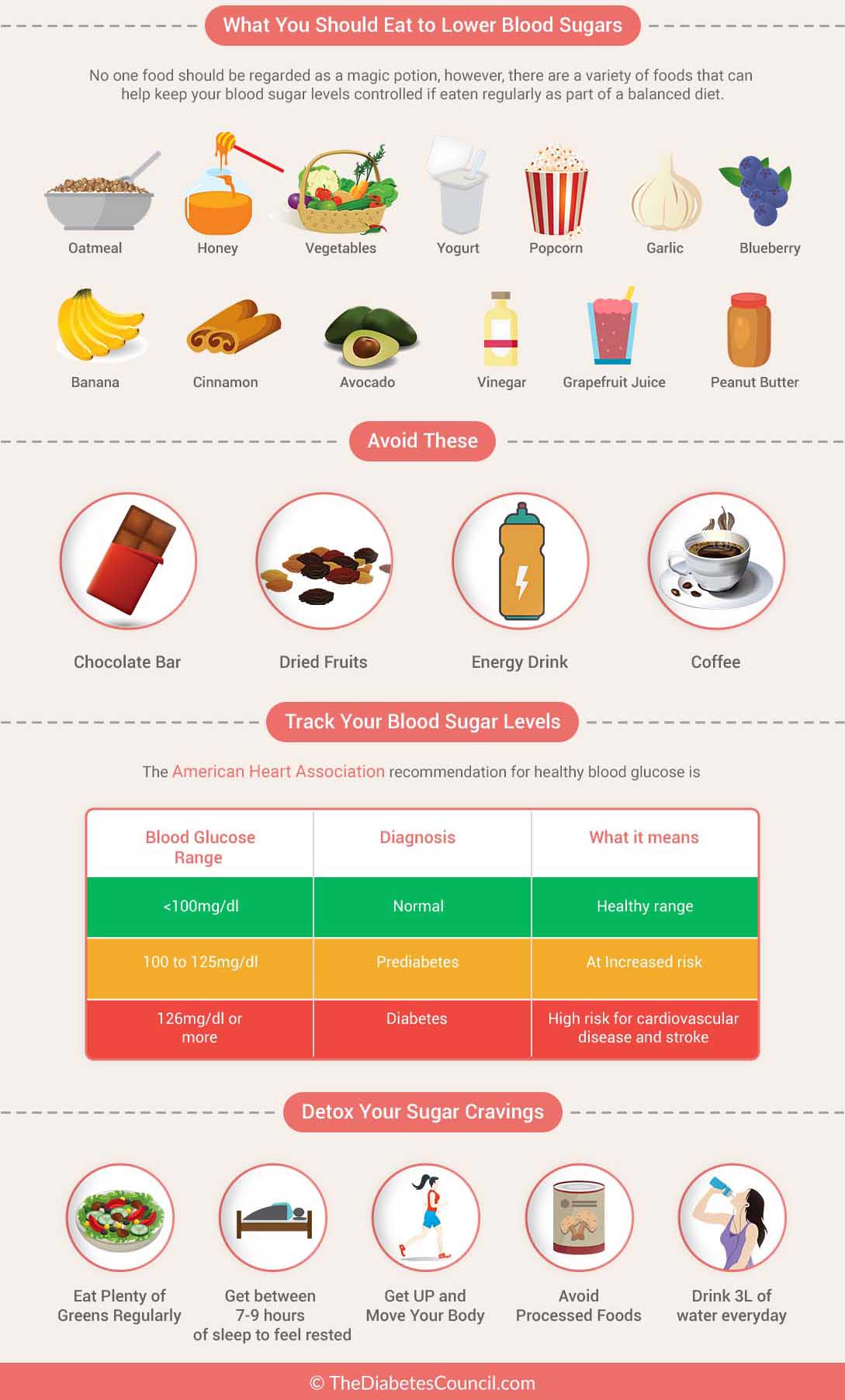
Check Your Blood Sugar Levels Before Sleeping
Checking your blood sugar levels before sleeping is a good idea to make sure you’re not going low. If you are using a glucose meter try to avoid going to bed with hypoglycemia. If you have a continuous glucose monitor make sure you review the
It might take some practice but eventually, this routine could become natural and we’ll be able to have an accurate representation of what our body needs without having to even think about it.
