How Are High Blood Sugar Levels Treated
To treat high blood sugar, it helps to know what is causing it. You might need to take more insulin or diabetes pills because you’re growing and eating more food, or you might need to get more exercise each day.
Having high blood sugar levels every once in a while isn’t a big deal. It happens to everyone with diabetes from time to time. But if your blood sugar levels are high a lot, your diabetes health care team will have to help you figure out how to get them back to a healthy level.
Blood Sugar Levels After Eating
Blood sugar fluctuates throughout the day, but the biggest changes happen around mealtimes. Before eating, a healthy sugar level is between 3.9-5.5mmol/L. Around 1-2 hours after eating, expect blood sugar to rise to 5-10mmol/L.
If your blood sugar doesn’t stick within these ranges, the body may have stopped regulating blood sugar effectively which can lead to prediabetes and diabetes.
How Blood Sugar Levels Without Diabetes Work
In a healthy, non-diabetic individual, blood sugar levels spike after meals as the glucose is released by the consumed food. This glucose is battery juice or fuel but it needs to be fed to the engines of the body, namely the muscles and the brain. Your brain and your muscles use the broken-down glucose to fuel all the physical and mental activity that you perform during the day.
If you feel tired after preparing an especially tedious presentation, after an especially challenging meeting, or hours of poring over spreadsheets it is because of the huge amount of glucose that your brain uses to perform these activities.
Some of the glucose is also stored in your liver. If you need energy for an evening workout later, or to run up a flight of stairs, your liver will release the stored glucose to fuel such physical activity. Thats how you are able to sustain between meals.
After the glucose has been broken down and used, with the remainder stored for future requirements, your glucose levels power back down. As expenditure of glucose continues and your reserves run low, your blood glucose levels will drop again and you will start to feel hungry once again.
In other words, blood sugar levels without diabetes do spike, but they also normalize naturally without a need for any external intervention.
Recommended Reading: What Is Elevated Blood Sugar
What Should You Do If You Are Prediabetic
If youve been to see your doctor, and a blood test confirms you are prediabetic, there are many simple steps you can take to reverse the condition and prevent it from developing into diabetes.
Your healthcare providers will suggest help and guidance, like the best lifestyle changes considering your medical history and circumstances. Steps they may recommend include cutting out processed sugar, consuming more vegetables and whole grains, and taking a walk every morning.
A valuable resource for many prediabetic patients in the United States is the National Diabetes Prevention Program . Through private and public partnerships, it aims to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes by making it easier for Americans to make the lifestyle changes they need.
In some cases, they may even recommend medication. Whatever your doctor suggests, remember prediabetes can be reversed and its great you caught it early.
Low Blood Sugar: What To Watch Out For
Hypoglycemia can occur in people with diabetes who:
- Take too much medication or insulin
- Are late eating a meal or snack
- Have increased physical activity
- Drink too much alcohol
Symptoms of low blood sugar include feeling weak, sweaty or clammy, confused, hungry and/or irritable. Sometimes people experience a fast heartbeat and some symptoms may make a person appear to be drunk. A severely low blood sugar can result in unconsciousness, seizures, coma or death especially when a low occurs during the night.
Low blood sugar affects many parts of the body, but the most frustrating part can be that hypoglycemia can happen anytime and anywhere even when you think you are closely following the plan for your diabetes care. If low blood sugar is severe, people may need to go to the hospital to help raise their glucose level or miss work due to the side effects.
It can happen during a date, during a business meeting, or even while driving, which is the most dangerous scenario if there is confusion or loss of consciousness while behind the wheel. Its important to use your blood glucose meter to check your blood sugar before you drive to keep yourself and others safe. Frequent testing with your blood sugar meter and taking action when blood sugar is trending low can prevent a severe low and keep your life on track.
Don’t Miss: What Should Morning Blood Sugar Be For Type 2 Diabetes
How Much Does The Freestyle Libre Cost
You do need a prescription in order to purchase the Freestyle Libre 14 day systemand the sensors can often be pricey. The out-of-pocket price is around $129.99, but you can save with a SingleCare savings card. It can be used regardless of your insurance statuseven when youre on Medicare.
You can search for your Libre Freestyle diabetes monitor on our site before you go to the pharmacy. To find the best price, we always recommend that you compare our price with the cash price and/or your copay.
