What If The 15
If you dont feel better after three tries, or if your symptoms get worse, call your healthcare provider or 911. Healthcare providers can use a medication called glucagon. They inject it with a needle or squirt it up your nose. Glucagon is also available for home use. Your healthcare provider can prescribe it and teach a family member or friend how to use it in the event of severe hypoglycemia.
High Blood Sugar: Hidden Dangers
In the short term, high blood sugar levels can zap your energy, cause excessive thirst and urination, and blur your vision. High blood sugar levels can also lead to dehydration, dry and itchy skin, and infections. Minimizing the time spent above your target blood sugar range can help you feel your best and will help prevent complications and injury to your body.
Over time, high blood sugar affects many parts of the body. Chronic high blood sugar can start to cause noticeable changes, including:
- Memory problems
- Vision problems like blurriness, diabetic retinopathy, and blindness
- Gum disease that leads to tooth loss, which can make eating healthy foods difficult due to problems chewing
- Heart attack and stroke due to increased plaque build-up in the vessels and other vascular issues
- Kidney disease, which can lead to the need for dialysis or a kidney transplant
- Nerve damage that can cause decreased sensation in the feet and legs which increases the risk for wounds to turn into serious infections and even amputation
Nerve damage from high blood sugar can also cause a variety of symptoms including:
- Pain and tingling in the feet and hands
- Difficulty emptying your bladder
- Problems during the digestion process after eating, which can cause food to sit in the stomach too long and lead to nausea, vomiting, and erratic blood sugar levels
Checking your blood sugar frequently and taking immediate action when it is above range can reduce your risk of complications.
Are There Any Newer Technologies To Prevent Hypoglycemia
We are lucky that in this day and age, we can predict hypoglycemia and prevent it through technology like continuous glucose monitors, explains Dr. Shah. Additionally, he notes that there are newer insulins available to help decrease episodes of hypoglycemia.
One of our roles as your doctor is to educate every patient about the self-management of diabetes and to create a personalized care plan, explains Dr. Shah. By self-managing your condition you will really feel empowered enough to take control of your health.
Dr. Shah is located at the Hackensack Meridian Health Medical Group Diabetes Center, part of Hackensack Meridian Health Medical Group. Call to schedule an appointment at the office in Old Bridge.
Our care network can help you better manage your health. Visit HMHMedicalGroup.org to find a practice near you.
The material provided through HealthU is intended to be used as general information only and should not replace the advice of your physician. Always consult your physician for individual care.
Resources
Recommended Reading: Is Organic Cane Sugar Healthy
You May Like: How To Reduce Diabetes Instantly
Target Blood Sugar Ranges For Pregnant People With Diabetes
Blood sugar targets during pregnancy are lower due to hormonal influences. The ADA, AACE, and Joslin Diabetes Center have slightly different guidelines for target blood sugar levels during pregnancy. In general, pregnant women with diabetes will want to follow individual guidelines provided by their endocrinologist.
The ADA recommends maintaining blood sugar levels of 95-140 mg/dL for pregnant women. However, some providers recommend an even tighter goal of blood glucose levels below 89 mg/dL before a meal and below 120 mg/dL after a meal.
To keep close tabs on levels, most diabetes specialists recommend that women with diabetes during pregnancy check their blood sugar:
- First thing in the morning
- Before all meals
What Are The Causes Of Hypoglycaemia
The usual causes of low blood glucose level are:
- not eating enough carbohydrate with your meal, eg, steak and salad with no carbohydrate such as bread/potato/kumara/rice/pasta
- missing or delaying a meal
- missing snacks
- doing physical activity without either reducing your insulin or taking more carbohydrate before, during or after physical activity
- taking too much insulin
- drinking alcohol in excess or without taking carbohydrate food and/or reducing your insulin.
Also Check: How To Bring Down Sugar Level Quickly
How Do I Treat Low Blood Glucose
If you begin to feel one or more symptoms of low blood glucose, check your blood glucose level. If your blood glucose level is below your target or less than 70 mg/dL, follow these steps
Complications From Spells Of Hypoglycemia
Mildly low blood sugar levels are somewhat common for people with diabetes. However, severely low blood sugar levels can be life threatening. They may lead to seizures and nervous system damage if left untreated long enough. Immediate treatment is critical.
Its important to recognize your symptoms and treat them quickly. For people at risk for low blood sugar, having a glucagon kit a medication that raises blood sugar levels is important. Talk with your doctor for more information.
You may also want to talk with friends, family members, exercise partners, and co-workers about how to care for you if your blood sugar drops too low.
Its important for them to recognize low blood sugar symptoms and to know how to use the glucagon kit, as well as understand the importance of calling 911 if you lose consciousness.
