/dL is normal, it does not indicate what value is optimal for health.
Repeated high glucose spikes after meals contribute to inflammation, blood vessel damage, increased risk of diabetes, and weight gain.
What Affects Blood Glucose Levels
Before we get into normal blood sugar levels for people without diabetes, and for people with diabetes, letâs explore the factors that affect blood glucose levels:
This is not even nearly an exhaustive list – you can find a fuller list of factors that affect blood glucose here – but these are some of the most common reasons for blood glucose fluctuations. There are plenty of biological factors that affect blood sugar as well, like puberty, menstruation, and having Celiac disease.
Itâs also easy to overlook behavioural and decision-making factors that have a way bigger effect on our blood glucose levels than we actually think. In reality, the number of times you check your blood glucose, your decision-making biases and social pressures influences your attitude towards controlling your blood sugar levels, so often has a significant effect.
This really illustrates the strength of Time-in-Range, which is considered the gold standard in blood glucose monitoring. Instead of focusing on an average, like A1C, or one measurement, like fasting glucose, Time-in-Range accounts for all the variations in your blood sugar levels, giving you a percentage of time you are within your target glucose range.
See more about our Time-in-Range in this blog post.
Don’t Miss: How Much Sugar Is Ok On Keto
Low Blood Sugar Chart And Action Plan
Low blood sugar is also called hypoglycemia. The numbers below represent values in the hypoglycemic range and require action to bring blood sugar levels up into a normal range.
| Alert Level and Treatment Plan | |
| 50 mg/dL or under | Red Flag: Blood sugar is critically low and requires immediate treatment.
If a person is unable to speak and/or is not alert, treat with glucagon via injection or nasal spray. Call emergency medical response if necessary. Do not place food or drink into the mouth. If a person is alert and able to speak clearly, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate such as glucose gel, 4 oz regular soda, or fruit juice. Re-test blood sugar in 15 minutes and repeat as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 51-70 mg/dL | Red Flag: Blood sugar is below normal levels and requires immediate treatment.
Treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 71-90 mg/dL | Yellow Flag: Blood sugar levels should be watched and treated as needed.
If youre having symptoms of low blood sugar, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment or follow with a meal. If it is meal time, move forward with eating the meal. People often fall into this range when they are late for a meal or have been especially active. |