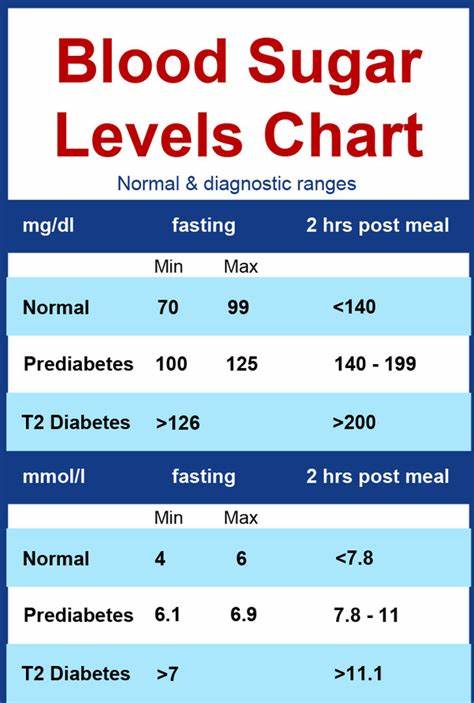
Normal Postmeal Blood Sugar Levels
Checking your blood glucose one to two hours after eating can help you understand how your blood sugar reacts to the food you consume. It can also offer insight into whether you’re taking the right dose of insulin or if you need to follow up with your doctor to discuss medication and diet or lifestyle adjustments.
There are two ways you can measure your blood glucose levels: by pricking your fingertip using a glucometer or by using continuous glucose monitoring. How often you should check your glucose levels varies from a few times per week to four to six times each day. As a general rule, the American Diabetes Association recommends keeping blood sugar below 180 mg/dL one to two hours after eating.
However, your target blood sugar range will depend on the following:
- Duration of diabetes
Animation: Blood Sugar Regulation In Diabetics
View the animation below, then complete the quiz to test your knowledge of the concept. 1 After eating a meal, blood sugar levels 2 Insulin, released after a meal is eaten by a person who does not have diabetes, will cause blood sugar levels to A) increase far above normal. B) return to about normal. C) decrease far below normal. 3 In Type I diabetes blood sugar levels remain high after a meal because A) too much insulin is released. B) protein is converted to glucose. D) muscle and liver cells do not receive a signal. 5 The treatment for Type I diabetes always includes A) oral thiazolidinedione.Continue reading > >
Translating Your A1c To A Blood Sugar Level
Using this easy calculator from the ADA, you can translate your most recent A1C result to an eAG or estimate average glucose level.
You can also use this translation when working to improve your A1c and achieving closer to normal blood sugar levels. If you know an A1c of 6.5 is an average blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or a range of 100 to 152 mg/dL, then you can look at your current blood sugar results on your CGM and meter and pinpoint which time of day youre frequently higher than this range.12% = 298 mg/dL or range of 240 347 11% = 269 mg/dL or range of 217 31410% = 240 mg/dL or range of 193 2829% = 212 mg/dL or range of 170 2498% = 183 mg/dL or range of 147 2177% = 154 mg/dL or range of 123 1856% = 126 mg/dL or range of 100 1525% = 97 mg/dL or range of 76 120
Normal blood sugar levels in a person without diabetes can result in an A1c as low as 4.6 or 4.7 percent and as high as 5.6 percent.
Just a decade or two ago, it was rare for a person with type 1 diabetes to achieve an A1c result below 6 percent. Thanks to new and improved insulin and better technology like continuous glucose monitors and smarter insulin pumps, more people with diabetes are able to safely achieve A1c levels in the higher 5 percent range.
You May Like: Will Coffee Affect Blood Sugar
Whats A Blood Sugar Spike And Why Do They Happen
Postprandial spikes are temporary high blood sugars that occur soon after eating. It is normal for the blood sugar to rise a small amount after eating, even in people who do not have diabetes. However, if the spike is too high, it can affect your quality of life today and contribute to serious health problems down the road.
The reason blood sugar spikes is a simple matter of timing. In a non-diabetic, consumption of carbohydrate results in two important reactions: the immediate release of insulin into the bloodstream, and production of a hormone called amylin which keeps food from reaching the intestines too quickly. In most cases, the after-meal blood sugar rise is barely noticeable.
However, in people with diabetes, the situation is like a baseball player with very slow reflexes batting against a pitcher who throws 98 mph fastballs: the timing is not good. Rapid-acting insulin that is injected at mealtimes takes approximately 15 minutes to start working, 60-90 minutes to peak, and four hours or more to finish working. And dont forget about the amylin hormone effect. In people with diabetes, amylin is either produced in insufficient amounts or not at all. As a result, food digests even faster than usual. The combination of slower insulin and faster food can cause blood sugar to rise absurdly high soon after eating. This is followed by a sharp drop once the mealtime insulin finally kicks in.
Whats My Target Range

You might be asking, what’s the normal range for blood sugar levels? The answer is, there is a healthy range that you should ideally be aiming for. The infographics above show the general guidelines, but your individual target range for your blood sugar levels may be different. Youll healthcare team will agree with you what it is.
