Random Blood Sugar Test
This measures your blood sugar at the time youre tested. You can take this test at any time and dont need to fast first. A blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher indicates you have diabetes.
| 140 mg/dL or below | N/A |
*Results for gestational diabetes can differ. Ask your health care provider what your results mean if youre being tested for gestational diabetes.Source: American Diabetes Association
If your doctor thinks you have type 1 diabetes, your blood may also tested for autoantibodies that are often present in type 1 diabetes but not in type 2 diabetes. You may have your urine tested for ketones , which also indicate type 1 diabetes instead of type 2 diabetes.
What Should I Do If My Blood Sugar Gets Too High
High blood sugar is also called hyperglycemia . It means that your blood sugar level is higher than your target level or over 180. Having high blood sugar levels over time can lead to long-term, serious health problems.
If you feel very tired, thirsty, have blurry vision, or need to pee more often, your blood sugar may be high.
Check your blood sugar and see if it is above your target level or over 180. If it is too high, one way to lower it is to drink a large glass of water and exercise by taking a brisk walk. Call your health care team if your blood sugar is high more than 3 times in 2 weeks and you dont know why.
How Do I Take Care Of My Blood Glucose Meter
- Set the date and time when you get a new meter.
- Make sure the date and time are right each time you use your meter.
- Use the control solution as needed. This will let you know the meter and test strips are working right. Use it:
- When you get a new meter.
- When you get new test strips.
- When you think that the meter is not giving you the right blood glucose number.
You May Like: How To Get Off Sugar And Carbs
Low Blood Sugar Chart And Action Plan
Low blood sugar is also called hypoglycemia. The numbers below represent values in the hypoglycemic range and require action to bring blood sugar levels up into a normal range.
| Alert Level and Treatment Plan | |
| 50 mg/dL or under | Red Flag: Blood sugar is critically low and requires immediate treatment.
If a person is unable to speak and/or is not alert, treat with glucagon via injection or nasal spray. Call emergency medical response if necessary. Do not place food or drink into the mouth. If a person is alert and able to speak clearly, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate such as glucose gel, 4 oz regular soda, or fruit juice. Re-test blood sugar in 15 minutes and repeat as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 51-70 mg/dL | Red Flag: Blood sugar is below normal levels and requires immediate treatment.
Treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 71-90 mg/dL | Yellow Flag: Blood sugar levels should be watched and treated as needed.
If youre having symptoms of low blood sugar, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment or follow with a meal. If it is meal time, move forward with eating the meal. People often fall into this range when they are late for a meal or have been especially active. |
Blood Sugar And A1c Levels In Prediabetes

When talking about blood glucose levels in prediabetes and diabetes, you might also hear about A1C. The glycated hemoglobin test, or A1C, is another test that your doctor could order to determine if you have prediabetes or diabetes.
The FBG and OGTT measure blood sugar at the single moment in time when your blood sample is taken. In contrast, A1C helps evaluate your average blood sugar control over the past three months.
The A1C is slightly less common and more expensive than FPG, but not by much. You do not need to fast for the A1C, and it takes only a single blood draw, like the FPG. Here are the A1C values for normal, prediabetes, and diabetes:
| Normal |
|---|
Also Check: Causes Of High Glucose Levels
Now That Youre Checking Your Blood Glucose What Do The Numbers Mean
Depending on your diabetes treatment plan, your doctor or diabetes educator may advise you to check once a week, once a day or up to 10 times a day . But what does it mean when you see a 67, 101 or 350 on your meter? And what is a normal blood sugar, anyway? Great questions! After all, if you dont know what the numbers on your meter mean, its hard to know how youre doing.
The American Diabetes Association provides guidelines for blood glucose goals for people with diabetes, and the goals vary depending on when youre checking your glucose:
Fasting and before meals: 80130 mg/dl
Postprandial : Less than 180 mg/dl
By the way, these guidelines are for non-pregnant adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Children, adolescents and pregnant women may have different goals.
Your blood glucose goals may be different, however. If youre younger, have had diabetes for a shorter amount of time or are not taking any medicine for your diabetes, your glucose goals might be a little tighter, or lower. Likewise, your blood glucose goals may be higher than what ADA recommends if youre older, have diabetes complications, or dont get symptoms when your blood glucose is low.
