General Treatment Of Diabetes
People with diabetes benefit greatly from learning about the disorder, understanding how diet and exercise affect their blood glucose levels, and knowing how to avoid complications. A nurse trained in diabetes education can provide information about managing diet, exercising, monitoring blood glucose levels, and taking drugs.
|
|
What Happens If I Have Kidney Disease
Your healthcare provider will create a special treatment plan for you. This may include taking medicines, limiting salt and certain foods, getting exercise, and more. You will also need regular checkups to monitor your kidney function. Having kidney disease or diabetes does not mean your kidneys will fail. Finding and treating it early can help keep kidney disease from getting worse.
The Basics Of High Blood Sugar
Diabetes is a problem with your body that causes blood sugar levels to rise higher than normal. This is also called hyperglycemia.
When you eat, your body breaks food down into sugar and sends it into the blood. Insulin then helps move the sugar from the blood into your cells. When sugar enters your cells, it is either used as fuel for energy right away or stored for later use. In a person with diabetes, there is a problem with insulin. But, not everyone with diabetes has the same problem.
There are different types of diabetestype 1, type 2 and gestational diabetes. If you have diabetestype 1, type 2 or gestationalyour body either doesn’t make enough insulin, can’t use the insulin well, or both.
Learn more about blood sugar Learn more about insulin
Don’t Miss: What Vitamin Deficiency Causes Sugar Cravings
The Endocrine System And Diabetes
Diabetes affects how the body regulates blood glucose levels. Insulin helps to reduce levels of blood glucose whereas glucagons role is to increase blood glucose levels.
In people without diabetes, insulin and glucagon work together to keep blood glucose levels balanced.
In diabetes, the body either doesnt produce enough insulin or doesnt respond properly to insulin causing an imbalance between the effects of insulin and glucagon.
In type 1 diabetes , the body isnt able to produce enough insulin and so blood glucose becomes too high unless insulin is injected.
In type 2 diabetes , the body is unable to respond effectively to insulin, which can also result in higher than normal blood glucose levels. Medications for type 2 diabetes include those which help to increase insulin sensitivity, those which stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin and other medications which inhibit the release of glucagon.
Response To An Increase In Blood Glucose
In the absorptive state, an increase in blood glucose is detected by the beta cells of the pancreatic islets, causing them to increase the release of insulin into the blood. Insulin stimulates cells, especially adipose and muscle cells, to take up glucose from the blood.
Insulin and the transport of glucose into cells – To enter cells, glucose requires trans-membrane transporters and there is a family of these called GLUT . The most numerous is GLUT4, which is found on muscle and fat cells.
When insulin binds to insulin receptors on the cell membrane, cells are stimulated to increase the number of glucose transporters. The more transporters are produced, the more glucose is transported into cells – with a corresponding drop in blood glucose.
The precise mechanism whereby insulin binds to receptors causing translocation is still to be determined .
Not all tissues require insulin to take up glucose, for example brain and liver cells use GLUT transporters that are not dependent on insulin.
Further effects of insulin – The hormone also has other effects on the bodys cells, all of which contribute to an increase in glucose usage and storage – and therefore a reduction in blood glucose. These include:
– The promotion of glycolysis, a process that breaks down glucose for cellular energy
– The promotion of glycogenesis, a process that converts glucose into glycogen for storage
– The inhibition of lipolysis, a process that breaks down lipids to release energy.
Read Also: Reduce Sugar Level Immediately
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Treated
Sometimes people with type 2 diabetes take pills that help the insulin in their bodies work better. Some also need insulin shots or an insulin pump to control their diabetes.
People with type 2 diabetes have to pay a little more attention to what they’re eating and doing than people who don’t have diabetes. They may need to:
- Eat a healthy diet, as determined by the care team.
- Get regular physical activity to achieve a healthy weight and allow insulin to work more effectively.
- Check their blood sugar levels on a regular basis.
- Get treatment for other health problems that can happen more often in people with type 2 diabetes, like high blood pressure or problems with the levels of fats in their blood.
- Have regular checkups with doctors and other people on their diabetes health care team so they can stay healthy and get treatment for any diabetes problems.
