What Are Abnormal Glucose Levels And Why Do They Matter
Why is it unhealthy for glucose levels to be too high or too low ?
Hyperglycemia refers to elevated blood glucose levels. This usually occurs because the body does not appropriately remove glucose from the blood this can happen due to many complex reasons. Elevated glucose levels can damage blood vessels and nerves over time this can then lead to problems in the eyes, kidneys, and heart, as well as numbness in the hands and feet. Very high levels can lead to coma and even death in some cases. People with fasting glucose levels higher than 100 mg/dl have impaired glucose tolerance and should speak with their healthcare provider.
Some people may think that to avoid all these issues, they should just keep their blood glucose levels as low as possible. If too high is bad, then low must be good, right? Not exactly. When glucose gets too low, its called hypoglycemia. The threshold for hypoglycemia is typically thought to be when glucose falls below 70 mg/dl. When this happens, the body may release epinephrine , the fight or flight hormone, which can lead to a fast heart rate, sweating, anxiety, blurry vision, and confusion, but also helps the body mobilize glucose into the blood. If blood glucose levels stay too low for too long, it can cause seizures, coma, and in very rare instances, death.
When Should I Check My Blood Sugar
How often you check your blood sugar depends on the type of diabetes you have and if you take any diabetes medicines.
Typical times to check your blood sugar include:
- When you first wake up, before you eat or drink anything.
- Two hours after a meal.
If you have type 1 diabetes, have type 2 diabetes and take insulin, or often have low blood sugar, your doctor may want you to check your blood sugar more often, such as before and after youre physically active.
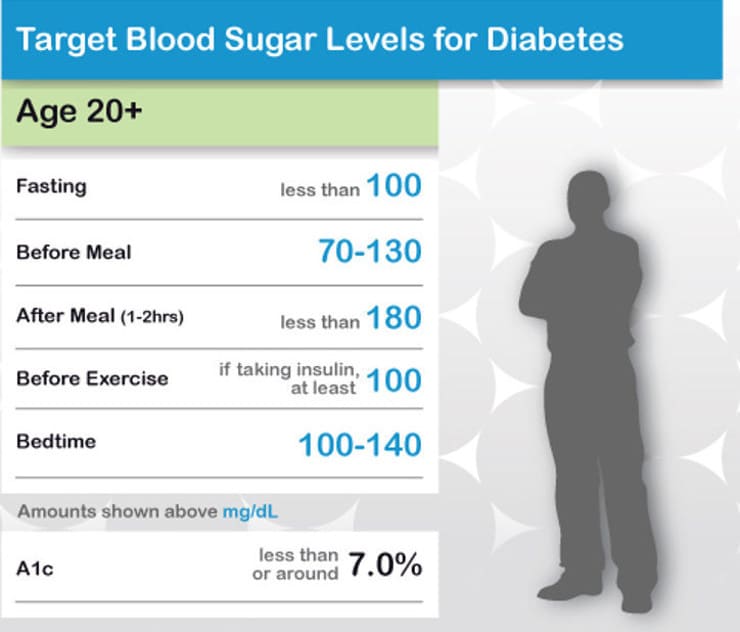
Recommended Target Blood Glucose Level Ranges
The NICE recommended target blood glucose levels are stated below for adults with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and children with type 1 diabetes.
In addition, the International Diabetes Federations target ranges for people without diabetes is stated.
The table provides general guidance. An individual target set by your healthcare team is the one you should aim for.
| Target Levels by Type |
|---|
*The non-diabetic figures are provided for information but are not part of NICE guidelines.
Don’t Miss: What Is Acceptable Blood Sugar
Fasting Glucose Goal: 72
Why? Previously we discussed that the ADA considers normal fasting glucose as anything < 100 mg/dl. However, multiple research studies show that as fasting glucose increases, there is an increased risk of health problems like diabetes and heart disease even if it stays within the normal range. The highlights of some of the study results include:
- Men whose fasting blood glucose was greater than 85 mg/dl had a significantly higher mortality rate from cardiovascular diseases than men with blood sugars less than 85 mg/dl.
- People with fasting glucose levels in the high normal range had significantly increased cardiovascular disease risk than people whose levels remained below 80 mg/dl.
- Children with fasting glucose levels 86-99 mg/dl had more than double the risk of developing prediabetes and type 2 diabetes as adults when compared with children whose levels were less than 86 mg/dl.
- People with fasting glucose levels between 91-99 mg/dl had a 3-fold increase in type 2 diabetes risk compared to those with levels less than 83 mg/dl.
- Among young, healthy men, higher fasting plasma glucose levels within the normal range constitute an independent risk factor for type 2 diabetes. This means that as fasting glucose increases, even if the level is still considered normal, it could indicate a significantly higher risk of developing diabetes, and this is particularly pronounced if BMI is greater than 30. .