Wearing a medical identification bracelet is a good idea. It can help emergency responders care for you properly if you need urgent medical attention.
Treat low blood sugar as soon as possible. Avoid driving if you are experiencing low blood sugar, as it can increase your risk for having an accident.
There are several ways you can prevent low blood sugar. Well look at each of these prevention methods in more detail below.
You May Like: Blood Sugar Increase Symptoms
Recommended Target Blood Glucose Level Ranges
The NICE recommended target blood glucose levels are stated below for adults with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and children with type 1 diabetes.
In addition, the International Diabetes Federations target ranges for people without diabetes is stated.
The table provides general guidance. An individual target set by your healthcare team is the one you should aim for.
| Target Levels |
|---|
*The non-diabetic figures are provided for information but are not part of NICE guidelines.
How To Test Your Blood Sugar At Home
To perform a blood sugar test, you will need to prick your finger with a lancet . Youll put a small sample of blood from this onto a strip inserted into the blood glucose meter.
Before you test your blood sugar at home, its important to find out from your doctor what a healthy blood sugar range is for you. Your doctor will determine this range based on factors such as:
- the type of diabetes you have
- how long youve had diabetes
- your age
- whether you have any other chronic health conditions
If you dont have a blood sugar testing machine on hand and are experiencing signs or symptoms of low blood sugar with diabetes, your symptoms may be enough to diagnose low blood sugar.
Don’t Miss: Banana Bad For Diabetes
Your Hypoglycemia Action Plan
If you experience symptoms of hypoglycemia, its important to take action. Start with these steps:
Test your blood sugar. If you recognize any of these symptoms and believe your blood sugar may be too low, the first step you should take is to test your blood sugar with your glucose meter, Tan says. Anything less than 70 milligrams per deciliter is considered low blood sugar, according to the National Library of Medicine . However, target levels are often individualized, so talk with your healthcare provider about your optimal numbers, Tan adds.
Eat or drink fast-acting carbs. If you have low blood sugar, you need to take action right away. Your best bet is to consume about 15 grams of carbohydrates, the NLM says. Some options include:
- ½ cup or 4 ounces of orange juice
- ½ cup or 4 ounces of regular soda
- 1 tablespoon of sugar dissolved in water
- 1 tablespoon of honey or maple syrup
- 5 or 6 hard candies, jelly beans, or gumdrops
- 1 tablespoon of cake frosting
- 2 tablespoons of raisins
- ½ cup of applesauce
You can also take three to four glucose tablets or a tube of glucose gel. Everyone who takes medications for diabetes should always have glucose tablets with them, Galindo urges.
Wait, then retest. The next step is to wait 15 minutes, then test your blood sugar again. If blood sugar has reached 100 mg/dl or greater, youre fine. If not…
Treatment For Severe Hypoglycaemia
In cases of severe hypoglycaemia the person cannot treat themselves, and needs the help of someone else. Call triple zero for an ambulance immediately.
If the person can’t swallow or follow instructions do not give them any treatment by mouth.
If you are trained in how to prepare and inject glucagon and feel comfortable injecting it, then this can be administered.
Ambulance paramedics have the resources to manage severe hypoglycaemia.
You May Like: How To Come Sugar Disease
High Blood Sugar Level Causes
Several types of diabetes and medical conditions are the primary cause of high blood sugar levels. Most of which are unpreventable issues but are the reason for a spike in high blood sugar. The causes for high blood sugar levels are as follows:
Causes of low blood sugar levels are very different and are as important to be aware of, as they are in fact easier to control.
Why Your Blood Sugar Level May Be High

Based on the ADA guidelines above, if your blood sugar is above 180 mg/dL two hours after a meal, it is considered above the normal range. What might cause your glucose or blood sugar to rise? Consider the following factors:
- Consuming more carbohydrates or a larger meal than usual
- Not taking enough insulin or oral diabetes medication based on carbohydrates or activity levels
- Reduced physical activity
- Side effects from medications like steroids or antipsychotics
Read Also: When To Take Sugar Tablet
Why Am I Having Lows
If you are experiencing low blood sugar and youre not sure why, bring a record of blood sugar, insulin, exercise and food data to a health care provider. Together, you can review all your data to figure out the cause of the lows.
The more information you can give your health care provider, the better they can work with you to understand what’s causing the lows. Your provider may be able to help prevent low blood sugar by adjusting the timing of insulin dosing, exercise and meals or snacks. Changing insulin doses or the types of food you eat may also do the trick.
What Are The Complications Of Low Blood Glucose
Mild-to-moderate low blood glucose can be easily treated. But severely low blood glucose can cause serious complications, including passing out, coma, or death.