People with type 2 diabetes might have to eat smaller food portions and less salt or fat, too. Those who eat healthy foods, stay active, and get to a healthy weight may bring their blood sugar levels into a healthier range. Their doctors may even say they don’t need to take any medicines at all.
Flax Seeds And Chia Seeds
Chia and flax seeds are both rich in fiber and omega fatty acids and have a glycemic index score below 10. The fiber improves blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity by encouraging a steady rise in blood sugar, preventing roller coaster spikes and drops. This stabilizing effect helps you avoid a sluggish feeling after meals.
Theyâre also one of the most flexible foods on this list, making simple, tasty additions to your favorite salads, yogurt, and smoothies. You can even try making chia seed pudding as a low glycemic dessert option!
Don’t Miss: Reduce Sugar Level Instantly
What Is The Function Of Glucagon
Your body normally carefully regulates your blood glucose primarily with the hormones glucagon and insulin. When your blood glucose levels trend lower or fall too low , your pancreas releases more glucagon. Glucagon helps blood glucose levels rise back up in multiple ways, including:
- Glucagon triggers your liver to convert stored glucose into a usable form and then release it into your bloodstream. This process is called glycogenolysis.
- Glucagon can also prevent your liver from taking in and storing glucose so that more glucose stays in your blood.
- Glucagon helps your body make glucose from other sources, such as amino acids.
If your blood glucose levels trend higher, your pancreas releases insulin to bring it back into range.
The Important Roles Of Insulin And Glucagon: Diabetes And Hypoglycemia
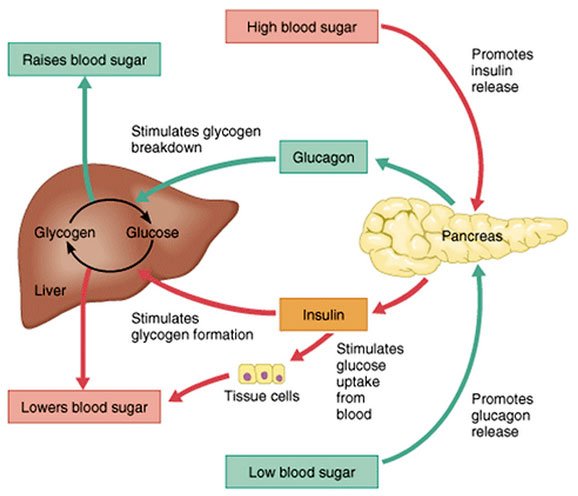
The human body wants blood glucose maintained in a very narrow range. Insulin and glucagon are the hormones which make this happen. Both insulin and glucagon are secreted from the pancreas, and thus are referred to as pancreatic endocrine hormones. The picture on the left shows the intimate relationship both insulin and glucagon have to each other. Note that the pancreas serves as the central player in this scheme. It is the production of insulin and glucagon by the pancreas which ultimately determines if a patient has diabetes, hypoglycemia, or some other sugar problem.
You May Like: How To Bring Down Sugar Level Quickly
Response To A Decrease In Blood Glucose
Several hours after eating a meal, when the body is in the post-absorptive state, insulin levels fall along with blood glucose and this results in the hormone glucagon being released by the alpha cells of the pancreas.
The role of glucagon – Glucagon has the opposite effect to insulin in that it increases blood-glucose levels and promotes processes that spare glucose utilisation.
Glucagon works primarily on the hepatocytes in the liver to:
– Convert stored glycogen into glucose and release it into the blood
– Promote gluconeogenesis, the manufacture of new glucose from lactic acid and other metabolites.
Glucagon binds to glucagon receptors, which are part of the G-protein-coupled receptor family. This stimulates a series of linked enzyme reactions, resulting in the activation of glycogen phosphorylase, the enzyme responsible for the mobilisation of glycogen reserves into free glucose. Glucagon release is inhibited by both insulin and somatostatin.
