Can Hyperglycemia Be Treated
Your doctor may recommend a low-impact exercise program as your first line of defense. If youre already following a fitness plan, they may recommend that you increase your overall level of activity.
Your doctor may also suggest that you eliminate glucose-rich foods from your diet. Its important to maintain a balanced diet and stick to healthy food portions. If you arent sure where to begin, your doctor can refer you to a dietician or nutritionist who can help you establish a diet plan.
If these changes dont help lower your high blood sugar, your doctor may prescribe medication. If you have diabetes, your doctor may prescribe oral medications or change the amount or type of insulin youve already been prescribed.
Can My Blood Sugar Drop After My Run
Engaging in very long exercise sessions can result in reducing blood sugars, hours or even days after exercising. To combat this, one strategy you may implement is to reduce post-exercise basal or bolus insulin.
Kirpitch says, “Aerobic exercise most commonly will lower glucose. Reducing basal rates on an insulin pump may be utilized to help mitigate hypoglycemia, however it should be noted that reducing basal rates one to two hours pre-exercise alone has not been consistently effective in reducing hypoglycemia during exercise and can sometimes result in hyperglycemia post activity. The increase in insulin sensitivity can be sustained for 24-48 hours with the highest risk of hypoglycemia overnight following the exercise. Exercising in the afternoon further increases the risk for nocturnal hypoglycemia. Reducing bolus insulin for food around activity and utilizing carbohydrate-containing snacks as needed can help to balance out the amount of circulating insulin and risk for hypoglycemia.”
Can My Blood Sugar Rise During A Run
Typically, hyperglycemia occurs during short bouts of high-intensity workouts such as interval training. These types of exercises can cause the body to release hormones such as adrenaline, which is released as part of a stress response and raises blood sugar by increasing the production of glucose by the liver.
Sometimes, it is recommended to do these types of exercise before running so that blood sugar levels are less likely to drop. But its also not entirely out of the ordinary for blood sugar to rise, particularly during longer runs when runners are ingesting carbohydrates to fuel their run.
To combat potentially high blood sugars, some experienced long-distance runners, Find it helpful to utilize increased basal rates or a small bolus of insulin to counteract the rising glucose levels that can occur during a run, says Kirpitch. This is highly individualized and is typically utilized when a person with diabetes has more experience with blood sugar management and longer runs.
But, whether or not you bolus for high blood sugar or increase your basal rate during your run will really depend on your level of experience and comfort in managing your blood sugars.
You May Like: Will Apple Cider Vinegar Help Lower Blood Sugar
What To Expect From Your Blood Sugar In The Morning
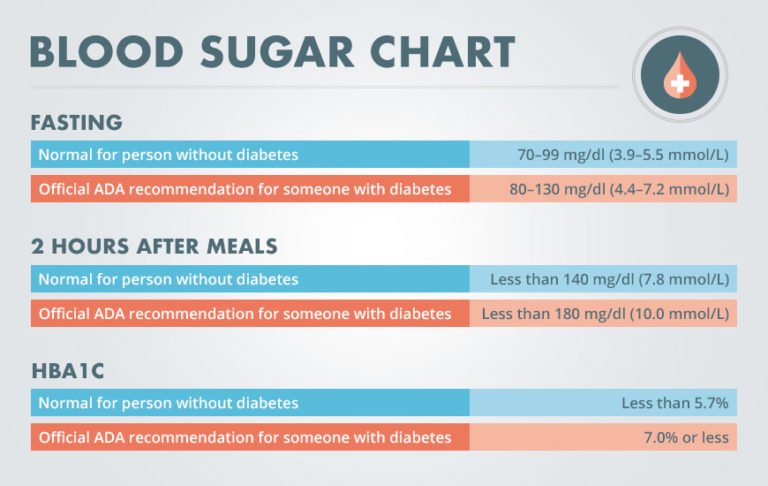
After an overnight fast, a normal blood sugar level is less than 100 milligrams per deciliter , according to the American Diabetes Association . But, according to Susan Spratt, MD, an endocrinologist and associate professor of medicine at Duke University School of Medicine, not everyone with type 1 or type 2 diabetes has to shoot for “normal” levels.
“If you’re young, the goal may be to get your fasting blood sugar levels to less than 120 mg/dL,” Dr. Spratt says. But if you’re older and have other health conditions, that number may be higher, she says.