Repeated episodes of low blood glucose can lead to
- high blood glucose levels, if worry or fear of low blood glucose keeps you from taking the medicines you need to manage your diabetes8
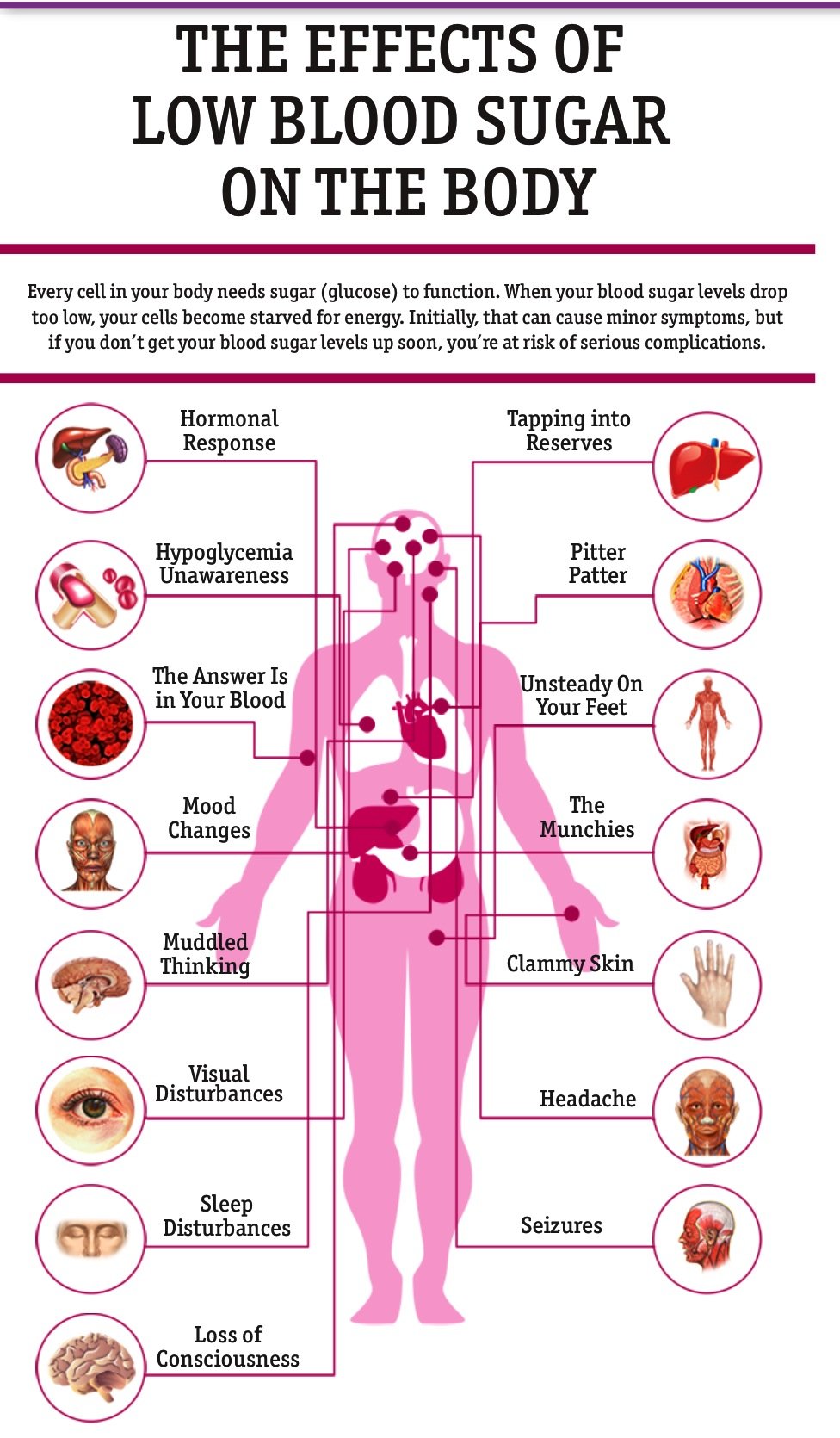
- hypoglycemia unawareness, a condition in which you dont notice any symptoms of low blood glucose until your blood glucose level has dropped very low
Read Also: How To Reduce High Sugar Level Immediately
How Can I Prevent Hypoglycemic Episodes
The key to preventing hypoglycemic events is managing diabetes:
- Follow your healthcare providers instructions about food and exercise.
- Track your blood sugar regularly, including before and after meals, before and after exercise and before bed.
- Take all your medications exactly as prescribed.
- When you do have a hypoglycemic event, write it down. Include details such as the time, what you ate recently, whether you exercised, the symptoms and your glucose level.
Does Everyone Have Symptoms From Hypoglycemia
Some people dont have symptoms or dont notice them. Healthcare providers call that situation hypoglycemia unawareness. People with such a challenge arent aware when they need to do something about their blood sugar. Theyre then more likely to have severe episodes and need medical help. People with hypoglycemia unawareness should check their blood sugar more often.
