What Is Being Tested
This test measures the amount of glucose in your blood. Glucose is a simple sugar that provides energy for the body.
People with diabetes often monitor their own blood glucose at home. This is done using a finger-prick test and a special machine, rather than a blood sample taken from a vein.
You might have blood taken for a blood sugar level. You might or might not be asked to fast beforehand.
There is also a test called an oral glucose tolerance test, abbreviated as OGTT or GTT. For this test you fast, then have a blood sample taken, then drink glucose, then have a number of samples taken over a few hours.
Normal Postmeal Blood Sugar Levels
Checking your blood glucose one to two hours after eating can help you understand how your blood sugar reacts to the food you consume. It can also offer insight into whether you’re taking the right dose of insulin or if you need to follow up with your doctor to discuss medication and diet or lifestyle adjustments.
There are two ways you can measure your blood glucose levels: by pricking your fingertip using a glucometer or by using continuous glucose monitoring. How often you should check your glucose levels varies from a few times per week to four to six times each day. As a general rule, the American Diabetes Association recommends keeping blood sugar below 180 mg/dL one to two hours after eating.
However, your target blood sugar range will depend on the following:
- Duration of diabetes
How To Lower Blood Sugar Immediately
Michael Menna, DO, is a board-certified, active attending emergency medicine physician at White Plains Hospital in White Plains, New York.
If you have high blood sugar, a condition also known as hyperglycemia, theres too much sugar in your blood and not enough insulin in your body to lower it. In people with diabetes, hyperglycemia can be caused by things like eating too many carbohydrates, lack of physical activity, stress from an illness or infection, nondiabetes medications , or skipping or not taking enough glucose-lowering medication.
Hyperglycemia requires immediate treatment to prevent serious complications, including nerve, tissue, and organ damage diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome . While taking rapid-acting insulin is the quickest way to lower your blood sugar, there are other ways like exercising and staying hydrated that can help. In cases of an emergency, contact your doctor immediately.
You May Like: How To Get Blood Sugar Up
Checking Your Blood Glucose Levels Will Help You To:
- Develop confidence in looking after your diabetes.
- Better understand the relationship between your blood glucose levels and the exercise you do, the food you eat and other lifestyle influences such as travel, stress and illness.
- Know how your lifestyle choices and medication, if used, are making a difference.
- Find out immediately if your blood glucose levels are too high or too low , helping you to make important decisions such as eating before exercise, treating a hypo or seeking medical advice if sick.