Bottom line: talk with your health-care provider about the following:
When to check your blood glucose How often to check your blood glucose What your blood glucose goals are
What Is Low Blood Sugar
Hypoglycaemia is a condition wherein blood sugar levels are too low. This condition affects a number of diabetic people when their bodies do not have enough glucose to use as energy. Hypoglycaemia is commonly the result of taking too much of the medication/s prescribed to treat diabetes, eating less than expected, exercising more than normal or skipping meals.
Some of the symptoms of hypoglycaemia include:
- A pale face
Recommended Reading: Most Sugar Fruit
Your Blood Sugar Isnt Just Because Of What You Eat
Mainstream media would have you believe that your blood sugar levels are impacted only by what you eat and how much you exercise, but people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes who test their blood sugars frequently could tell you otherwise.
Its especially important to keep this mind when looking at your own blood sugars and your goals because there are certain variables and challenges that impact blood sugar levels that you cant always control.
For example:
- Menstrual cycles: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Adrenaline rushes from competitive sports, heated arguments, rollercoaster rides: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- The common cold and other illnesses: usually raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Hormonal changes due to puberty and healthy growth in young adults: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- An injury which raises overall inflammation levels: raises blood sugar and insulin needs
- Glucogenesis during anaerobic exercise: raises blood sugar
While you cant necessarily prevent these factors that affect your blood sugar from occurring, you can work with your diabetes healthcare team to adjust your insulin, other diabetes medications, nutrition and activity levels to help compensate for them when they do occur.
For example, when engaging in anaerobic exercise like weightlifting many people with type 1 diabetes find it necessary to take a small bolus of insulin prior to or during their workout because anaerobic exercise can actually raise blood sugar.
Cgm Studies In Nondiabetic Individuals
One study from 2009 entitled Reference Values for Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Chinese Subjects looked at the glucose levels of 434 healthy adults using CGM and found the following:
- On average, their daily glucose levels stayed between 70140 mg/dl for 93% of the day, with very small portions of the day spent above 140 mg/dl or below 70 mg/dl.
- Also, their mean 24-hour glucose levels were around 104 mg/dl
- 1-hour post-meal glucose values average 121-123 mg/dl for breakfast, lunch, and dinner
- 3-hour post-meal glucose values were around 97-114 mg/dl.
- Peak post-meal values appeared to be around 60 minutes after eating.
- Mean fasting glucose was 86 ± 7 mg/dl.
- Mean daytime glucose was 106 ± 11 mg/dl.
- Mean nighttime glucose was 99 ± 11 mg/dl.
A 2010 study, Variation of Interstitial Glucose Measurements Assessed by Continuous Glucose Monitors in Healthy, Nondiabetic Individuals, looked at a healthy population of 74 individuals that included children, adolescents, and adults during daily living using CGM. This research showed that:
- Glucose levels stayed between 71-120 mg/dl for 91% of the day.
- Levels were lower than 70 mg/dl for 1.7% of the time and greater than 140 mg/dl, only 0.4% of the time.
- Mean 24-hour glucose was 98 ± 10 mg/dl.
- Mean fasting glucose of 86 ± 8 mg/dl.
Compared to the first study mentioned, these healthy, nondiabetic individuals appeared to have a tighter range of glucose, spending the vast majority of the 24-hour period between 71-120 mg/dl.
Read Also: Can Prediabetes Eat Bananas
How Is Blood Sugar Measured
In the United States, blood sugar is measured in milligrams per deciliter . This is abbreviated as mg/dl.
In Europe and Canada, blood sugar is measured a little differently, by millimole per liter, which is abbreviated mmol. However its measured, blood sugar is the concentration of sugar or glucose in the bloodstream.
If you multiply the Canadian or European mmol, by the number 18, you can calculate milligrams per deciliter.
In other words, if a person in Canada reports their blood sugar as an 8, multiply 8 times 18 to give you the number 144 . Using this calculation, this persons blood sugar = 144 mg/dl, .