What Are Dangerous Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar can be dangerously highor dangerously low. Your healthcare provider will give you individual target ranges and tell you when to take action on dangerously high or low blood sugar levels. These numbers, especially high numbers, differ by individual. Hypoglycemia is generally defined as a blood sugar less than 70 mg/dl, but it can vary depending on the individual. Severe hypoglycemia may occur if your blood sugar drops to a level where you need help recoveringyour healthcare provider may prescribe glucagon that a family member or caregiver can use in a low blood sugar emergency.
Also Check: What Does Insulin Do To Blood Sugar
What Is The Best Time To Test For Blood Sugar
Doctors usually do a fasting blood sugar test in the morning, after fasting for 8 hours . People can do a random test or an OGTT at any time, without fasting, but the OGTT takes 2 to 3 hours to complete.
A post-prandial test is specifically for use after eating or drinking. An A1C test shows how glucose levels have fluctuated over the last 3 months.
Types Of Glucose Tests
There are several types of glucose tests your doctor may order. They each have different fasting requirements and procedures. Here is a list of most of the tests that you will encounter.
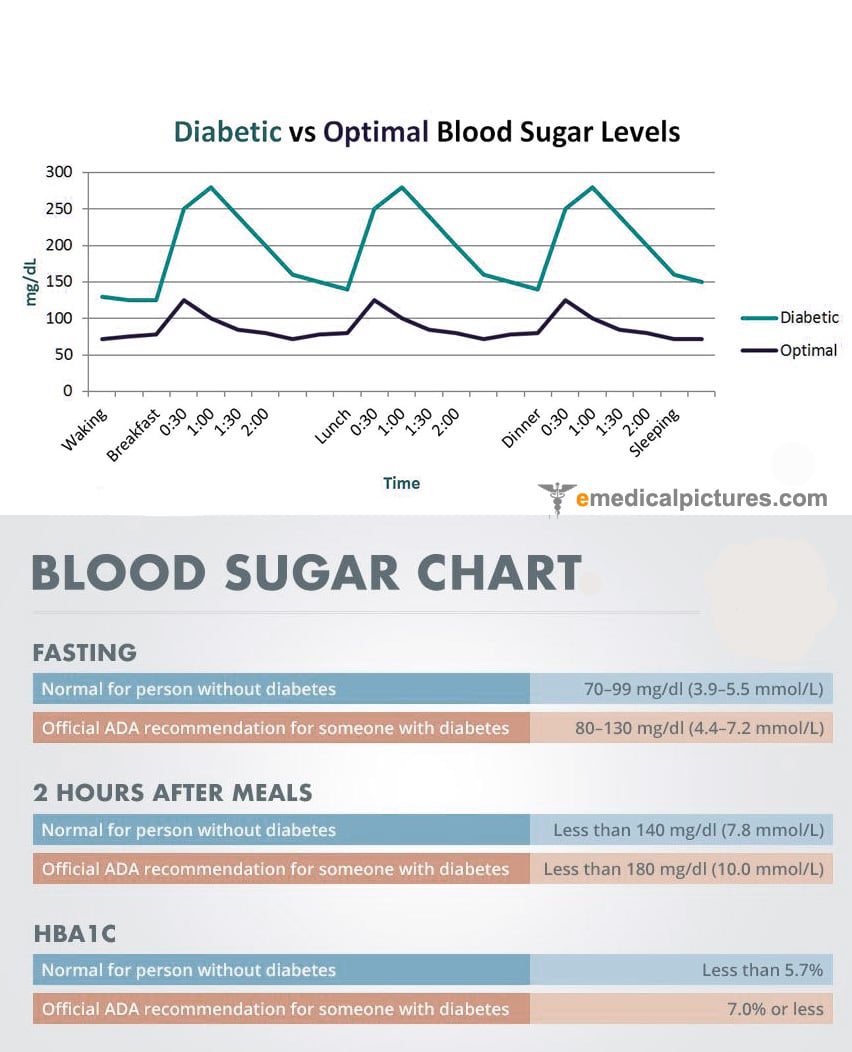
Fasting Blood Glucose Tests The most common test for diabetes is a blood test measured after the patient has fasted for at least 8 hours. A reading of 126 mg/dL is an indication of the possibility of diabetes while 100 mg/dL is considered normal. Anything in-between is considered pre-diabetic, which is a risk factor for diabetes but can be reversed.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Tests These tests also require an 8-hour fast. The test involves taking a blood sample, then drinking a liquid filled with sugar and waiting at the office. After two hours , the health care practitioner will take another sample. A reading of 200 mg/dL or higher is considered a diabetes diagnosis.