- Know when to seek the advice of your diabetes health team about adjusting your insulin, tablets, meal or snack planning when blood glucose goals are not being met.
What Is Causing My Blood Sugars To Be Out Of Range
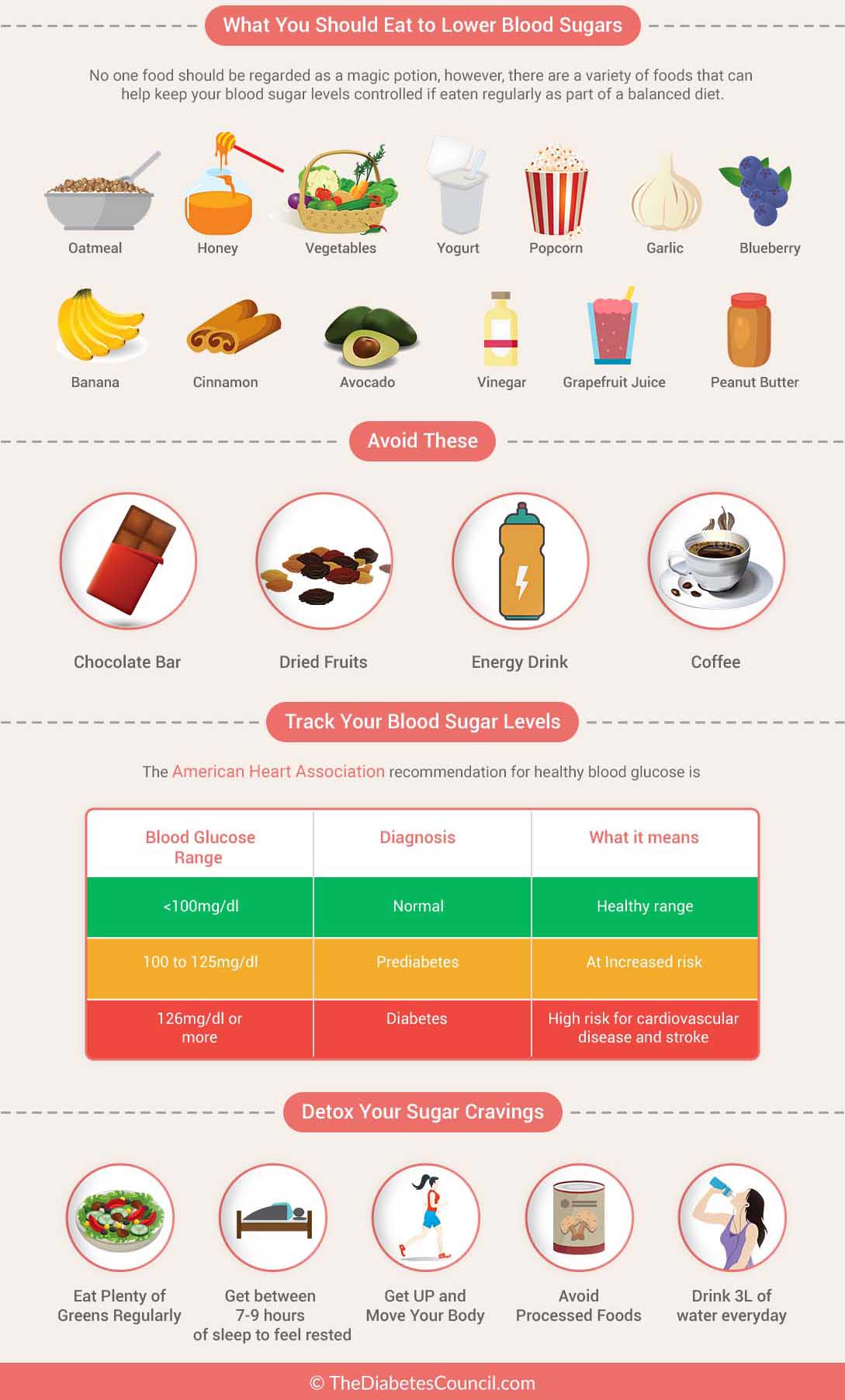
Here are some common scenarios of blood sugars being out of range, possible reasons for them and what to do if you face these scenarios.
High glucose levels before breakfast
Morning glucose levels are often referred to as fasting glucose levels. If these levels are out of range, you may find that it is difficult to keep your levels down for the rest of the day. Possible reasons why your blood sugar is high in the morning include:
-
Consuming sweet drinks in the morning before measuring your sugar levels
-
Forgetting to take medication
What to do if your blood sugar is high in the morning:
-
If this is the first time you notice it happening or if it only happens occasionally, try taking note of what you had the night before and the duration of sleep you had
-
If your blood sugar has been high in the mornings continuously for a few days, speak to your healthcare team about it
High glucose levels before meals
If your levels are out of the target range before your meals, think about whether you had anything to eat or drink within the last two hours. If the answer is yes, your glucose levels may have been caused by this. Perhaps you had a chocolate bar on the way home, or a sweet drink before dinner? If you have not consumed any food or drink, and your glucose levels are high before your meals, speak with your healthcare team as you may need to adjust your medication.
High glucose levels after meals
Hypoglycemia
Don’t Miss: How To Use Cinnamon To Lower Blood Sugar
How Is Blood Glucose Monitoring Performed
Before you begin, wash your hands thoroughly to prevent infection at the finger-prick site. If you use alcohol wipes instead of washing, be sure to let the site dry before testing.
Next, put a testing strip into the meter. Prick your finger with the lancet to get a small drop of blood. Use the sides of the fingertips instead of the tip to decrease finger discomfort.
The blood goes on the test strip you inserted into the meter. Your monitor will analyze the blood and give you the blood glucose reading on its digital display usually within a minute.
Finger pricks rarely require a bandage, but you may want to use one if bleeding continues beyond a few drops. Its important to follow all the instructions that came with your glucometer to ensure accurate results.
If you have type 1 diabetes, you may need to test your blood glucose four or more times per day. This includes before and after meals and exercise, and more often when you are sick.
If you have type 2 diabetes, your doctor will let you know when and how often to test your blood glucose.
Why Would I Need This Test
You might need this test if you are at risk of developing diabetes, or if you have had any symptoms or test results suggesting diabetes.
