What Are Blood Sugar Levels
Your blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose levels, are a measurement that show how much glucose you have in your blood. Glucose is a sugar that you get from food and drink. Your blood sugar levels go up and down throughout the day and for people living with diabetes these changes are larger and happen more often than in people who don’t have diabetes.
How Does A Continuous Glucose Monitor Work
A CGM works through a tiny sensor inserted under your skin, usually on your belly or arm. The sensor measures your interstitial glucose level, which is the glucose found in the fluid between the cells. The sensor tests glucose every few minutes. A transmitter wirelessly sends the information to a monitor.
The monitor may be part of an insulin pump or a separate device, which you might carry in a pocket or purse. Some CGMs send information directly to a smartphone or tablet. Several models are available and are listed in the American Diabetes Associations product guide.
When Should I Check My Blood Glucose Level
When you should check your blood glucose levels and how often you should check varies depending on each individual, the type of diabetes and the tablets and/or insulin being used. Your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator will help you decide how many checks are needed and the levels to aim for. Possible times to check are:
- Before breakfast
- Before rigorous exercise
- When you are feeling unwell
Even though your meter may have a memory, it is important to keep a record of your readings in a diary and to take this with you to all appointments with your diabetes health team. This will provide both you and your diabetes health team with important information in deciding if and how your treatment may need to be adjusted.
Most meters on the market have software which allows you to download your records in different formats such as graphs and charts. Even if you can do this, it is still helpful to keep a diary, not only for your checks but also details of your daily activities, the food you eat and other relevant information. There are some apps that record all of this information in one place. Ask your doctor or diabetes educator how you can use a diary to help you to better manage your diabetes.
Checking four times a day is usually recommended for people with type 1 diabetes. However many people check more often, such as those using an insulin pump .
Recommended Reading: How Much Sugar In Multigrain Cheerios
Why It Is Done
If you have diabetes, testing your blood glucose levels at home provides information about:
- Your blood sugar level at the time of testing. It is important to know when your blood sugar is high or low, to prevent emergency situations from developing. It is also important to treat consistently high blood sugar levels so you can decrease your chances of developing heart, blood vessel, and nerve complications from diabetes.
- How much insulin to take before each meal. If you take rapid-acting or short-acting insulin before meals, the blood sugar test results can help you determine how much insulin to take before each meal. If your blood sugar level is high, you may need extra insulin. If your blood sugar level is low, you may need to eat before you take any insulin.
- How exercise, diet, stress, and being ill affect your blood sugar levels. Testing your blood sugar can help you learn how your body responds to these things. Where possible, you can adjust your lifestyle to improve your blood sugar level.
Home blood sugar testing also may be used to:
- Test blood sugar levels in people who have symptoms of high blood sugar or low blood sugar .
Signs & Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar
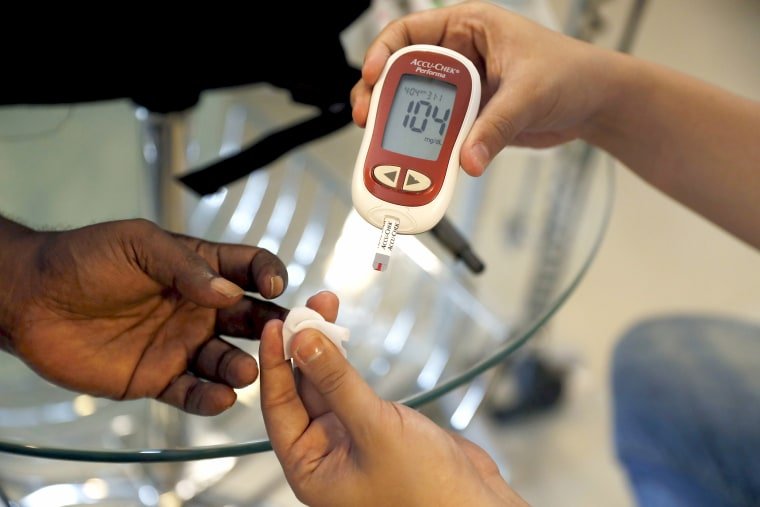
Keeping blood glucose levels in a healthy range can be challenging.