Oral Glucose Challenge Tests This test does not require fasting and checks pregnant women between 24 28 weeks into their pregnancy for gestational diabetes. Like the oral glucose tolerance test, it involves drinking a sugary liquid and having a blood sample taken before and after, whereby 130 mg/dL or higher is considered a potentially positive diagnosis.
Random Blood Glucose Tests If you present with severe symptoms associated with diabetes, a doctor may order this test without requiring fasting. A result of 200 mg/dL or higher is an indication of diabetes.
You May Like: What Can I Substitute For Brown Sugar For Diabetics
Why Elevated Glucose May Lead To Weight Gain
Foods high in sugar and refined carbs may promote weight gain because of their impact on blood sugar and insulin levels. These foods are considered high-glycemic carbs because they are quickly digested and lead to rapid rises in blood sugar.
Examples of high-glycemic foods include:
- White bread, bagels, white rice, white-flour pasta
- Muffins, croissants, doughnuts, flavored instant oatmeal, most cereals
- Cakes, candy, cookies, and most desserts
- Corn and white potatoes
< p class=”pro-tip”> < strong> Learn more about < /strong> < a href=”/blog/foods-to-avoid-for-weight-loss”> 8 foods to avoid for weight loss< /a> < /p>
Occasionally eating some cake at a birthday party isn’t a big deal, but a diet high in these foods and low in other blood sugar balancing nutrients like fiber and protein can mean you have higher insulin levels than usual as your body tries to lower blood sugar. Over time, insulin can promote fat storage.
When your glucose spikes and you don’t burn the excess energy, your body converts the extra glucose to glycogen stored in your muscle tissue and liver or as fat stored in your adipose cells.
By learning how your blood sugar responds to food and exercise, you can keep your glucose in a target range that also promotes a healthy weight.
< p class=”pro-tip”> < strong> Learn more about < /strong> < a href=”/blog/ultra-processed-foods”> how ultra-processed foods affect blood sugar< /a> < /p>
What Else Can I Do To Help Manage My Blood Sugar Levels
Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular physical activity can all help. Other tips include:
- Keep track of your blood sugar levels to see what makes them go up or down.
- Eat at regular times, and dont skip meals.
- Choose foods lower in calories, saturated fat, trans fat, sugar, and salt.
- Track your food, drink, and physical activity.
- Drink water instead of juice or soda.
- Limit alcoholic drinks.
- For a sweet treat, choose fruit.
- Control your food portions .
Don’t Miss: How To Make Sugar Wax Without Lemon
Diagnosing Prediabetes Type 2 And Type 1 Diabetes
Depending on which country or medical organization you ask, the qualifying numbers for normal versus prediabetes versus diagnosed type 1 or type 2 diabetes can vary slightly.
The following blood sugar and A1c results are used to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes according to sources including the American Diabetes Association and Diabetes UK:
Prediabetes
- HbA1c: 5.7 to 6.4 percent
- Fasting: 100 to 125 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL
Type 1 or 2 diabetes
- HbA1c: 6.5 percent or higher
- Fasting: 126 mg/dL or higher
- 2 hours after a meal: 200 mg/dL or higher
Please note:Type 1 diabetes tends to develop very quickly which means that by the time symptoms are felt, blood sugar levels are generally well above 200 mg/dL all the time. For many, symptoms come on so quickly that they are dismissed as the lingering flu or another seemingly ordinary virus.
By the time blood sugar levels are tested, many newly diagnosed type 1 patients will see levels above 400 mg/dL or higher. If you do suspect that you or a loved one has type 1 diabetes, visit your primary care or urgent care immediately and ask for a urine test to measure ketones in addition to testing blood sugar levels and A1c.
Read more about ketones at diagnosis in ourDiabetic Ketoacidosis Guide.
What Can I Expect During A Blood Glucose Test
You can expect the following during a venous glucose test, or blood draw:
- Youll sit in a chair, and a phlebotomist will check your arms for an easily accessible vein. This is usually in the inner part of your arm on the other side of your elbow.
- Once theyve located a vein, theyll clean and disinfect the area.
- Theyll then insert a small needle into your vein to take a blood sample. This may feel like a small pinch.
- After they insert the needle, a small amount of blood will collect in a test tube.
- Once they have enough blood to test, theyll remove the needle and hold a cotton ball or gauze on the site to stop the bleeding.
- Finally, theyll place a bandage over the site, and youll be finished.
You can expect the following during a capillary blood glucose test :
- A healthcare provider will ask you which finger youd like them to use.
- Theyll disinfect your fingertip with an alcohol swab and prick it with a small needle called a lancet, which is usually contained within a small plastic device.
- Theyll squeeze your fingertip to form a drop of blood.