The standard blood glucose tests measure your blood sugar level at a particular time. The OGTT measures how you respond to glucose.
Pregnant women can develop a particular type of diabetes called gestational diabetes, and will be asked to have an OGTT around 24 to 28 weeks of pregnancy. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after the baby is born.
Don’t Miss: What Happens When You Have High Blood Sugar
Target Blood Sugar Levels For People With Diabetes
People with diabetes have difficulty creating or using enough insulin, which is the hormone that helps convert glucose into energy. Although there is no universal blood sugar chart for everyone with diabetes, clinical organizations like the ADA and American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists offer guidelines on target blood sugar levels as a starting point.
Healthcare providers typically tailor normal blood sugar target ranges to an individual diabetes care plan. This includes considering your:
- Age
How To Reduce The Pain Of Blood Sugar Checks
Nobody gets excited about pricking their fingertip. In fact, studies have shown that it’s one of the main reasons people refrain from regularly checking their blood glucose.6,7 So how can you make this less of a hurdle in your self-care?
Select a less-painful lancing device
Naturally, one factor that can contribute to the pain is your lancing device. That’s why we’ve worked hard to ensure that Accu-Chek lancing devices keep discomfort to a minimum. For example, our lancing devices feature:
- Technology that minimizes side-to-side motion, so there’s less skin tearing
- 11 customizable depth settings to help match your skin type
- Precisely manufactured, beveled, thin-gauge lancets to ensure smoother entry
You can reduce pain by using a fresh lancet for every test. Today’s lancets are so tiny that just a single use can bend or dull the tips. This can make them hurt more as you reuse them.
5 tips for reducing fingertip pain
You can make testing more comfortable and help ensure that you get a good sample on the first try by following these 5 easy steps.
You May Like: What Causes High Blood Sugar Without Eating
Testing Your Blood Glucose
Testing your blood glucose
Testing your blood glucose, also known as Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose , is a method of checking how much glucose is in the blood using a glucose meter anywhere, anytime. Your doctor can also test your glucose from a blood sample that is checked in the lab.
Blood glucose targets for non-pregnant adults*
|
After meal |
Less than 180 mg/dL |
|---|
Your doctor uses what is called an A1C test to see what your average blood glucose level has been over the recent 3 months. Used for all types of diabetes, this test gives you and your doctor an indication on how well you are responding to your treatment plan. The recommended goal is to keep the level below seven percent . Your doctor will talk to you about the goal that is right for you. The A1C test is sometimes referred to as the hemoglobin A1c, HbA1c or glycohemoglobin test.
The importance of self-testing
Your A1C test result will not show the daily effects of food choices and activity on your blood glucose levels. A blood glucose meter is a good way to test and track the immediate effects of food, activity and other changes in your blood glucose levels. This allows you to take immediate action to bring your glucose levels within range as recommended by your doctor. Your doctor may also rely on your blood glucose meter results, in addition to your A1C test result, to assess and adjust your treatment plan.
The connection between A1C and average blood sugar levels.
Recording your blood glucose results
If You Start Stop Or Change Any Medications
Different medications can have an effect on your blood sugar, for example, steroids and anti-psychotic medications increase your blood sugar levels according to the American Diabetes Association. Several medications, such as beta-blockers, bactrim, MAO inhibitors, and metformin can cause low blood sugar according to MedLinePlus. Whenever you start, stop or change medication, it is a good idea to frequently test your blood sugar until you understand how the medication affects your glucose levels.
Also Check: How To Not Be Addicted To Sugar
What Causes Low Blood Sugar
Low blood sugar has many causes, including missing a meal, taking too much insulin, taking other diabetes medicines, exercising more than normal, and drinking alcohol. Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL is considered low.
Signs of low blood sugar are different for everyone. Common symptoms include:
- Shaking.
- Dizziness.
- Hunger.
Know what your individual symptoms are so you can catch low blood sugar early and treat it. If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms. Low blood sugar can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible.