When the amount of sugar in your blood has dropped below your target range , it is called low blood sugar .
If your blood sugar has dropped, you may feel:
- shaky, light-headed, nauseated
- an increase in heart rate
- sweaty, headachy
- weak, drowsy
- numbness or tingling on your tongue or lips
Symptoms of very low blood sugar are more severe and can make you:
- confused and disoriented
- lose consciousness
- have a seizure
Make sure you always wear your MedicAlert® identification and talk to your doctor or diabetes educator about prevention and emergency treatment for severe low blood sugar.
You May Like: What Should I Eat If My Blood Sugar Is High
Instructions For Checking Your Blood Sugar
Your healthcare provider will tell you how often to check your blood sugar. Theyll also tell you what your blood sugar level should be. This is called your blood sugar target range. Your blood sugar target range is based on your overall health and current treatment plan.
When youre ready to start, wash your hands with soap and water. Dry them very well. Touching a blood glucose test strip with damp hands can damage it or make your result less accurate.
About Your Contour Next One Blood Glucose Meter
A blood glucose meter measures the amount of sugar in your blood. It has 3 main parts .
Figure 2. Contour Next One blood glucose meter
- The test strip port is where youll put the blood glucose test strip into the meter. Your Contour Next One glucose meter will only work with Contour Next test strips.
- The screen shows information such as the meters status, your blood sugar level, and the date and time.
- The buttons are how you control the meter.
- To scroll up, press the up button. Hold it to keep scrolling.
- To scroll down, press the down button. Hold it to keep scrolling.
- To accept a selection, press the OK button.
- To turn your meter on or off, press and hold the OK button.
You need to set up your meter before using it for the first time. You do this by accepting the blood glucose target range of 70-180 mg/dL and setting the time and date. Your meter will not work until you set it up.
Do not put your glucose meter under water. If you notice its dirty, wipe it with a damp cloth or alcohol pad.
Also Check: Can Too Much Sugar Cause Diabetes
Risk Factors For High Blood Sugar
According to Dr. Mitchell, “There are a number of different factors that can contribute to high blood sugar levels. One of the most important is diet. Foods that are high in simple sugars and refined carbohydrates can cause spikes in blood sugar levels. Other risk factors include lack of physical activity, certain medications, and medical conditions such as diabetes and prediabetes. High stress levels can also lead to increases in blood sugar. To help keep blood sugar levels under control, it is important to eat a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and manage stress. If you have any concerns about your blood sugar levels, be sure to speak with your healthcare provider.”
What Is Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous glucose monitoring is another way to check your glucose levels. Most CGM systems use a tiny sensor that you insert under your skin. The sensor measures glucose levels in the fluids between your bodys cells every few minutes and can show changes in your glucose level throughout the day and night. If the CGM system shows that your glucose is too high or too low, you should check your glucose with a blood glucose meter before making any changes to your eating plan, physical activity, or medicines. A CGM system is especially useful for people who use insulin and have problems with low blood glucose.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Treat Low Blood Sugar
How Do Carbs Affect Blood Sugar
Carbs in food make your blood sugar levels go higher after you eat them than when you eat proteins or fats. You can still eat carbs if you have diabetes. The amount you can have and stay in your target blood sugar range depends on your age, weight, activity level, and other factors. Counting carbs in foods and drinks is an important tool for managing blood sugar levels. Make sure to talk to your health care team about the best carb goals for you.
What Are The Target Ranges
Blood glucose targets are individualized based on:
- duration of diabetes
- conditions a person may have
- cardiovascular disease or diabetes complications
- hypoglycemia unawareness
- individual patient considerations
The American Diabetes Association suggests the following targets for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. A1C targets differ based on age and health. Also, more or less stringent glycemic goals may be appropriate for each individual.