You can either choose to text, email, or print the coupon to yourself from the SingleCare website or request a physical card to be sent home to you, so you can easily pick up your Freestyle Libre sensors at one of our partner pharmacies, which include: CVS, Walmart, Kroger, Walgreens, Target, Longs Drugs, Frys, Kroger, Rite Aid, and Duane Reade. To check on savings, you simply have to type in your zip code to get the pharmacies near you and adjust for quantity .
If you forget or dont have time to look up before, you could also ask your pharmacist to ring up all options at the counter.
Join the millions savings billions on thousands of drugs with SingleCare. You will always get the most up to date prices on our site. Happy savings!
Are Low Blood Sugar Levels Dangerous
Yes, low blood sugar symptoms can cause problems such as hunger, nervousness, perspiration, dizziness and even confusion if untreated, low blood sugar may result in unconsciousness, seizures, coma, or death. Low blood sugar levels begin at 70 mg/dL or less. People with diabetes who take too much medication or take their usual amount but then eat less or exercise more than usual can develop hypoglycemia. Although much rarer, hypoglycemia may develop in some people without diabetes when they take someone elses medication, have excessive alcohol consumption, develop severe hepatitis, or develop a rare tumor of the pancreas . The treatment for hypoglycemia is oral glucose intake (15. 0 grams of sugar, for example, 1 tablespoon of sugar, honey, corn syrup, or IV fluids containing glucose. Recheck your blood sugar levels in about 15 minutes after treatment is advised.
Recommended Reading: What Happens When Blood Sugar Is Too Low
Controlling Blood Glucose Levels
Uncontrolled blood sugar can result in regular episodes of hyperglycemia . This can cause a variety of symptoms including:
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Fatigue
These symptoms are uncomfortable to experience but there are things you can do at home to reduce your blood sugar. In terms of drinks, water is the best as it will help to maintain hydration and dilute excess sugar in the blood. Also, try to add more fiber to your diet to reduce your blood sugar apples, bananas, oranges, and strawberries are all fibrous fruits.
However, uncontrolled blood sugar levels can also lead to more severe, long term disease. Poorly managed diabetes leads to vision loss, kidney problems, nerve damage, heart attack, and stroke. Therefore, if your blood sugar level reaches 16.7mmol/L, this could be dangerous and you need to seek immediate medical attention.
A Few Final Notes On Keeping Blood Sugar Stable
Taking an active, intentional approach to your blood sugar levels is crucial to your quality of life and overall health, ONeill says. Avoiding too-high or too-low blood sugar levels will help you avoid adverse symptoms and health complications, and staying within your target range can enable you to feel your best and do whatever you want to do in life, she says.
Test your blood sugar regularly, listen to your body, and dont ever hesitate to reach out to your doctor.
Additional reporting by Karen Appold.
Also Check: How To Play Suga Suga On Guitar
Low Blood Sugar Chart And Action Plan
Low blood sugar is also called hypoglycemia. The numbers below represent values in the hypoglycemic range and require action to bring blood sugar levels up into a normal range.
| Alert Level and Treatment Plan | |
| 50 mg/dL or under | Red Flag: Blood sugar is critically low and requires immediate treatment.
If a person is unable to speak and/or is not alert, treat with glucagon via injection or nasal spray. Call emergency medical response if necessary. Do not place food or drink into the mouth. If a person is alert and able to speak clearly, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate such as glucose gel, 4 oz regular soda, or fruit juice. Re-test blood sugar in 15 minutes and repeat as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 51-70 mg/dL | Red Flag: Blood sugar is below normal levels and requires immediate treatment.
Treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment as needed to bring blood sugar within range. |
| 71-90 mg/dL | Yellow Flag: Blood sugar levels should be watched and treated as needed.
If youre having symptoms of low blood sugar, treat with 15 grams of rapid-acting carbohydrate and re-test in 15 minutes. Repeat treatment or follow with a meal. If it is meal time, move forward with eating the meal. People often fall into this range when they are late for a meal or have been especially active. |
How To Measure Blood Sugar Levels
There are two main ways to check your blood sugar levels:
Type 1 diabetics, along with some type 2 diabetics, who require insulin medication, must check their blood sugar at least four times per day, says Mathioudakis. Typically, this should be done before a meal, one to two hours after a meal, and at bedtime.