If any numbers seem high at all – don’t hesitate check with your doctor as soon as possible so they can help you figure out how best to get them under control. We want those numbers right where they should be!
What To Expect From Your Blood Sugar In The Morning
After an overnight fast, a normal blood sugar level is less than 100 milligrams per deciliter , according to the American Diabetes Association . But, according to Susan Spratt, MD, an endocrinologist and associate professor of medicine at Duke University School of Medicine, not everyone with type 1 or type 2 diabetes has to shoot for “normal” levels.
“If you’re young, the goal may be to get your fasting blood sugar levels to less than 120 mg/dL,” Dr. Spratt says. But if you’re older and have other health conditions, that number may be higher, she says.
The ADA points out that not everyone will have the same blood sugar level goals. Instead, your endocrinologist or doctor will calculate your target number based on your age, how long you’ve had diabetes, whether you have health conditions like heart disease and other factors.
Keep in mind, too, that your fasting blood sugar levels can be too low. For example, a morning blood sugar reading below 70 mg/dL can indicate a hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar.
Read more:Which Helps You More in the Morning: Tea, Water or Coffee?
Recommended Blood Glucose Targets For People With Diabetes
| AIC* | Fasting blood glucose/ blood glucose before meals | Blood glucose two hours after start of meal |
| Target for most patients with diabetes | 7.0% | |
| If A1C targets not being met** | 4.0 to 5.5 | 5.0 to 8.0 |
*An A1C is an average of your blood glucose levels over the past three months. Learn more about the A1C here.
**Must be balanced against the risk of hypoglycemia
Don’t Miss: What Causes High Glucose
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating
Your blood sugar level is influenced by several factors, including the food you eat. During digestion, carbohydrates are converted into sugar which your body uses as an energy source. Excess sugar from any source is stored in your cells for later use. When your cells contain too much sugar, though, it can lead to type 2 diabetes. This is why eating a balanced diet to maintain a normal blood sugar range is important.
Blood sugar levels can vary based on many factors, including age and life expectancy, comorbidities like heart disease, stress, and lifestyle factors like physical activity, smoking, or drinking alcohol.
What Is The Treatment For High Ketones

Normally if your ketone levels are a bit high, you dont need any treatment. High ketone caused by starvation or a low-carb diet normally corrects itself.
However, if your ketone levels are dangerously high, you need immediate medical attention. Extremely high ketone levels turn the blood acidic. This leads to ketoacidosis and may even result in death.
The treatments to reverse ketoacidosis are:
You May Like: Low Blood Sugar At Night
Recommended Reading: Which Cells Produce Hormones To Regulate Blood Sugar
Exercise Benefits Blood Glucose
Along with fasting, exercise either resistance or endurance training is a proven strategy for improving blood glucose regulation. For instance, endurance training in a fasted state has been shown to have profound effects on glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. All the more reason to work out before breakfast.
But you neednt fast to benefit from exercise. In one study, researchers found that a single session of low-intensity resistance training significantly improved blood sugar regulation in type 2 diabetics. So when it comes to blood glucose, perhaps you dont need to go hard to get results.
Though sometimes it does pay to go hard. In fact, high-intensity interval training can dramatically improve insulins ability to handle blood sugar. Just three sessions a week appears to do the trick.
Why does exercise have these positive effects on blood sugar? Think cellular. Exercise activates GLUT 4 transporters in your muscle cells which then shove blood glucose out of your blood and into your muscles.
Now to the question on your mind: how does diet affect blood glucose?
Know Your Blood Sugar
Blood sugar is the amount of sugar in your blood at a given time. It’s important to check your blood sugar level, because it will:
- determine if you have a high or low blood sugar level at a given time
- show you how your lifestyle and medication affect your blood sugar levels
- help you and your diabetes health-care team make lifestyle and medication changes to improve your blood sugar levels
Read Also: Dangers Of High Blood Sugar
Can Fasting Raise Your Blood Sugar
Yes, fasting can raise your blood sugar levels if you have insulin resistance.
In fact:
With this condition, when you wake up in the morning after going for all those hours without food, your blood sugar levels will typically be at their peak before they go back to normal over the course of the day, even when you are consuming foods rich in sugars.