Blood Sugar Target Ranges For Gestational Diabetes
The strictest and tightest control of blood sugars is necessary when a patient has gestational diabetes. This tight control is necessary to keep mother and baby safe when the mother has gestational diabetes.
In addition to increased complications for the mother, an infant born to a mother with gestational diabetes is at an increased risk of being born with a high birth weight . This condition is called macrosomia. Later on in life, the infant may be more prone to becoming obese, and to developing Type 2 Diabetes.
When the extra sugar in the mothers bloodstream crosses the placenta, the infants pancreas is signaled to make more insulin. Therefore, the infant grows too large in utero.
After birth, the infant is at increased risk of hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar related to the excessive amounts of insulin their pancreas produces.
Blood sugar target ranges for gestational diabetes from the American Diabetes Association
The blood sugar target ranges for gestational diabetes coincide with an A1C of less than 6 percent. As long as this is able to be achieved without episodes of low blood sugar or hypoglycemia, this tight control is sought out
- Fasting and pre-meal less than or equal to 95 mg/dl
- One-hour post-meal less than or equal to 140 mg/dl
- Two-hour post-meal less than or equal to 120 mg/dl
For women with preexisting diabetes who become pregnant, blood sugar target levels are as follows:
If you need more information:
Recommended Reading: Can Sugar Cause Afib
Whats My Target Range
You might be asking, what’s the normal range for blood sugar levels? The answer is, there is a healthy range that you should ideally be aiming for. The infographics above show the general guidelines, but your individual target range for your blood sugar levels may be different. Youll healthcare team will agree with you what it is.
Youll get different readings at different times of the day, depending on things like what youve eaten and how much you are moving around. Heres a guide to help you get started on finding your target range:
If youre a child with Type 1 diabetes
- when you wake up and before meals: 4 to 7mmol/l
- after meals: 5 to 9mmol/l
If youre an adult with Type 1 diabetes
- when you wake up and before meals: 5 to 7mmol/l
- before meals at other times of the day: 4 to 7mmol/l
If you have Type 2 diabetes
- before meals: 4 to 7mmol/l
- two hours after meals: less than 8.5mmol/l
Low Blood Sugar: What To Watch Out For
Hypoglycemia can occur in people with diabetes who:
- Take too much medication or insulin
- Are late eating a meal or snack
- Have increased physical activity
- Drink too much alcohol
Symptoms of low blood sugar include feeling weak, sweaty or clammy, confused, hungry and/or irritable. Sometimes people experience a fast heartbeat and some symptoms may make a person appear to be drunk. A severely low blood sugar can result in unconsciousness, seizures, coma or death especially when a low occurs during the night.
Low blood sugar affects many parts of the body, but the most frustrating part can be that hypoglycemia can happen anytime and anywhere even when you think you are closely following the plan for your diabetes care. If low blood sugar is severe, people may need to go to the hospital to help raise their glucose level or miss work due to the side effects.
It can happen during a date, during a business meeting, or even while driving, which is the most dangerous scenario if there is confusion or loss of consciousness while behind the wheel. Its important to use your blood glucose meter to check your blood sugar before you drive to keep yourself and others safe. Frequent testing with your blood sugar meter and taking action when blood sugar is trending low can prevent a severe low and keep your life on track.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take To Lower Blood Sugar
What Blood Sugar Level Is Prediabetic
Exercise, Fitness & Nutrition Expert | Lark Health
Prediabetes is a condition with increased blood sugar, but how is it measured? Exactly what sugar level range is considered prediabetic, and how is that different from diabetes? Here is what you need to know about blood sugar levels in prediabetes, and what you can do about yours.
If you have been told that you have prediabetes, or you think that you might have it or be at risk for it, you can take your awareness in a positive way. While nobody actually wants to think about having a chronic health condition, being aware of prediabetes can be seen as a fork in the road of life.
On one branch of the fork in the road, prediabetes can lead to type 2 diabetes. Most people who get prediabetes take this branch, and end up with diabetes. However, you can choose to take the other branch in the road because in most cases, prediabetes is reversible.
Are you at risk for type 2 diabetes? Lark Diabetes Prevention Program is a personalized program to help you lower your risk by making healthy lifestyle changes, such as losing weight and increasing physical activity. Your personal Lark coach is available to support you 24/7 on your smartphone. Lark can help you make small changes that fit into your lifestyle and have big results for your health!