The timing of these measurements can help determine how much insulin to use. For example, it can be important to use more insulin after a high-sugar meal, or to avoid falling into hypoglycemia while you’re sleeping.
To check your blood sugar at home, you should use blood glucose tests, such as a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor . Both devices measure blood sugar with the unit mg/dL, which means a milligram of sugar per deciliter of blood.
If you don’t have diabetes, but you may be at risk, your doctor might have you take an A1C test during a yearly check-up. This test reports results as a percentage the higher the percentage, the higher your blood sugar has been in the past three months. Those with diabetes should get an A1C test at least twice a year and sometimes every three months.
Also Check: What Is The Best Blood Sugar Test Kit
Normal Blood Glucose Levels In Healthy Individuals
Blood glucose levels, also known as blood sugar levels, can be normal, high, or low. The blood sugar levels are generally measured after 8 hours of eating.
A normal blood sugar range for a healthy adult after 8 hours of fasting is > 70 mg/dL. and < 100 mg/dL.
While a normal blood sugar level in a healthy person after 2 hours of eating is between 90 to 100 mg/dL.
Blood glucose levels change throughout the day. The major factors for such change in the blood glucose levels are as follows:
|
90 to 150 mg/dL |
Normal Blood Sugar Ranges In Healthy Non

For a person without any type of diabetes, blood sugar levels are generally between 70 to 130 mg/dL depending on the time of day and the last time they ate a meal. Newer theories about non-diabetic blood sugar levels have included post-meal blood sugar levels as high as 140 mg/dL.
Here are the normal blood sugar ranges for a person without diabetes according to the American Diabetes Association:
- Fasting blood sugar : under 100 mg/dL
- 1 hour after a meal: 90 to 130 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 90 to 110 mg/dL
- 5 or more hours after eating: 70 to 90 mg/dL
Read Also: What To Eat When You Crave Sugar
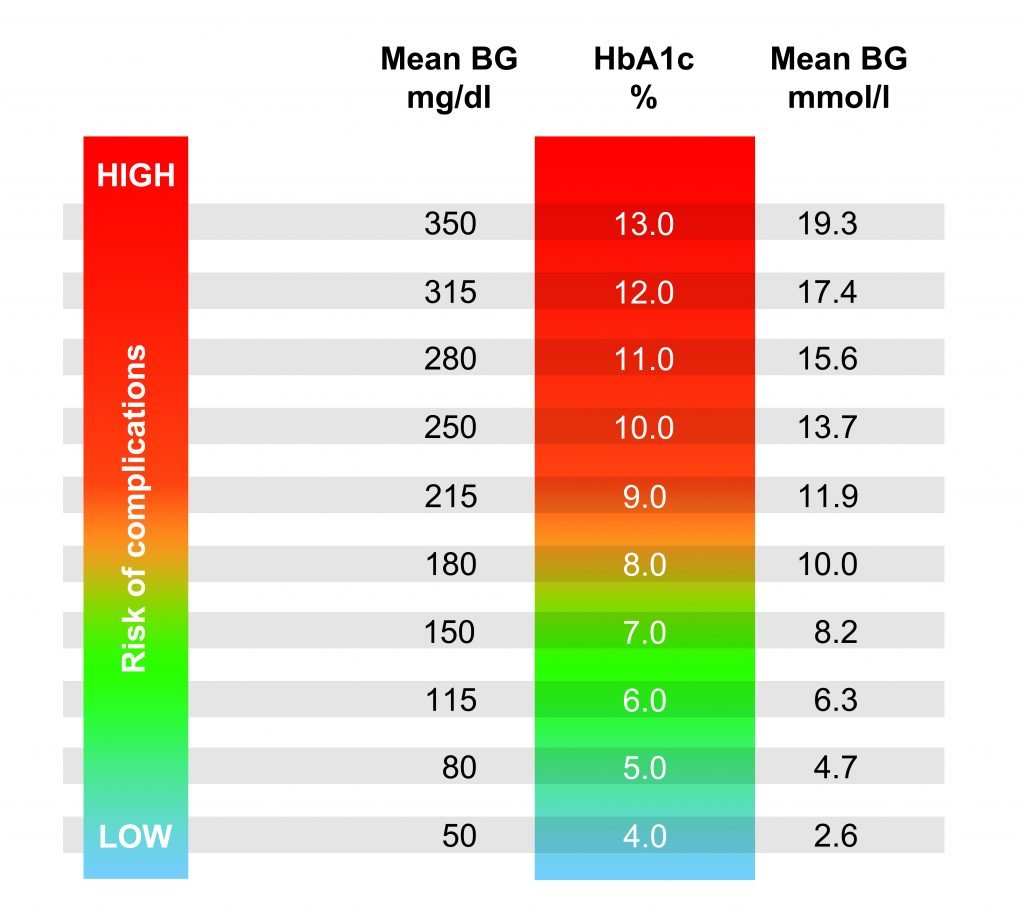
Translating Your A1c To A Blood Sugar Level
Using this easy calculator from the ADA, you can translate your most recent A1C result to an eAG or estimate average glucose level.