Fasting brings about certain hormonal changes in the body that result in a rise in blood sugar levels. In people without insulin resistance issues, the increased blood sugar triggers the release of more insulin which gets the blood sugar levels back to normal.
However, insulin resistance is not the only culprit as far as increased fasting blood sugar levels go, the foods you had before the fast also play a role.
But generally, when you fast, your body releases hormones that encourage the body to create glucose from stored energy.
So, in cases of inadequate insulin or insulin resistance, glucose levels can get too high. However, for people with proper insulin response, the fasting levels of blood sugar never get too high as the body will respond appropriately by releasing more insulin to ensure there is no excess glucose in the body.
Blood Sugar Levels: What’s Normal What’s Not And How To Measure
What do blood glucose levels mean and what range is healthy? Here’s what you need to know.
Sugar can lead to high blood sugar and contributes to the development of diabetes.
We all want to keep track of our health in every way we can — you may weigh yourself, keep track of your blood pressure or monitor your resting heart rate. But how close of an eye do you keep on your blood sugar?
People with diabetes are all too familiar with their blood sugar levels, but the rest of us might not even think about it much. However, consistently high blood sugar levels can coexist with Type 2 diabetes and cause serious health conditions like kidney disease, nerve problems or stroke.
While that’s no reason to panic, when it comes to our health, it’s important to know exactly what’s going on inside of our bodies. Without further ado, let’s get into what blood sugar means, how to measure it and everything else you need to know.
Our Health & Wellness newsletter puts the best products, updates and advice in your inbox.
Recommended Reading: Hyperglycemic Diet
Is Diabetes More Common In Men Or Women
Studies show that type 1 diabetes is more common in men, and theyre more likely to pass it on to their offspring. However, although women previously showed more indication of type 2 diabetes, it is now equally prevalent between men and women.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition that usually starts in childhood. With type 1 diabetes, your body attacks its own pancreas so it cannot produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes is far more common in adults, and although often milder than type 1, can still cause major health implications, including kidney disease or damage, heart disease, or stroke. Unlike type 1, with type 2 diabetes some insulin can be produced, but the body is either resistant to it or there is not enough. This insulin resistance develops in fat, liver, and muscle cells, hence the extensively researched correlation between obesity and type 2 diabetes.
What Is The Normal Blood Sugar Level
Blood sugar level means the amount of glucose dissolved in the blood at any given time. It is an important indicator which shows the bodys overall metabolic condition. The normal range of blood sugar is from 3.5 mmol/L to 6.1 mmol/L during fasting and less than 7 mmol/L after having a meal.
If your blood sugar is higher than the normal range, it could be a sign of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes is the name of the condition where the body cannot properly process and absorb the glucose taken during eating, causing it to remain in the bloodstream. This can lead to many serious complications like nerve damage and loss of vision.
Read Also: Does Smirnoff Have Sugar
Why Is My Blood Sugar Level High
The clinical term for high blood sugar is hyperglycemia. The most common cause of high blood sugar is Diabetes Mellitus or DM. It is a condition where the body cannot absorb glucose due to any abnormality in the production or action of a hormone called Insulin. Diabetes is mainly of two types: Type 1 and Type 2. Majority of diabetics are suffering from type 2 diabetes, caused by reduced action of Insulin.
However, blood sugar can be high for various other reasons. Illness or injury, hormone disorders, overeating, obesity, some medications can increase blood sugar levels.
Cgm Studies In Nondiabetic Individuals
One study from 2009 entitled Reference Values for Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Chinese Subjects looked at the glucose levels of 434 healthy adults using CGM and found the following:
- On average, their daily glucose levels stayed between 70140 mg/dl for 93% of the day, with very small portions of the day spent above 140 mg/dl or below 70 mg/dl.
- Also, their mean 24-hour glucose levels were around 104 mg/dl
- 1-hour post-meal glucose values average 121-123 mg/dl for breakfast, lunch, and dinner
- 3-hour post-meal glucose values were around 97-114 mg/dl.
- Peak post-meal values appeared to be around 60 minutes after eating.
- Mean fasting glucose was 86 ± 7 mg/dl.
- Mean daytime glucose was 106 ± 11 mg/dl.
- Mean nighttime glucose was 99 ± 11 mg/dl.