The ADA points out that not everyone will have the same blood sugar level goals. Instead, your endocrinologist or doctor will calculate your target number based on your age, how long you’ve had diabetes, whether you have health conditions like heart disease and other factors.
Keep in mind, too, that your fasting blood sugar levels can be too low. For example, a morning blood sugar reading below 70 mg/dL can indicate a hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar.
Read more:Which Helps You More in the Morning: Tea, Water or Coffee?
What Causes Blood Sugar To Be High
Many things can cause high blood sugar , including being sick, being stressed, eating more than planned, and not giving yourself enough insulin. Over time, high blood sugar can lead to long-term, serious health problems. Symptoms of high blood sugar include:
- Feeling very tired.
- Having blurry vision.
- Needing to urinate more often.
If you get sick, your blood sugar can be hard to manage. You may not be able to eat or drink as much as usual, which can affect blood sugar levels. If youre ill and your blood sugar is 240 mg/dL or above, use an over-the-counter ketone test kit to check your urine for ketones and call your doctor if your ketones are high. High ketones can be an early sign of diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Real Sugar Mummy Online
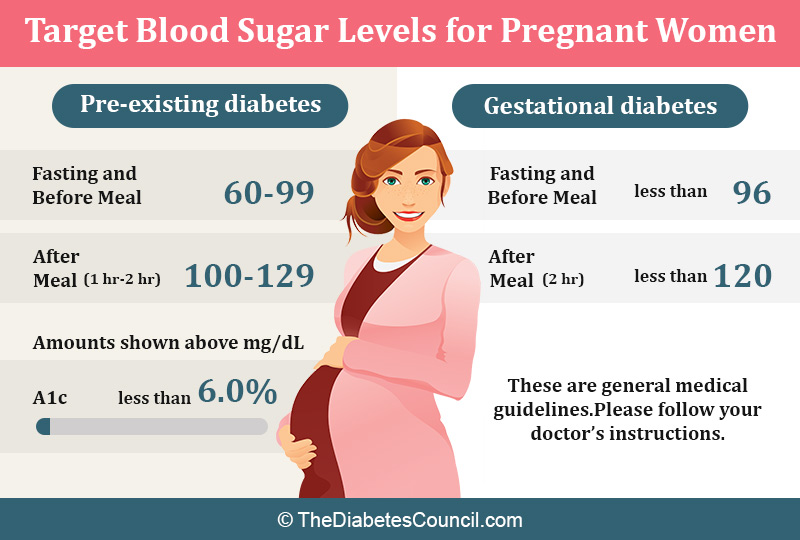
Target Blood Sugar Levels For Pregnant Women With Diabetes
It’s possible for diabetes to cause problems during pregnancy. For example, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, women with type 1 and type 2 diabetes who have uncontrolled blood sugar levels could experience an increased risk of having a premature baby, needing a C-section and more.
Gestational diabetes a type of diabetes that occurs in a pregnant woman who has never been diagnosed with diabetes before can also cause complications. These include giving birth to a baby who is larger than average and an increased risk of needing a C-section. The ADA suggests that pregnant women shoot for a target fasting blood sugar level of 95 mg/dL or less before a meal.
Read more:Do Oranges Raise Your Blood Sugar?
Blood Sugar And Exercise
There are a few ways that exercise lowers blood sugar:
- Insulin sensitivity is increased, so your muscle cells are better able to use any available insulin to take up glucose during and after activity.
- When your muscles contract during activity, your cells are able to take up glucose and use it for energy whether insulin is available or not.
This is how exercise can help lower blood sugar in the short term. And when you are active on a regular basis, it can also lower your A1C.
You May Like: How Much Sugar Is In Honey
Recommended Target Blood Glucose Level Ranges
The NICE recommended target blood glucose levels are stated below for adults with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and children with type 1 diabetes.
In addition, the International Diabetes Federations target ranges for people without diabetes is stated.
The table provides general guidance. An individual target set by your healthcare team is the one you should aim for.
| Target Levels |
|---|
*The non-diabetic figures are provided for information but are not part of NICE guidelines.