How To Test Your Blood Sugar Levels
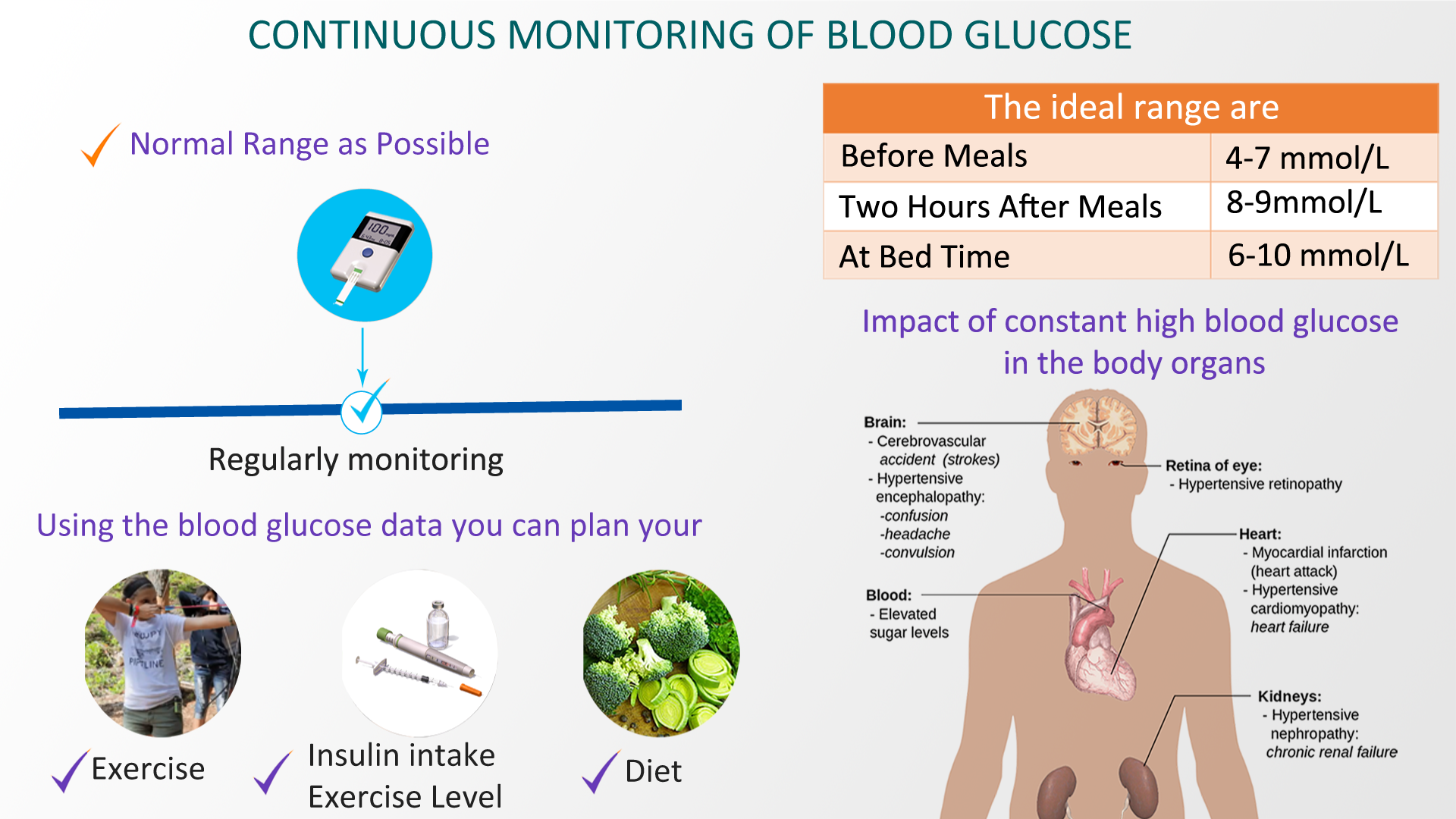
After you wake up in the morning, check your fasting blood sugar levels using a blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor . Before you use a blood glucose meter, the ADA recommends washing your hands and using the lancing device to get a drop of blood. After you hold the test strip against the drop of blood, your blood sugar levels should appear on the meter.
Read Also: What Should Your Blood Sugar Be After Exercising
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis
If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms.
When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up in your body and cause diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA. DKA is very serious and can cause a coma or even death. Common symptoms of DKA include:
- Fast, deep breathing.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Stomach pain.
If you think you may have DKA, test your urine for ketones. Follow the test kit directions, checking the color of the test strip against the color chart in the kit to see your ketone level. If your ketones are high, . DKA requires treatment in a hospital.
DKA happens most in people with type 1 diabetes and is sometimes the first sign of type 1 in people who havent yet been diagnosed. People with type 2 diabetes can also develop DKA, but its less common.