How Can I Look After My Pancreas
Diet and lifestyle are important for maintaining a healthy pancreas, for example:
- drinking little or no alcohol can reduce your risk of pancreatitis and diabetes
- if you smoke, quitting can reduce your risk of developing pancreatic cancer. Smokers are two to 3 times more likely to develop pancreatic cancer than non-smokers
If you are worried that you may have pancreas problems, check your symptoms with healthdirect’s Symptom Checker and see your doctor.
You May Like: How To Control Pp Sugar
What Organ Controls Blood Sugar Level
Low Blood Sugar Levels what organ controls blood sugar level Blood Sugar Levels Chart By Age, Which Of The Following Is Characteristic Of Type 1 Diabetes?.
Due to past struggles with insomnia, she is particularly passionate about the role quality sleep plays in our physical and mental health, and loves helping readers to sleep better.The G6PD variants called Gastonia, Marion, and Minnesota were all from patients with nonspherocytic hemolytic .
Diabetes Medications That Work With The Pancreas

Most people who have type 2 diabetes need to take prescription medications, some of which act specifically on the pancreas to lower A1C.
Sulfonylureas and Meglitinides
How they work: Lower blood sugar by encouraging the pancreas to produce more insulin
DPP-4 Inhibitors
How they work: Block the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase 4, which increases the amount of GLP1 in the body
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
How they work: Mimic the effects of the hormone GLP-1, which triggers your pancreas to produce more insulin after you eat and decreases glucagon. These drugs also help you feel full after a meal and slow the rate at which the stomach empties, which may help you lose weight
Recommended Reading: Banana Bad For Diabetes
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed
Doctors can say for sure if a person has diabetes by testing blood samples for glucose. Even if someone doesn’t have any symptoms of type 2 diabetes, doctors may order blood tests to check for it if the person has certain risk factors .
Some kids and teens with diabetes may go to a pediatric endocrinologist â a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating children and teens living with diseases of the endocrine system, such as diabetes and growth problems.
p
How Your Body Makes Glucose
It mainly comes from foods rich in carbohydrates, like bread, potatoes, and fruit. As you eat, food travels down your esophagus to your stomach. There, acids and enzymes break it down into tiny pieces. During that process, glucose is released.
It goes into your intestines where it’s absorbed. From there, it passes into your bloodstream. Once in the blood, insulin helps glucose get to your cells.
Recommended Reading: Can We Control Sugar Without Medicine
Which Organ Controls The Level Of Sugar In Our Blood
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Insulin Levels Throughout The Day
To keep the blood glucose in a narrow range throughout the day, there is a low steady secretion of insulin overnight, fasting and between meals with spikes of insulin at mealtimes. Adapted: Jacobs DM Care 20:1279, 1997
There are other hormones that work together with insulin to regulate blood sugar including incretins and gluco-counterregulatory hormones, but insulin is the most important.
Recommended Reading: How To Control High Sugar Level Immediately
The Role Of The Pancreas In The Body
The pancreas plays a part in two different organ systems, the endocrine system and the exocrine system.
The endocrine system includes all the organs which produce hormones, chemicals which are delivered via the blood to help regulate our mood, growth, metabolism and reproduction.
Two of the hormones produced by the pancreas are insulin and glucagon
The exocrine system is made up of a number of glands which release substances such as sweat , saliva or, in the case of the pancreas, digestive enzymes
How Do Health Problems From Diabetes Begin
If your diabetes is not well controlled, the sugar level in your blood goes up. This is called hyperglycemia . High blood sugar can cause damage to very small blood vessels in your body. Imagine what happens to sugar when it is left unwrapped overnight. It gets sticky. Now imagine how sugar sticks to your small blood vessels and makes it hard for blood to get to your organs. Damage to blood vessels occurs most often in the eyes, heart, nerves, feet, and kidneys. Lets look at how this damage happens.
Also Check: What Is Signs Of High Blood Sugar
Understanding The Processes Behind The Regulation Of Blood Glucose
20 April, 2004
VOL: 100, ISSUE: 16, PAGE NO: 56
Pat James, PhD, is senior lecturer in applied physiology
Roger McFadden, MSc, is senior lecturer in applied physiology both at the School of Health and Policy Studies, The University of Central England in Birmingham
Pat James, PhD, is senior lecturer in applied physiology
Glucose is one of the bodys principal fuels. It is an energy-rich monosaccharide sugar that is broken down in our cells to produce adenosine triphosphate. ATP is a small packet of chemical energy that powers the millions of biochemical reactions that take place in the body every second.