- A1C: Less than 7%A1C may also be reported as eAG: Less than 154 mg/dL
- Before a meal : 80130 mg/dL
- 1-2 hours after beginning of the meal *: Less than 180 mg/dL
Don’t Miss: What Are The Symptoms Of Your Sugar Being High
Random Plasma Glucose Test
Another test that might identify something is awry with your blood sugar is a random plasma glucose test. Diabetes can also be diagnosed when a random glucose is greater than or equal to 200 mg/dL in the setting of symptoms of high blood glucose, explains Dr. Lonier. So, if someone were to randomly prick their finger and use a glucometer to check their blood sugar, and the reading was greater than or equal to 200 mg/dL, this might indicate diabetes when certain symptoms are also present. These symptoms, she notes, are excess thirst, frequent urination, blurry vision, and weight loss.
Sure Signs You Need To Have Your Blood Sugar Checked Now

A healthy blood sugar level is essential for overall well-being, especially if you’re diabetic. “Too much or too little blood sugar can harm our health,” Dr. Tomi Mitchell, a Board-Certified Family Physician with Holistic Wellness Strategies tells us. “When blood sugar levels are too high, it can lead to diabetes. But, on the other hand, if blood sugar levels drop too low , it can lead to dizziness, confusion, and even unconsciousness. That’s why it’s essential to maintain healthy blood sugar levels by eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly,” she adds. The Mayo Clinicstates, “A blood sugar level less than 140 mg/dL is normal. A reading of more than 200 mg/dL after two hours indicates diabetes. A reading between 140 and 199 mg/dL indicates prediabetes.” Read on for the five signs of high blood sugar to pay attention toand to ensure your health and the health of others, don’t miss these Sure Signs You’ve Already Had COVID.
Also Check: When My Sugar Is High
If You Have Questions About Your Diagnosis
It’s usually difficult to take in everything the GP tells you during the appointment.
Talk to family and friends about what the GP told you, and write down any questions you have.
Then make another GP appointment and take your list of questions with you.
There’s also a lot of information on diabetes available.
How Do I Check My Blood Sugar
You will be taught how to check a small drop of blood with a glucose meter. Get all of your supplies together, such as your meter, test strips, and lancet device. Be sure to read the information that came with your meter. Use the following steps as a guide:
- Wash your hands. Use warm water to help blood flow. Dry your hands completely.
- Put the test strip in the meter. This will turn on your meter.
- Use the lancing device to stick your finger or area. Do not use the same finger or area every time. Stick the side of your fingertip, not the middle. The side may cause less pain.
- Squeeze your fingertip or area gently.
- Touch the drop of blood to the test strip. A number will appear on the meter after a few seconds. This is your blood sugar level.
Recommended Reading: How Many Grams Of Sugar Can You Have On Keto
Special Features Of A Cgm
CGMs are always on and recording glucose levelswhether youre showering, working, exercising, or sleeping. Many CGMs have special features that work with information from your glucose readings:
- An alarm can sound when your glucose level goes too low or too high.
- You can note your meals, physical activity, and medicines in a CGM device, too, alongside your glucose levels.
- You can download data to a computer or smart device to more easily see your glucose trends.
Some models can send information right away to a second persons smartphoneperhaps a parent, partner, or caregiver. For example, if a childs glucose drops dangerously low overnight, the CGM could be set to wake a parent in the next room.
Currently, one CGM model is approved for treatment decisions, the Dexcom G5 Mobile. That means you can make changes to your diabetes care plan based on CGM results alone. With other models, you must first confirm a CGM reading with a finger-stick blood glucose test before you take insulin or treat hypoglycemia.
How Can I Pay For Tests And Diabetes Supplies
Medicareexternal icon, Medicaid, and most private insurance plans pay for the A1C test and fasting blood sugar test as well as some diabetes supplies. Check your plan or ask your health care team for help finding low-cost or free supplies, and see How to Save Money on Diabetes Care for more resources.
Recommended Reading: What Is In Sugar Free Candy
Types Of Blood Sugar Tests
You can take a blood sugar test two ways. People who are monitoring or managing their diabetes prick their finger using a glucometer for daily testing. The other method is drawing blood.
Blood samples are generally used to screen for diabetes. Your doctor will order a fasting blood sugar test. This test measures your blood sugar levels, or a glycosylated hemoglobin, also called a hemoglobin A1C test. The results of this test reflect your blood sugar levels over the previous 90 days. The results will show if you have prediabetes or diabetes and can monitor how your diabetes is controlled.