A 2010 study, Variation of Interstitial Glucose Measurements Assessed by Continuous Glucose Monitors in Healthy, Nondiabetic Individuals, looked at a healthy population of 74 individuals that included children, adolescents, and adults during daily living using CGM. This research showed that:
- Glucose levels stayed between 71-120 mg/dl for 91% of the day.
- Levels were lower than 70 mg/dl for 1.7% of the time and greater than 140 mg/dl, only 0.4% of the time.
- Mean 24-hour glucose was 98 ± 10 mg/dl.
- Mean fasting glucose of 86 ± 8 mg/dl.
Compared to the first study mentioned, these healthy, nondiabetic individuals appeared to have a tighter range of glucose, spending the vast majority of the 24-hour period between 71-120 mg/dl.
Also Check: Dangers Of High Glucose Levels
Sleeping Habits And Diabetes
According to research, insomnia affects how well you respond to insulin. People who sleep more than 9 hours each night also tend to have higher rates of diabetes. Sleep apnea can also increase someone’s probability of diabetes. Researchers have discovered that sleep-induced diabetes could raise the risk of other types of diabetes. More than 400 respondents reported how much sleep they get the night before.
Therefore it’s quite important to have a good night’s rest so you have enough strength throughout the day. Below you can find a few tips to create the perfect routine.
Normal Blood Sugar 30 Minutes After Eating
Blood sugar is a very familiar term these days. With a huge amount of individuals suffering from diabetes, trying to maintain a healthy level of sugar in the blood has become one of the daily challenges many of us face. As a matter of fact, checking the normal blood sugar 30 minutes after eating is a key indicator for getting an idea of the state of diabetes and overall health.
In this article, well go over the normal blood sugar, how to check it, what is the normal blood sugar after meals and how to control it.
Table of Content
Read Also: 15-15-15 Rule Hypoglycemia
What Is Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. As a result, the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Type 1 diabetes is also characterized by the presence of certain autoantibodies against insulin or other components of the insulin-producing system such as glutamic acid decarboxylase , tyrosine phosphatase, and/or islet cells.
When the body does not have enough insulin to use the glucose that is in the bloodstream for fuel, it begins breaking down fat reserves for energy. However, the breakdown of fat creates acidic by-products called ketones, which accumulate in the blood. If enough ketones accumulate in the blood, they can cause a potentially life-threatening chemical imbalance known as ketoacidosis.
Type 1 diabetes often develops in children, although it can occur at any age. Symptoms include unusual thirst, a need to urinate frequently, unexplained weight loss, blurry vision, and a feeling of being tired constantly. Such symptoms tend to be acute.
Diabetes is diagnosed in one of three ways a fasting plasma glucose test, an oral glucose tolerance test, or a random plasma glucose test all of which involve drawing blood to measure the amount of glucose in it.
Type 1 diabetes requires insulin treatment for survival. Treatment may also include taking other drugs to prevent kidney damage or to treat diabetes-related conditions such as high blood pressure.**
Blood Sugar Level Immediately After Eating:
Blood sugar level changes rapidly according to the intake of the meal. The normal blood sugar level before eating or during fasting is between 3.5 to 6.1 mmol/L.
Normal blood sugar right after eating rises drastically as the digestive tract acts quickly to digest the food through mechanical actions, digestive enzymes and different hormones. So the blood glucose rises sharply during this time. The rate at which the blood sugar rises depends on the type of food, the amount is taken, the metabolic condition of the individual, etc.
