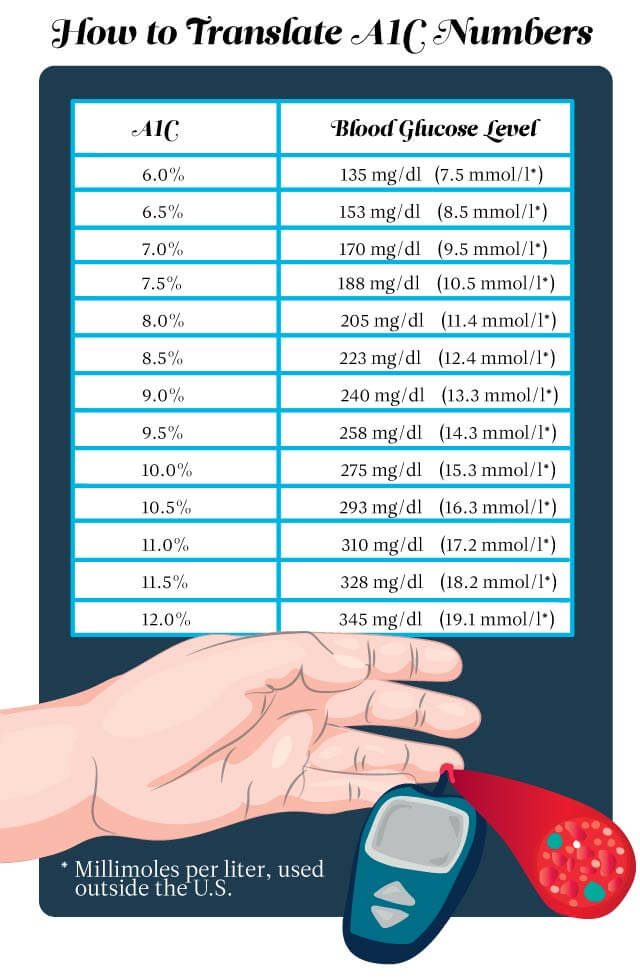
Translating Your A1c To A Blood Sugar Level
Using this easy calculator from the ADA, you can translate your most recent A1C result to an eAG or estimate average glucose level.
You can also use this translation when working to improve your A1c and achieving closer to normal blood sugar levels. If you know an A1c of 6.5 is an average blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or a range of 100 to 152 mg/dL, then you can look at your current blood sugar results on your CGM and meter and pinpoint which time of day youre frequently higher than this range.12% = 298 mg/dL or range of 240 347 11% = 269 mg/dL or range of 217 31410% = 240 mg/dL or range of 193 2829% = 212 mg/dL or range of 170 2498% = 183 mg/dL or range of 147 2177% = 154 mg/dL or range of 123 1856% = 126 mg/dL or range of 100 1525% = 97 mg/dL or range of 76 120
Normal blood sugar levels in a person without diabetes can result in an A1c as low as 4.6 or 4.7 percent and as high as 5.6 percent.
Just a decade or two ago, it was rare for a person with type 1 diabetes to achieve an A1c result below 6 percent. Thanks to new and improved insulin and better technology like continuous glucose monitors and smarter insulin pumps, more people with diabetes are able to safely achieve A1c levels in the higher 5 percent range.
What Are Considered Normal Blood Sugar Levels
You might not have diabetes now, but do you know the risk factors?
In 2015, 22% of Canadian adults were pre-diabetic and the number of Canadians suffering from diabetes has increased by 44% in the last 10 years. As the leading cause of blindness, kidney problems, and non-trauma amputations, it is important to protect ourselves against diabetes.
But its not all bad news, diabetes is often a preventable disease. Knowing whether you have normal blood sugar levels is one of the best indicators of risk. If your blood sugar levels are high, mindful eating and lifestyle changes can reduce your risk of developing diabetes.
Read on for all the hottest tips on how to manage your blood sugar levels and prevent diabetes.
Managing Blood Sugar When Youre Ill
When you get sick, your blood sugar levels may fluctuate and become unpredictable.
If you’re sick, it’s very important that you:
- drink plenty of water or sugar-free fluids
- check your blood sugar levels more often than usual
- take 15 grams of carbohydrate every hour if you are not able to follow your usual meal plan
- replace food with fluids that contain sugar if you can’t eat solid food
- continue to take your insulin or other diabetes medication
If you have a cold or flu and want to use a cold remedy or cough syrup, ask your pharmacist to help you make a good choice. Many cold remedies and cough syrups contain sugar, so try to pick sugar-free products.