You May Like: What Vitamin Deficiency Causes Sugar Cravings
Preventing Low Blood Sugar
Preventing low blood sugar is better than having to treat it. Always have a source of fast-acting sugar with you.
- When you exercise, check your blood sugar levels. Make sure you have snacks with you.
- Talk to your provider about reducing insulin doses on days that you exercise.
- Ask your provider if you need a bedtime snack to prevent low blood sugar overnight. Protein snacks may be best.
DO NOT drink alcohol without eating food. Women should limit alcohol to 1 drink a day and men should limit alcohol to 2 drinks a day. Family and friends should know how to help. They should know:
- The symptoms of low blood sugar and how to tell if you have them.
- How much and what kind of food they should give you.
- When to call for emergency help.
- How to inject glucagon, a hormone that increases your blood sugar. Your provider will tell you when to use this medicine.
If you have diabetes, always wear a medical alert bracelet or necklace. This helps emergency medical workers know you have diabetes.
How We Care For Hypoglycemia
At Boston Childrens Hospital, we treat hypoglycemia in our General Endocrinology Program, a multi-disciplinary program dedicated to the treatment of a wide range of endocrinological disorders. Caring for more than 7,000 patients each year, our division is one of the largest pediatric endocrinology practices in the country. We provide state-of-the-art diagnosis, treatment, and clinical management for children with hypoglycemia and related disorders.
Don’t Miss: Can We Control Sugar Without Medicine
What Causes Hypoglycemia
The vast majority of episodes of hypoglycemia in children and adolescents occur when a child with diabetes takes too much insulin, eats too little, or exercises strenuously or for a prolonged period of time.
For young children who do not have diabetes, hypoglycemia may be caused by:
Single episodes:
- stomach flu or another illness that may cause them to not eat enough
- fasting for a prolonged period of time
- prolonged strenuous exercise and lack of food
Recurrent episodes:
- accelerated starvation, also known as ketotic hypoglycemia, a tendency for children without diabetes, or any other known cause of hypoglycemia, to experience repeated hypoglycemic episodes
- medications your child may be taking
- a congenital error in metabolism or unusual disorder such as hypopituitarism or hyperinsulinism
No Symptoms Be Alarmed

Surprisingly, the most dangerous episodes of hypoglycemia occur with little or no warning. When low blood glucose occurs on a regular basis, the body can become used to the warning signs and the person may stop noticing symptoms. This is a particularly dangerous condition known as hypoglycemic unawareness. People with this condition might not realize they have low blood glucose until it’s dangerously low seizures and coma are sometimes the first indication of a problem. The good news is that this condition can often be reversed allowing people to once again notice the signs of low blood glucose if hypoglycemia is avoided for a few weeks through careful monitoring of blood glucose.
You May Like: Sugar In Low Blood Pressure
Causes Of Blood Sugar Levels
Whilst the liver and muscles produce some glucose, most comes from the foods we eat. Food and drinks that are high in carbohydrates are most impactful on blood sugar level. What we eat provides us most of the nutrients our body needs and sometimes, does not need. That is not to say that food is a major cause of blood sugar level increasing or decreasing too dramatically.
Typically, if a person has health conditions or poor nutrition, this will lead to a spike or decline in blood sugar level. The causes differ from high to low blood sugar levels and are as follows:
How To Treat Someone Who’s Having A Seizure Or Fit
Follow these steps if someone has a seizure or fit caused by a low blood sugar level:
Tell your diabetes care team if you ever have a severe hypo that caused you to have a seizure or fit.
Don’t Miss: Sugar Tablets Side Effects
Low Blood Sugar Chart And Action Plan
Low blood sugar is also called hypoglycemia. The numbers below represent values in the hypoglycemic range and require action to bring blood sugar levels up into a normal range.
| Alert Level and Treatment Plan | |
| 50 mg/dL or under | Red Flag: Blood sugar is critically low and requires immediate treatment.
If a person is unable to speak and/or is not alert, treat with glucagon via injection or nasal spray. Call emergency medical response if necessary. Do not place food or drink into the mouth. If a person is alert and able to speak clearly, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate such as glucose gel, 4 oz regular soda, or fruit juice. Re-test blood sugar in 15 minutes and repeat as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 51-70 mg/dL | Red Flag: Blood sugar is below normal levels and requires immediate treatment.
Treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 71-90 mg/dL | Yellow Flag: Blood sugar levels should be watched and treated as needed.
If youre having symptoms of low blood sugar, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment or follow with a meal. If it is meal time, move forward with eating the meal. People often fall into this range when they are late for a meal or have been especially active. |