Youll get different readings at different times of the day, depending on things like what youve eaten and how much you are moving around. Heres a guide to help you get started on finding your target range:
If youre a child with Type 1 diabetes
- when you wake up and before meals: 4 to 7mmol/l
- after meals: 5 to 9mmol/l
If youre an adult with Type 1 diabetes
- when you wake up and before meals: 5 to 7mmol/l
- before meals at other times of the day: 4 to 7mmol/l
If you have Type 2 diabetes
- before meals: 4 to 7mmol/l
- two hours after meals: less than 8.5mmol/l
You May Like: How To Control High Sugar
How To Avoid Diabetic Ketoacidosis
It might have been a really long time since youve been in diabetic ketoacidosis , or maybe youve never had it.
But if you have Type 1 diabetes, you are at risk. Sometimes when you havent recently experienced a situation, you kind of forget about what you were told to do for prevention or treatment. Thats why a refresher might be a great idea!
How Long Will The Effects Last
The effects of low blood sugar will continue and may even get worse until treatment brings your blood sugar level back to normal. It may take several minutes for the symptoms to go away after you start treatment. This may be a temporary problem while you and your healthcare provider are adjusting your medicine. If you are always prone to having low blood sugar, you may need to take special care for the rest of your life to keep your blood sugar at the proper level.
Don’t Miss: How And When To Check Blood Sugar
What Are Blood Sugar Levels
Your blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose levels, are a measurement that show how much glucose you have in your blood. Glucose is a sugar that you get from food and drink. Your blood sugar levels go up and down throughout the day and for people living with diabetes these changes are larger and happen more often than in people who don’t have diabetes.
You can check your sugar levels yourself by doing a finger-prick test, by using a flash glucose monitor or with a continuous glucose monitor . You can do this a number of times a day helping you keep an eye on your levels as you go about your life and help you work out what to eat and how much medication to take. Find out your ideal target range.
But not everyone with diabetes needs to check their levels like this. Youll need to if you take certain diabetes medication. Always talk to your healthcare team if youre not sure whether thats you theyll give you advice on whether to check them yourself and how often.
And theres also something called an HbA1c, which measures your average blood sugar level from the previous few months. Everyone with diabetes is entitled to this check.
High blood sugar levels increase your risk of developing serious complications. However you manage your diabetes, stay in the know about your blood sugar levels.
Hba1c Test For Diabetes Diagnosis
An HbA1c test does not directly measure the level of blood glucose, however, the result of the test is influenced by how high or low your blood glucose levels have tended to be over a period of 2 to 3 months.
Indications of diabetes or prediabetes are given under the following conditions:
- Normal: Below 42 mmol/mol
- Prediabetes: 42 to 47 mmol/mol
- Diabetes: 48 mmol/mol
There are two types of blood sugar levels that may be measured. The first is the blood glucose level we get from doing finger prick blood glucose tests. These give us a reading of how high our levels are at that very point in time.
The second is the HbA1c reading, which gives a good idea of our average control over a period of 2 to 3 months. The target blood glucose levels vary a little bit depending on your type of diabetes and between adults and children.
Where possible, try to achieve levels of between 4 and 7 mmol/L before meals and under 8.5 mmol/L after meals. The target level for HbA1c is under 48 mmol/mol .
Research has shown that high blood glucose levels over time can lead to organ and circulation damage.
Keeping blood glucose above 4 mmol/l for people on insulin or certain medications for type 2 diabetes is important to prevent hypos occurring, which can be dangerous.
Your doctor may give you different targets. Children, older people and those at particular risk of hypoglycemia may be given wider targets.
FREE blood glucose level chart
You May Like: How Much Sugar Should You Have On Keto
Reason #: Im A Pig And I Cant Go 2 Hours Without Eating
Ehh that might be a slight exaggeration but really, the main reason I wait 1 hour is because a lot of my tests are of small things that arent really a meal.
I may be testing something as small as a piece of Halloween candy. Or maybe a shitty granola bar. Or a single tamale.
And the best way to get what I would consider to be accurate glucose results from these tests is to do them when Im fasting. As in empty stomach. As in Im probably already hungry before doing the test.
And whenever I do a glucose test for this blog, I dont eat anything until after checking the glucose results, even if Im testing something really small.
So waiting only 1 hour before I can eat again is a practical matter of me not wanting to starve to death. Waiting an extra hour beyond that would be torture.
Blood Sugar Levels After Eating
Blood sugar fluctuates throughout the day, but the biggest changes happen around mealtimes. Before eating, a healthy sugar level is between 3.9-5.5mmol/L. Around 1-2 hours after eating, expect blood sugar to rise to 5-10mmol/L.
If your blood sugar doesn’t stick within these ranges, the body may have stopped regulating blood sugar effectively which can lead to prediabetes and diabetes.
You May Like: How To Stop Taking Sugar
Target Blood Sugar Levels For People With Diabetes
People with diabetes have difficulty creating or using enough insulin, which is the hormone that helps convert glucose into energy. Although there is no universal blood sugar chart for everyone with diabetes, clinical organizations like the ADA and American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists offer guidelines on target blood sugar levels as a starting point.