As an extra precaution, you should always check with your health-care team about guidelines for insulin adjustment or medication changes during an illness.
Read Also: What Can You Do When Your Sugar Is High
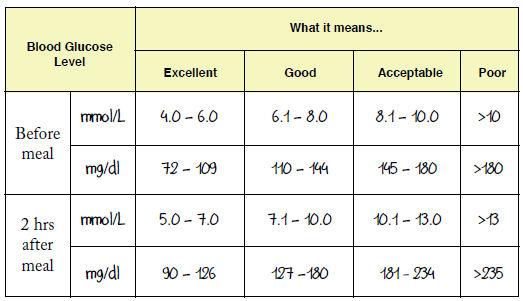
Normal Blood Sugar 30 Minutes After Eating
Blood sugar is a very familiar term these days. With a huge amount of individuals suffering from diabetes, trying to maintain a healthy level of sugar in the blood has become one of the daily challenges many of us face. As a matter of fact, checking the normal blood sugar 30 minutes after eating is a key indicator for getting an idea of the state of diabetes and overall health.
In this article, well go over the normal blood sugar, how to check it, what is the normal blood sugar after meals and how to control it.
Table of Content
Beyond Normal Goals: Whats An Optimal Glucose Level And Why Does It Matter
Exact numbers for what is considered optimal glucose levels to strive for while using CGM to achieve your best health are not definitively established this is a question that is individual-specific and should be discussed with your healthcare provider. With that said, research shows that there is an increased risk of health problems as fasting glucose increases, even if it stays within the normal range, making finding your optimal glucose levels all the more important.
While the International Diabetes Federation and other research studies have shown that a post-meal glucose spike should be less than 140 mg/dL in a nondiabetic individual, this does not determine what value for a post-meal glucose elevation is truly optimal for your health. All that number tells us is that in nondiabetics doing an oral glucose tolerance test, researchers found that these individuals rarely get above a glucose value of 140 mg/dL after meals.
So, while this number may represent a proposed upper limit of whats normal, it may not indicate what will serve you best from a health perspective. Many people may likely do better at lower post-meal glucose levels. Similarly, while the ADA states that a fasting glucose less than 100 mg/dL is normal, it does not indicate what value is optimal for health.
The following is a summary of insights from our review of research. You should consult with your doctor before setting any glucose targets or changing dietary and lifestyle habits.
Read Also: How To Measure Your Blood Sugar
Controlling Blood Glucose Levels
Uncontrolled blood sugar can result in regular episodes of hyperglycemia . This can cause a variety of symptoms including:
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Fatigue
These symptoms are uncomfortable to experience but there are things you can do at home to reduce your blood sugar. In terms of drinks, water is the best as it will help to maintain hydration and dilute excess sugar in the blood. Also, try to add more fiber to your diet to reduce your blood sugar apples, bananas, oranges, and strawberries are all fibrous fruits.
However, uncontrolled blood sugar levels can also lead to more severe, long term disease. Poorly managed diabetes leads to vision loss, kidney problems, nerve damage, heart attack, and stroke. Therefore, if your blood sugar level reaches 16.7mmol/L, this could be dangerous and you need to seek immediate medical attention.
What Should You Do If You Are Prediabetic
If youve been to see your doctor, and a blood test confirms you are prediabetic, there are many simple steps you can take to reverse the condition and prevent it from developing into diabetes.
Your healthcare providers will suggest help and guidance, like the best lifestyle changes considering your medical history and circumstances. Steps they may recommend include cutting out processed sugar, consuming more vegetables and whole grains, and taking a walk every morning.
A valuable resource for many prediabetic patients in the United States is the National Diabetes Prevention Program . Through private and public partnerships, it aims to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by making it easier for Americans to make the lifestyle changes they need.
In some cases, they may even recommend medication. Whatever your doctor suggests, remember prediabetes can be reversed and its great you caught it early.
Also Check: How Do I Lower My Sugar Level
Stick To Your Medication And Insulin Regimen
Skipping a dose of medication or insulin can be harmful to your body and increase your blood sugar levels.
Its important to stick to your treatment plan and follow your doctors instructions for taking your medication.
Summary
Healthful lifestyle habits can help people manage their blood sugar levels over the long term, such as eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, staying hydrated, and getting good sleep.
Normal Blood Sugar Ranges In Healthy Non
For a person without any type of diabetes, blood sugar levels are generally between 70 to 130 mg/dL depending on the time of day and the last time they ate a meal. Newer theories about non-diabetic blood sugar levels have included post-meal blood sugar levels as high as 140 mg/dL.