Why Your Blood Sugar Level May Be Low
If blood sugar drops below 70 mg/dL, it is below normal levels. This can be caused by a variety of factors, such as:
- Not eating enough or missing a meal or snack
- Reducing the amount of carbohydrates you normally eat
- Alcohol consumption especially if youre drinking on an empty stomach
- Taking too much insulin or oral diabetes medication based on carbohydrates or activity levels
- Increased physical activity
- Side effects from medications
If you have diabetes, keep your blood glucose meter and sources of fast-acting glucose close by in case your blood sugar drops. This is especially important for people with hypoglycemia unawareness, which is a condition that causes symptoms of low blood sugar to go unnoticed.
Eating balanced meals and snacks at regular times throughout the day is a big part of maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Check out our article on meal planning for diabetes to better understand the three macronutrients where calories come from and which have the biggest effect on blood sugar.
Meal Planning for Diabetes: How to Optimize Your Diet >
Everyone will respond differently to certain factors, which is why its important to have individualized target glucose levels. To help you reach your target blood glucose goals, work with your healthcare provider to discuss modifications to your diet, physical activity, or medications, and alert them of other factors like a recent illness or stressful event.
Read Also: Can Lack Of Sleep Cause Blood Sugar To Rise
Ideal Blood Glucose Levels
The specific level of blood glucose that’s considered ideal for you depends on your age, how long you have had diabetes, medications you take, and any other medical conditions you may have, among other factors.
What’s more, various health organizations differ in what they consider to be ideal glucose levels.
If you have diabetes and blood glucose monitoring is a part of your treatment strategy, your doctor will have the last word on what your target glucose levels at any given time during the day should be.
That said, there are some general parameters worth knowing about, according to the American Diabetes Association.
When Things Go Awry
When we eat food, the pancreas goes to work, releasing enzymes that help to break down food and hormones that help the body handle the influx of glucose. One of these hormones is insulin, and it plays a key role in managing glucose levels in the blood.
And here is where things can go wrong. If the pancreas doesnt make enough insulin or stops making it altogether, in the case of type 1 diabetes glucose levels in the blood can rise too high. Another scenario is that the pancreas makes enough insulin but the cells have trouble using it properly, causing blood glucose levels to rise. This is called insulin resistance and is the hallmark of type 2 diabetes.
In the short term, high blood glucose levels can make you feel downright bad. Thirst, frequent trips to the bathroom, fatigue and weight loss are all symptoms of high blood glucose . If not treated, more serious issues can occur, such as diabetic ketoacidosis. Chronic high blood glucose levels can lead to complications such as heart, kidney and eye disease, as well as nerve damage. So, its all about the blood glucose.
Read Also: What Is Blood Sugar Level
How To Use A Glucose Meter
Glucometers are easy to use. Take the following steps to successfully test blood glucose:
People with type 2 diabetes normally need to test blood sugar concentrations at least once each day.
Those who need to take insulin, which includes all people with type 1 diabetes and some with type 2, have to test their blood several times a day.
An accurate reading of the blood glucose level can help achieve good diabetes control.
Low Blood Sugar Chart And Action Plan
Low blood sugar is also called hypoglycemia. The numbers below represent values in the hypoglycemic range and require action to bring blood sugar levels up into a normal range.
| Alert Level and Treatment Plan | |
| 50 mg/dL or under | Red Flag: Blood sugar is critically low and requires immediate treatment.
If a person is unable to speak and/or is not alert, treat with glucagon via injection or nasal spray. Call emergency medical response if necessary. Do not place food or drink into the mouth. If a person is alert and able to speak clearly, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate such as glucose gel, 4 oz regular soda, or fruit juice. Re-test blood sugar in 15 minutes and repeat as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 51-70 mg/dL | Red Flag: Blood sugar is below normal levels and requires immediate treatment.
Treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 71-90 mg/dL | Yellow Flag: Blood sugar levels should be watched and treated as needed.
If youre having symptoms of low blood sugar, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment or follow with a meal. If it is meal time, move forward with eating the meal. People often fall into this range when they are late for a meal or have been especially active. |
Recommended Reading: What Happens If Blood Sugar Drops Too Low
What To Know About High Blood Sugar When Living With Diabetes:
What is hyperglycemia?
After eating a meal, the body signals the release of insulin. Insulin is like a key that unlocks the cells in order to store glucose for later use. This process reduces the amount of glucose in your blood stream. In people with diabetes, this process does not work as well because either there isnt enough insulin being produced, or because the body is resistant to the effects of the insulin. As a result, levels of glucose in the blood stream can reach high levels, causing hyperglycemia or high blood sugar.