We obtain glucose from the food that we eat, predominantly starch-rich foods such as potatoes, rice, bread, and pasta. Starch is a polysaccharide that is broken down by digestive enzymes into individual glucose molecules.
In the small intestine, glucose is absorbed into the blood and travels to the liver via the hepatic portal vein. The hepatocytes absorb much of the glucose and convert it into glycogen, an insoluble polymer of glucose.
This is stored in the liver and can be reconverted into glucose when blood-glucose levels fall. Other types of simple sugars in our diet such as fructose, sucrose and lactose are also fuels that contribute to the production of ATP.
If glucose levels fall to too low a concentration or rise too high then this situation can lead to the neurological processes in the brain being compromised.
Keeping Blood Sugar In Control

Stephenson-Laws said healthy individuals can keep their blood sugar at the appropriate levels using the following methods:
Maintaining a healthy weight
Talk with a competent health care professional about what an ideal weight for you should be before starting any kind of weight loss program.
Improving diet
Look for and select whole, unprocessed foods, like fruits and vegetables, instead of highly processed or prepared foods. Foods that have a lot of simple carbohydrates, like cookies and crackers, that your body can digest quickly tend to spike insulin levels and put additional stress on the pancreas. Also, avoid saturated fats and instead opt for unsaturated fats and high-fiber foods. Consider adding nuts, vegetables, herbs and spices to your diet.
Getting physical
A brisk walk for 30 minutes a day can greatly reduce blood sugar levels and increase insulin sensitivity.
Getting mineral levels checked
Research also shows that magnesium plays a vital role in helping insulin do its job. So, in addition to the other health benefits it provides, an adequate magnesium level can also reduce the chances of becoming insulin-tolerant.
Get insulin levels checked
Many doctors simply test for blood sugar and perform an A1C test, which primarily detects prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. Make sure you also get insulin checks.
Additional resources
Don’t Miss: How To Reduce High Sugar Level Immediately
Hormones Of The Pancreas
Regulation of blood glucose is largely done through the endocrine hormones of the pancreas, a beautiful balance of hormones achieved through a negative feedback loop. The main hormones of the pancreas that affect blood glucose include insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and amylin.
Insulin lowers BG levels, whereas glucagon elevates BG levels.
Somatostatin is formed in the delta cells of the pancreas and acts as the pancreatic policeman, balancing insulin and glucagon. It helps the pancreas alternate in turning on or turning off each opposing hormone.
Amylin is a hormone, made in a 1:100 ratio with insulin, that helps increase satiety, or satisfaction and state of fullness from a meal, to prevent overeating. It also helps slow the stomach contents from emptying too quickly, to avoid a quick spike in BG levels.
In a healthy liver, up to 10% of its total volume is used for glycogen stores. Skeletal muscle cells store about 1% of glycogen. The liver converts glycogen back to glucose when it is needed for energy and regulates the amount of glucose circulating between meals. Your liver is amazing in that it knows how much to store and keep, or break down and release, to maintain ideal plasma glucose levels. Imitation of this process is the goal of insulin therapy when glucose levels are managed externally. Basalbolus dosing is used as clinicians attempt to replicate this normal cycle.
Test Your Knowledge
Apply Your Knowledge
Online Resource
Insulin Resistance: Understanding What Happens In Type 2 Diabetes
In type 2 diabetes, the body has become insulin resistant, meaning insulin is no longer able to effectively remove sugar from the blood. As a result, the pancreas ramps up its insulin production to try to keep up with the amount of carbohydrates youre eating a state of overproduction that can lead to B-cell fatigue.
When B-cells become fatigued , they can no longer make enough insulin to shuttle glucose out of your bloodstream. The end result: hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar.
Don’t Miss: How To Reduce Diabetes Instantly