Here are the normal blood sugar ranges for a person without diabetes according to the American Diabetes Association:
- Fasting blood sugar : under 100 mg/dL
- 1 hour after a meal: 90 to 130 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 90 to 110 mg/dL
- 5 or more hours after eating: 70 to 90 mg/dL
Read Also: Does Olive Oil Lower Blood Sugar
How Do I Check My Blood Sugar
You use a blood glucose meter to check your blood sugar. This device uses a small drop of blood from your finger to measure your blood sugar level. You can get the meter and supplies in a drug store or by mail.
Read the directions that come with your meter to learn how to check your blood sugar. Your health care team also can show you how to use your meter. Write the date, time, and result of the test in your blood sugar record. Take your blood sugar record and meter to each visit and talk about your results with your health care team.
When To Go To The Er
High blood sugar can be very concerning because your body can start burning fat for energy instead of blood glucose.
This can cause conditions such as DKA and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome . These conditions are medical emergencies and can be fatal if left untreated.
DKA is a serious complication of type 1 diabetes. Its rare in people with type 2 diabetes, but can occur.
Symptoms that can indicate you should go to the emergency room include:
- ketones in your urine, as diagnosed using a urine dipstick test
- confusion
- stomach pain
- vomiting
High blood sugar levels can cause a fluid imbalance in the body and can cause the blood to become acidic in a manner that doesnt support life.
Medical treatments for these conditions include administering intravenous insulin on a continuous basis and IV fluids to correct dehydration.
Summary
High blood sugar can become a medical emergency. Go to the ER if you suspect DKA or HHS.
Read Also: How Do You Lower Your Blood Sugar Level
Blood Sugar Levels For Adults With Diabetes
Each time you test your blood sugar, log it in a notebook or online tool or with an app. Note the date, time, results, and any recent activities: What medication and dosage you took What you ate How much and what kind of exercise you were doing That will help you and your doctor see how your treatment is working. Well-managed diabetes can delay or prevent complications that affect your eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Diabetes doubles your risk for heart disease and stroke, too. Fortunately, controlling your blood sugar will also make these problems less likely. Tight blood sugar control, however, means a greater chance of low blood sugar levels, so your doctor may suggest higher targets.Continue reading > >
Recommended Reading: Insulin Alpha Cells
Now That Youre Checking Your Blood Glucose What Do The Numbers Mean

Depending on your diabetes treatment plan, your doctor or diabetes educator may advise you to check once a week, once a day or up to 10 times a day . But what does it mean when you see a 67, 101 or 350 on your meter? And what is a normal blood sugar, anyway? Great questions! After all, if you dont know what the numbers on your meter mean, its hard to know how youre doing.
The American Diabetes Association provides guidelines for blood glucose goals for people with diabetes, and the goals vary depending on when youre checking your glucose:
Fasting and before meals: 80130 mg/dl
Postprandial : Less than 180 mg/dl
By the way, these guidelines are for non-pregnant adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Children, adolescents and pregnant women may have different goals.
Your blood glucose goals may be different, however. If youre younger, have had diabetes for a shorter amount of time or are not taking any medicine for your diabetes, your glucose goals might be a little tighter, or lower. Likewise, your blood glucose goals may be higher than what ADA recommends if youre older, have diabetes complications, or dont get symptoms when your blood glucose is low.
Bottom line: talk with your health-care provider about the following:
When to check your blood glucose How often to check your blood glucose What your blood glucose goals are
Read Also: What Fruits Are Good For Lowering Blood Sugar
Summary Of Normal Glucose Ranges
In summary, based on ADA criteria, the IDF guidelines, a persons glucose values are normal if they have fasting glucose < 100 mg/dl and a post-meal glucose level < 140 mg/dl. Taking into account additional research performed specifically using continuous glucose monitors, we can gain some more clarity on normal trends and can suggest that a nondiabetic, healthy individual can expect:
- Fasting glucose levels between 80-86 mg/dl
- Glucose levels between 70-120 mg/dl for approximately 90% of the day
- 24-hour mean glucose levels of around 89-104 mg/dl
- Mean daytime glucose of 83-106 mg/dl
- Mean nighttime glucose of 81-102 mg/dl
- Mean post-meal glucose peaks ranging from 99.2 ± 10.5 to 137.2 ± 21.1 mg/dl
- Time to post-meal glucose peak is around 46 minutes 1 hour
These are not standardized criteria or ranges but can serve as a simple guide for what has been observed as normal in nondiabetic individuals.