You May Like: Smirnoff Vodka Sugar Content
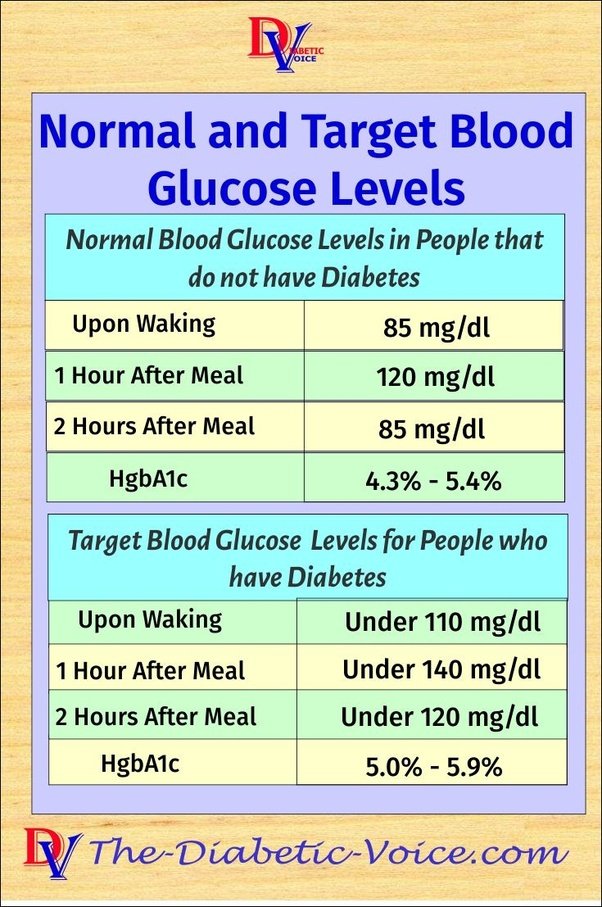
Normal Hba1c For Person Without Diabetes
For someone who does not have diabetes, a normal HbA1C level is below 5.7%. An A1C between 5.7% to 6.4% is indicative of prediabetes.
Its recommended that adults over the age of 45 or adults under 45 who are overweight and have one or more risk factors for diabetes have a baseline A1C checked. If the result is normal, the A1C should be checked every 3 years. If the result indicates prediabetes, the A1C should be checked every 1 to 2 years.
What Is A Normal Blood Sugar Level
The answer to the question what is a normal blood sugar level is as follows:
Fasting normal blood sugarNormal for person without diabetes: 7099 mg/dl Official ADA recommendation for someone with diabetes: 80130 mg/dl
Normal blood sugar 2 hours after mealsNormal for person without diabetes: Less than 140 mg/dl Official ADA recommendation for someone with diabetes: Less than 180 mg/dl
Normal for person without diabetes: Less than 5.7%Official ADA recommendation for someone with diabetes: Less than 7.0%
Source: American Diabetes Association
Recommended Reading: Which Fruit Contains The Most Sugar
Are Low Blood Sugar Levels Dangerous
Yes, low blood sugar symptoms can cause problems such as hunger, nervousness, perspiration, dizziness and even confusion if untreated, low blood sugar may result in unconsciousness, seizures, coma, or death. Low blood sugar levels begin at 70 mg/dL or less. People with diabetes who take too much medication or take their usual amount but then eat less or exercise more than usual can develop hypoglycemia. Although much rarer, hypoglycemia may develop in some people without diabetes when they take someone elses medication, have excessive alcohol consumption, develop severe hepatitis, or develop a rare tumor of the pancreas . The treatment for hypoglycemia is oral glucose intake (15. 0 grams of sugar, for example, 1 tablespoon of sugar, honey, corn syrup, or IV fluids containing glucose. Recheck your blood sugar levels in about 15 minutes after treatment is advised.
How To Avoid Diabetic Ketoacidosis
It might have been a really long time since youve been in diabetic ketoacidosis , or maybe youve never had it.
But if you have Type 1 diabetes, you are at risk. Sometimes when you havent recently experienced a situation, you kind of forget about what you were told to do for prevention or treatment. Thats why a refresher might be a great idea!
Don’t Miss: How Long To Wait After Eating To Check Blood Sugar
Do I Have To Monitor My Blood Glucose Levels If I Am On Metformin
Do I have to monitor my blood glucose levels if I am on metformin? Not everyone agrees with me on this, but I very strongly feel that everyone with diabetes should be checking their blood sugar. Diabetes is a progressive disease, it will get worse on its own, even when you do everything right. I dont believe in giving diabetes any foothold, handhold, or toehold in your body and as such, the meter is the first line of defense to see change for the worst when it starts to happen. The meter is the sentinel in the watch tower. Now many people feel that diabetics who take oral meds with little to no risk of low blood sugar, like your metformin, dont need to be testing blood sugar because there is nothing the patient can do if they find they are high. Again, I disagree, and this time because the fact that there is nothing you can do is false. First and foremost you can look at what you did to get yourself high in the first place and avoid doing it again. Testing before and several hours after various meals will help you learn what foods your body can tolerate and which ones it cant. If you numbers are always depressingly high, no matter what you eat, then your therapy needs adjusting.Continue reading > >