- Theyll place your finger/the drop of blood against a test strip thats inserted into a glucometer.
- After they have enough blood for the test, theyll give you a cotton ball or gauze to hold against your fingertip to stop the bleeding.
- The glucometer will show your blood glucose level within seconds.
Read Also: How Can You Test Blood Sugar At Home
Being Extra Thirsty And Having To Urinate More Than Usual
This is a common but not-so-obvious sign of blood sugar that is too high: feeling really thirsty and needing to drink more than usual. Excessive urination, known as polyuria, occurs when glucose builds up in your blood, and your kidneys begin working harder to get rid of the extra glucose, says Zanini. If your kidneys cant keep up and adjust blood sugar so that it returns to a normal level, the excess sugar is flushed out of your body through urine, she adds. You may become dehydrated and get dizzy.
Recommended Reading: Dario Blood Glucose Monitoring System
Alarming Facts About Diabetes
Don’t Miss: Does Sugar Raise Blood Pressure
How To Measure Blood Sugar Levels
There are two main ways to check your blood sugar levels:
Type 1 diabetics, along with some type 2 diabetics, who require insulin medication, must check their blood sugar at least four times per day, says Mathioudakis. Typically, this should be done before a meal, one to two hours after a meal, and at bedtime.
The timing of these measurements can help determine how much insulin to use. For example, it can be important to use more insulin after a high-sugar meal, or to avoid falling into hypoglycemia while you’re sleeping.
To check your blood sugar at home, you should use blood glucose tests, such as a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor . Both devices measure blood sugar with the unit mg/dL, which means a milligram of sugar per deciliter of blood.
If you don’t have diabetes, but you may be at risk, your doctor might have you take an A1C test during a yearly check-up. This test reports results as a percentage the higher the percentage, the higher your blood sugar has been in the past three months. Those with diabetes should get an A1C test at least twice a year and sometimes every three months.
How Do Carbs Affect Blood Sugar
Carbs in food make your blood sugar levels go higher after you eat them than when you eat proteins or fats. You can still eat carbs if you have diabetes. The amount you can have and stay in your target blood sugar range depends on your age, weight, activity level, and other factors. Counting carbs in foods and drinks is an important tool for managing blood sugar levels. Make sure to talk to your health care team about the best carb goals for you.
You May Like: How Do You Monitor Your Blood Sugar
How Can I Treat High Blood Sugar
Talk to your doctor about how to keep your blood sugar levels within your target range. Your doctor may suggest the following:
- Be more active. Regular exercise can help keep your blood sugar levels on track. Important: dont exercise if ketones are present in your urine. This can make your blood sugar go even higher.
- Take medicine as instructed. If your blood sugar is often high, your doctor may change how much medicine you take or when you take it.
- Follow your diabetes meal plan. Ask your doctor or dietitian for help if youre having trouble sticking to it.
- Check your blood sugar as directed by your doctor. Check more often if youre sick or if youre concerned about high or low blood sugar.
- Talk to your doctor about adjusting how much insulin you take and what types of insulin to use.
What Is A Normal Blood Sugar
Ideas about normal blood sugar levels are based on individuals eating a standard American diet. This type of diet usually contains about 50% of calories from carbohydrate, the nutrient that tends to raise blood sugar the most.2
If your own carbohydrate intake is much lower than this, you may have a different normal. You can jump to How a low-carb diet affects blood sugar measurements for more information.
Fasting blood sugar levels
A normal fasting blood sugar level in someone who does not have diabetes is generally between 70 and 100 mg/dL .3
Fasting blood sugar that consistently falls in the range of 100 to 125 mg/dL is considered prediabetes, which is also referred to as impaired fasting glucose.
If your fasting blood sugar is above 126 mg/dL on two separate occasions, then you may have diabetes.
If you are concerned about the measurements youre getting, especially if you are already on a low-carbohydrate diet, see How a low-carb diet affects blood sugar measurements. A few blood sugar measurements may not always provide an accurate picture of your health.
Post-meal blood sugar levels
If your healthcare provider has not given you specific instructions regarding when to test post-meal blood sugar, you may want to try measuring it one to two hours after you begin eating. Whichever reading is the highest is the one that you should pay attention to, because blood sugar levels may peak at different times.
Blood glucose chart
You May Like: What Wine Is Low In Sugar
When And Why Should You Monitor Your Blood Sugar
Your healthcare provider will tell you how often to monitor your blood sugar. People with diabetes, especially those who use insulin, will need to monitor blood sugar much more frequently than those with prediabetes or normal blood sugar. People with normal blood sugar may only require periodic testing, for example, once yearly, at their physical examination. Maintaining blood sugar in the target range is important in preventing long-term complications.