Also Check: How Long Does Someone With Diabetes Live
Why Do I Need To Know My Blood Sugar Numbers
Your blood sugar numbers show how well your diabetes is managed. And managing your diabetes means that you have less chance of having serious health problems, such as kidney disease and vision loss.
As you check your blood sugar, you can see what makes your numbers go up and down. For example, you may see that when you are stressed or eat certain foods, your numbers go up. And, you may see that when you take your medicine and are active, your numbers go down. This information lets you know what is working for you and what needs to change.
Don’t Miss: What Foods Will Not Raise Blood Sugar
How To Lower Your A1c Levels
Its important to get your hemoglobin A1C levels as close to normal as possible, says Dr. Bellatoni, Decreasing your hemoglobin A1C decreases your risk of having complications from diabetes. Even if you cannot get your A1C back to the normal range, any improvement lowers your risk of diabetes complications.
Who Should Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
If you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes, monitoring your blood sugar regularly will help you understand how medication like insulin, food, and physical activity affect your blood glucose. It also allows you to catch rising blood sugar levels early. It is the most important thing you can do to prevent complications from diabetes such as heart attack, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and amputation.
Other people who may benefit from checking their blood glucose regularly include those:
- Taking insulin
Recommended Reading: What Is Your Normal Sugar Level Supposed To Be
Blood Sugar Chart: Summary
The fasting blood sugar, 2-hour post-meal blood sugar, and HbA1C tests are important ways to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes, as well as indicate how well a persons diabetes is being managed. If you think you have diabetes, its important to not try and diagnose yourself by doing a finger-stick with a home blood glucose meter. There are strict standards and procedures that laboratories use for diagnosing diabetes therefore, you should get tested at your doctors office or at a laboratory.
Its also important to talk with your doctor to make sure you understand a) how often you should have certain tests, such as a fasting blood glucose or HbA1C test b) what your results mean and c) what your blood sugar and HbA1C targets are.
If you have not been previously diagnosed with prediabetes or diabetes but your results are above normal, your doctor may recommend other tests and should discuss a plan of treatment with you. Treatment may include lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, a healthy eating plan, and regular physical activity. You may need to start taking diabetes medications, including insulin. If you are diagnosed with diabetes, its recommended that you learn how to check your blood sugars with a meter so that you and your healthcare team can determine how your treatment plan is working for you.
How To Stay In Target
Eating healthy, exercising and taking medication, if necessary, will help you keep your blood sugar levels within their target range. Target ranges for blood sugar can vary depending on your age, medical condition and other risk factors.
Targets are different for pregnant women, older adults and children 12 years of age and under.
Also Check: How To Control Blood Sugar Spikes After Meals
Normal Postmeal Blood Sugar Levels
Checking your blood glucose one to two hours after eating can help you understand how your blood sugar reacts to the food you consume. It can also offer insight into whether you’re taking the right dose of insulin or if you need to follow up with your doctor to discuss medication and diet or lifestyle adjustments.
There are two ways you can measure your blood glucose levels: by pricking your fingertip using a glucometer or by using continuous glucose monitoring. How often you should check your glucose levels varies from a few times per week to four to six times each day. As a general rule, the American Diabetes Association recommends keeping blood sugar below 180 mg/dL one to two hours after eating.
However, your target blood sugar range will depend on the following:
- Duration of diabetes
How Can Continuous Glucose Monitoring Help You Maintain Optimal Glucose Levels
It is not uncommon for your glucose levels to increase after a meal: you just ate food that may contain glucose, and now your body is working on getting it out of the bloodstream and into the cells. We know that we want to prevent excessive spiking of glucose levels because studies show that high post-meal glucose spikes over 160 mg/dl are associated with higher cancer rates. Spikes are also associated with heart disease. Repeated high glucose spikes after meals contribute to inflammation, blood vessel damage, increased risk of diabetes, and weight gain. Additionally, the data shows that the big spikes and dips in glucose are more damaging to tissues than elevated but stable glucose levels. Therefore, you should strive to keep your glucose levels as steady as possible, at a low and healthy baseline level, with minimal variability after meals.
Keeping your glucose levels constant is more complicated than just following a list of eat this, avoid that foods. Each person has an individual response to food when it comes to their glucose levels studies have shown that two people can have different changes in their glucose levels after eating identical foods. The difference can be quite dramatic. One study found that some people had equal and opposite post-meal glucose spikes in response to the same food.
Don’t Miss: How To Lower Morning Blood Sugar