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
A fasting plasma glucose test is taken after at least eight hours of fasting and is therefore usually taken in the morning.
The NICE guidelines regard a fasting plasma glucose result of 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l as putting someone at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, particularly when accompanied by other risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
You May Like: Can High Blood Sugar Cause Anxiety
Check Your Blood Sugar If:
- You have symptoms of low blood sugar . This includes dizziness, shaking, sweating, chills, and confusion.
- You have symptoms of high blood sugar , which include sleepiness, blurry vision, frequent urination, and excessive thirst.
- You have a job in which poor blood sugar control could cause safety problems.
- You need help deciding if its safe to drive or perform other tasks that require concentration if you are taking insulin or have had hypoglycemia in the past.
You need to learn how meals, physical activity, and medicine affect your blood sugar level.
How To Use A Blood Glucose Meter:
- After washing your hands, insert a test strip into your meter.
- Use your lancing device on the side of your fingertip to get a drop of blood.
- Touch and hold the edge of the test strip to the drop of blood and wait for the result.
- Your blood glucose level will appear on the meter’s display.
Note: All meters are slightly different, so always refer to your user’s manual for specific instructions.
You May Like: What Can You Eat For Low Blood Sugar
What Is Low Blood Sugar
Hypoglycaemia is a condition wherein blood sugar levels are too low. This condition affects a number of diabetic people when their bodies do not have enough glucose to use as energy. Hypoglycaemia is commonly the result of taking too much of the medication/s prescribed to treat diabetes, eating less than expected, exercising more than normal or skipping meals.
Some of the symptoms of hypoglycaemia include:
- A pale face
What Are Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating
Dr. Danielle Weiss is the founder of Center for Hormonal Health and Well-Being, a personalized, proactive, patient-centered medical practice with a unique focus on integrative endocrinology. She enjoys giving lectures and writing articles for both the lay public and medical audiences. Dr. Weiss is Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine at the University of California, San Diego.
Your blood sugar level is influenced by several factors, including the food you eat. During digestion, carbohydrates are converted into sugar which your body uses as an energy source. Excess sugar from any source is stored in your cells for later use. When your cells contain too much sugar, though, it can lead to type 2 diabetes. This is why eating a balanced diet to maintain a normal blood sugar range is important.
Blood sugar levels can vary based on many factors, including age and life expectancy, comorbidities like heart disease, stress, and lifestyle factors like physical activity, smoking, or drinking alcohol.
Read Also: What Helps Raise Blood Sugar
What Other Tests Can Help Me Keep Track
Using a glucose meter can help you check your blood sugar levels, but other tests can help you know how well you’re controlling your diabetes too.
The glycosylated hemoglobin test will tell you how you’ve been controlling your blood sugar levels over the past few months. It’s usually done during regular visits with your diabetes health care team.
Hemoglobin is the substance inside red blood cells that carries oxygen to the cells of the body. The higher the glucose level in the blood, the more the glucose sticks to the hemoglobin. And once hemoglobin picks up glucose, the glucose stays on it for the life of the red blood cell, which is about 2 to 3 months.
The most commonly measured type of hemoglobin in the blood that has glucose attached to it is called HbA1c. In general, the lower your HbA1c, the better you’ve been controlling your blood sugar levels over the last 2 to 3 months. Having lower HbA1c levels may make it less likely that you’ll develop long-term diabetes problems.
Ketones are something else you’ll need to check for sometimes. Ketones are chemicals that show up in the urine and blood after the body breaks down fat for energy. The body will break down fat when it can’t use glucose. This can happen when you haven’t taken enough insulin to help the glucose get into the cells, or when you haven’t eaten enough to provide glucose for energy .
Target Blood Sugar Levels For Pregnant Women With Diabetes

It’s possible for diabetes to cause problems during pregnancy. For example, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, women with type 1 and type 2 diabetes who have uncontrolled blood sugar levels could experience an increased risk of having a premature baby, needing a C-section and more.
Gestational diabetes a type of diabetes that occurs in a pregnant woman who has never been diagnosed with diabetes before can also cause complications. These include giving birth to a baby who is larger than average and an increased risk of needing a C-section. The ADA suggests that pregnant women shoot for a target fasting blood sugar level of 95 mg/dL or less before a meal.
Read more:Do Oranges Raise Your Blood Sugar?
Recommended Reading: What Helps High Blood Sugar