Scale of normal blood sugar range
- Hyperglycemia occurs when the blood sugar is above 130 mg/dL while fasting, or greater than 180 mg/dL after eating a meal.
- American Diabetes Association Glucose Goals for people with Diabetes:
- Before meals or fasting: 70 to 130 mg/dL
- 1-2 hours after the start of a meal: Less than 180 mg/dL
Hb A1C If blood glucose is regularly higher than the normal ranges, then this will reflect in the Hemoglobin A1C test that your doctor will run. The Hemoglobin A1C gives your care team an idea of what your blood sugar typically is at.
Symptoms of hyperglycemia
- Illness, colds, infections, injuries, surgeries
- Emotional stress
- Not enough Diabetes Medication, or skipped doses of medication
- Too little exercise
How to treat hyperglycemia
When to call your doctor or seek emergency treatment:
REMEMBER: DO NOT DRIVE yourself if you think you may have very high blood Sugars or Diabetic Ketoacidosis
What Abnormal Results Mean
If you had a fasting blood glucose test:
- A level of 100 to 125 mg/dL means you have impaired fasting glucose, a type of prediabetes. This increases your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- A level of 126 mg/dL or higher usually means you have diabetes.
If you had a random blood glucose test:
- A level of 200 mg/dL or higher often means you have diabetes.
- Your provider will order a fasting blood glucose, A1C test glucose tolerance test , depending on your random blood glucose test result.
- In someone who has diabetes, an abnormal result on the random blood glucose test may mean that the diabetes is not well controlled.
Other medical problems can also cause a higher-than-normal blood glucose level, including:
- Overactive thyroid gland
- Swelling and inflammation of the pancreas ( pancreatitis
- Stress due to trauma, stroke, heart attack, or surgery
- Rare tumors, including
- Weight loss after weight loss surgery
- Vigorous exercise
Some medicines can raise or lower your blood glucose level. Before having the test, tell your provider about all the medicines you are taking.
For some thin young women, a fasting blood sugar level below 70 mg/dL may be normal.
You May Like: How Is Cane Sugar Made
High Blood Sugar: Hidden Dangers
In the short term, high blood sugar levels can zap your energy, cause excessive thirst and urination, and blur your vision. High blood sugar levels can also lead to dehydration, dry and itchy skin, and infections. Minimizing the time spent above your target blood sugar range can help you feel your best and will help prevent complications and injury to your body.
Over time, high blood sugar affects many parts of the body. Chronic high blood sugar can start to cause noticeable changes, including:
- Memory problems
- Vision problems like blurriness, diabetic retinopathy, and blindness
- Gum disease that leads to tooth loss, which can make eating healthy foods difficult due to problems chewing
- Heart attack and stroke due to increased plaque build-up in the vessels and other vascular issues
- Kidney disease, which can lead to the need for dialysis or a kidney transplant
- Nerve damage that can cause decreased sensation in the feet and legs which increases the risk for wounds to turn into serious infections and even amputation
Nerve damage from high blood sugar can also cause a variety of symptoms including:
- Pain and tingling in the feet and hands
- Difficulty emptying your bladder
- Problems during the digestion process after eating, which can cause food to sit in the stomach too long and lead to nausea, vomiting, and erratic blood sugar levels
Checking your blood sugar frequently and taking immediate action when it is above range can reduce your risk of complications.
What Can Cause Low Blood Sugar Levels
Some things that can make low blood sugar levels more likely are:
- skipping meals and snacks
- not eating enough food during a meal or snack
- exercising longer or harder than usual without eating some extra food
- getting too much insulin
- not timing the insulin doses properly with meals, snacks, and exercise
Also, some things may increase how quickly insulin gets absorbed into the bloodstream and can make hypoglycemia more likely. These include:
- taking a hot shower or bath right after having an insulin injection increases blood flow through the blood vessels in the skin, which can make the insulin be absorbed more quickly than usual
- injecting the shot into a muscle instead of the fatty layer under the skin
- injecting the insulin into a part of the body used a lot in a particular sport .
All of these situations increase the chances that a person may get hypoglycemia.
page 1
Recommended Reading: How To Check For Blood Sugar At Home