When and how often you should test your blood sugar depends on the type of diabetes you have and your treatment.
When Should I Check My Childs Blood Sugar
The diabetes care team will tell you when to check your childs blood sugar. Most kids and teens need to test:
- before each meal
- at bedtime
- before, during, and after exercise
Sometimes you may need to test more often, even while your child sleeps. For example, if:
- Your child was recently diagnosed with diabetes.
- Your child is sick.
- Your child is having a lot of high or low blood sugars.
- There are changes in your childs diabetes treatment or daily habits.
You May Like: How To Make Beet Sugar
Touch The Blood Glucose Test Strip To The Blood Drop
Figure 15. Touch the end of the test strip
It is important to look at the number on the screen, not just the color.
Times To Check More Often
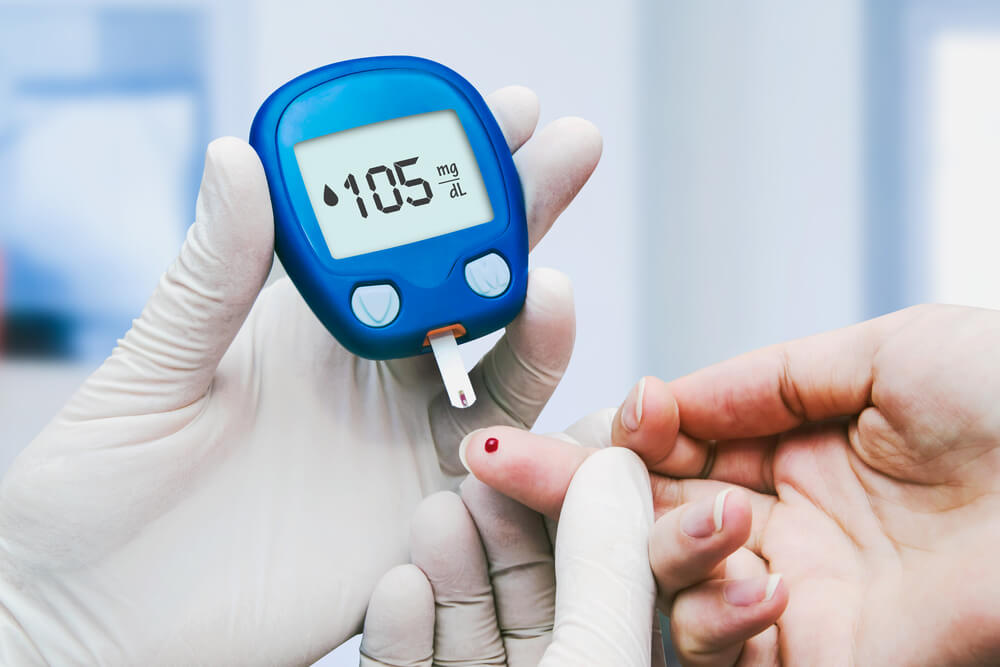
There will be times when you need to check more often, however you should first discuss this with your doctor or Credentialled Diabetes Educator. Example of these times include when you are:
- Being more physically active or less physically active
- Sick or stressed
- Experiencing changes in routine or eating habits, e.g. travelling
- Changing or adjusting your insulin or medication
- Experiencing symptoms of hypoglycaemia
- Experiencing night sweats or morning headaches
- A female planning pregnancy or are pregnant.
- Pre/post minor surgical day procedures
- Post dental procedures
Your Credentialled Diabetes Educator can help you work out self-monitoring approach especially for you.
Recommended Reading: Where Is Your Sugar Level Supposed To Be
What Number Should My Blood Glucose Be
Blood glucose is measured in mg/dl. The normal range for blood glucose for people without diabetes is 70 to 120 mg/dl.
The Diabetes Center has guidelines for blood glucose readings. This is called a target range. There may be times when your healthcare provider gives you a different target range, like for bedtime, with exercise, or after eating.
Nationwide Childrens Hospital Diabetes Center Target Blood Glucose Ranges
| Age |
The goal is to keep the blood glucose within the target range most of the time.