Healthcare providers typically tailor normal blood sugar target ranges to an individual diabetes care plan. This includes considering your:
- Age
The Best Healthcare Options To Prevent Diabetes
Health care is expensive. Canada spent an estimated $253.5 billion in 2018, and as the cost of health care increases, so does the cost to you. Pre-existing medical conditions, family history, and BMI are all factors that increase the cost of health care. These factors also increase your risk of diabetes, so you must be covered.
Of course, as a Canadian, you are entitled to some free and subsidized health care, which is great. But many people opt for private healthcare and for diabetes prevention this can be very useful. If youâre shopping around for private healthcare, itâs important to choose the right package.
Basic health insurance will usually cover health care, medical services, and prescriptions, but they tend to lack customizations. If you opt for a premium/guaranteed health insurance you have the bonus of a custom plan based on your needs if you are worried about your risk of diabetes this is like gold dust.
Private healthcare plans can cover the cost of many expenses related to diabetes such as blood tests, blood sugar monitors, specialist referrals, hospital stays, and much more! The most important thing to note about private health care is that it covers costs for preventative care, not just treatment for diseases.
There are many different options available, so make sure you search for the best quotes.
You May Like: How To Counter Low Blood Sugar
What Causes Low Blood Sugar
Low blood sugar has many causes, including missing a meal, taking too much insulin, taking other diabetes medicines, exercising more than normal, and drinking alcohol. Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL is considered low.
Signs of low blood sugar are different for everyone. Common symptoms include:
- Shaking.
- Dizziness.
- Hunger.
Know what your individual symptoms are so you can catch low blood sugar early and treat it. If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms. Low blood sugar can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible.
What Are Abnormal Glucose Levels And Why Do They Matter
Why is it unhealthy for glucose levels to be too high or too low ?
Hyperglycemia refers to elevated blood glucose levels. This usually occurs because the body does not appropriately remove glucose from the blood this can happen due to many complex reasons. Elevated glucose levels can damage blood vessels and nerves over time this can then lead to problems in the eyes, kidneys, and heart, as well as numbness in the hands and feet. Very high levels can lead to coma and even death in some cases. People with fasting glucose levels higher than 100 mg/dl have impaired glucose tolerance and should speak with their healthcare provider.
Some people may think that to avoid all these issues, they should just keep their blood glucose levels as low as possible. If too high is bad, then low must be good, right? Not exactly. When glucose gets too low, its called hypoglycemia. The threshold for hypoglycemia is typically thought to be when glucose falls below 70 mg/dl. When this happens, the body may release epinephrine , the fight or flight hormone, which can lead to a fast heart rate, sweating, anxiety, blurry vision, and confusion, but also helps the body mobilize glucose into the blood. If blood glucose levels stay too low for too long, it can cause seizures, coma, and in very rare instances, death.
Don’t Miss: How Much Sugar In Natural Light Beer
How Do I Check My Blood Glucose Levels
To check your blood glucose levels, you prick your finger with the lancet and add a small drop of blood onto a blood glucose checking strip. This strip is then inserted into the meter, which reads the strip and displays a number your blood glucose level.
When and how often you should check your blood glucose levels varies depending on each individual, the type of diabetes and the tablets and/or insulin being used. Blood glucose levels are measured in millimoles per litre of blood . Your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator will help you decide how many checks are needed and the levels to aim for.
Keeping a record of your blood glucose levels can be very helpful for you and your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator. You can keep a diary or use a mobile phone app or website to record your levels.
Are Low Blood Sugar Levels Dangerous
Yes, low blood sugar symptoms can cause problems such as hunger, nervousness, perspiration, dizziness and even confusion if untreated, low blood sugar may result in unconsciousness, seizures, coma, or death. Low blood sugar levels begin at 70 mg/dL or less. People with diabetes who take too much medication or take their usual amount but then eat less or exercise more than usual can develop hypoglycemia. Although much rarer, hypoglycemia may develop in some people without diabetes when they take someone elses medication, have excessive alcohol consumption, develop severe hepatitis, or develop a rare tumor of the pancreas . The treatment for hypoglycemia is oral glucose intake (15. 0 grams of sugar, for example, 1 tablespoon of sugar, honey, corn syrup, or IV fluids containing glucose. Recheck your blood sugar levels in about 15 minutes after treatment is advised.
Read Also: How Do Carbs Convert To Sugar
How Often Is A1c Tested
To keep A1C levels in check, patients should have the test repeated regularly. If the A1C is less than 5.7, indicating you dont have diabetes, you should have it checked every three years, according to Robert Williams, MD, a family doctor and geriatrician in Lakewood, Colorado, and a medical advisor for eMediHealth. If it is between 5.7 and 6.4, indicating you are at risk of developing diabetes, you should have it rechecked every one to two years. If you have a confirmed diabetes diagnosis, and your blood sugar is well-controlled, you should have an A1C test every six months. If you already have diabetes and your medications change, or your blood sugar is not well-controlled, you should have an A1C test every three months.
Read Also: Normal A1c Level