How Do I Prepare For The Plasma Glucose Level Test And How Are The Results Interpreted
To get an accurate plasma glucose level, you must have fasted for at least 8 hours prior to the test. When you report to the clinic or laboratory, a small sample of blood will be taken from a vein in your arm. According to the practice recommendations of the American Diabetes Association, the results of the blood test are interpreted as follows:
Fasting blood glucose level
- If your blood glucose level is 70 to 99* mg/dL . . .
- What it means: Your glucose level is within the normal range
*Values between 50 and 70 are often seen in healthy people
**The condition of “prediabetes” puts you at risk for developing Type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and blood lipid disorders
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 02/21/2018.
References
You May Like: Hyperglycemic Diet
What Is Your Blood Sugar
Your blood sugar, or glucose , is the sugar content found in your blood. Its a vital source of energy for your organs and muscles.
Think of it like the fuel in your gas tank. Without gas pumping through your cars system, youre going to slow down and eventually come to a halt. Same with blood sugar, which is why people with low blood sugar often feel tired.
You get it from the foods that you eat, and then a complex system involving the pancreas, liver, and small intestine regulates its distribution throughout your body. Your body is SUPER picky and only likes this stuff up to a certain level.
Well get to glucose levels in a minute, but lets cover what glucose is first.
Diagnosing Prediabetes Type 2 And Type 1 Diabetes
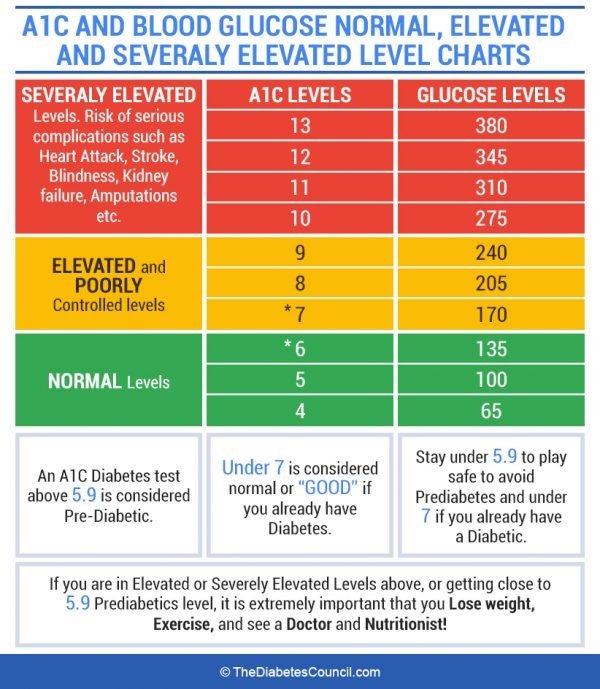
Depending on which country or medical organization you ask, the qualifying numbers for normal versus prediabetes versus diagnosed type 1 or type 2 diabetes can vary slightly. The following blood sugar and A1c the general results are used to diagnosed prediabetes and diabetes according to sources including the American Diabetes Association and Diabetes UK:
Prediabetes
- HbA1c: 5.7 to 6.4 percent
- Fasting: 100 to 125 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL
Type 1 or 2 diabetes
- HbA1c: 6.5 percent or higher
- Fasting: 126 mg/dL or higher
- 2 hours after a meal: 200 mg/dL or higher
Please note: Type 1 diabetes tends to develop very quickly which means that by the time symptoms are felt, blood sugar levels are generally well above 200 mg/dL all the time. For many, symptoms come on so quickly they are dismissed as the lingering flu or another seemingly ordinary virus.
By the time blood sugar levels are tested, many newly diagnosed type 1 patients will see levels above 400 mg/dL or higher. If you do suspect that you or a loved-one has type 1 diabetes, visit your primary care or urgent care immediately and ask for a urine test to measure ketones in addition to testing blood sugar levels and A1c.
Read more about ketones at diagnosis in Diabetes StrongsDiabetic Ketoacidosis Guide.
Also Check: Hyper Glycemic Diet