You can also use this translation when working to improve your A1c and achieving closer to normal blood sugar levels. If you know an A1c of 6.5 is an average blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or a range of 100 to 152 mg/dL, then you can look at your current blood sugar results on your CGM and meter and pinpoint which time of day youre frequently higher than this range.12% = 298 mg/dL or range of 240 347 11% = 269 mg/dL or range of 217 31410% = 240 mg/dL or range of 193 2829% = 212 mg/dL or range of 170 2498% = 183 mg/dL or range of 147 2177% = 154 mg/dL or range of 123 1856% = 126 mg/dL or range of 100 1525% = 97 mg/dL or range of 76 120
Normal blood sugar levels in a person without diabetes can result in an A1c as low as 4.6 or 4.7 percent and as high as 5.6 percent.
Just a decade or two ago, it was rare for a person with type 1 diabetes to achieve an A1c result below 6 percent. Thanks to new and improved insulin and better technology like continuous glucose monitors and smarter insulin pumps, more people with diabetes are able to safely achieve A1c levels in the higher 5 percent range.
Diagnosing Prediabetes Type 2 And Type 1 Diabetes
Depending on which country or medical organization you ask, the qualifying numbers for normal versus prediabetes versus diagnosed type 1 or type 2 diabetes can vary slightly. The following blood sugar and A1c the general results are used to diagnosed prediabetes and diabetes according to sources including the American Diabetes Association and Diabetes UK:
Prediabetes
- HbA1c: 5.7 to 6.4 percent
- Fasting: 100 to 125 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL
Type 1 or 2 diabetes
- HbA1c: 6.5 percent or higher
- Fasting: 126 mg/dL or higher
- 2 hours after a meal: 200 mg/dL or higher
Please note: Type 1 diabetes tends to develop very quickly which means that by the time symptoms are felt, blood sugar levels are generally well above 200 mg/dL all the time. For many, symptoms come on so quickly they are dismissed as the lingering flu or another seemingly ordinary virus.
By the time blood sugar levels are tested, many newly diagnosed type 1 patients will see levels above 400 mg/dL or higher. If you do suspect that you or a loved-one has type 1 diabetes, visit your primary care or urgent care immediately and ask for a urine test to measure ketones in addition to testing blood sugar levels and A1c.
Read more about ketones at diagnosis in Diabetes StrongsDiabetic Ketoacidosis Guide.
Don’t Miss: How Much Sugar In White Claw
Hyperinsulinemia: Is It Diabetes
Is hyperinsulinemia a form of diabetes? Answers from M. Regina Castro, M.D. Hyperinsulinemia means the amount of insulin in your blood is higher than what’s considered normal. Alone, it isn’t diabetes. But hyperinsulinemia is often associated with type 2 diabetes. Insulin is a hormone that’s normally produced by your pancreas, which helps regulate blood sugar. Hyperinsulinemia is a sign of an underlying problem. Hyperinsulinemia is most often caused by insulin resistance a condition in which your body doesn’t respond well to the effects of insulin. Your pancreas tries to compensate by making more insulin. Insulin resistance may eventually lead to the development of type 2 diabetes. This happens when your pancreas is no longer able to compensate by secreting the large amounts of insulin required to keep the blood sugar normal. Rarely, hyperinsulinemia is caused by: A rare tumor of the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas Excessive numbers or growth of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas Hyperinsulinemia usually causes no signs or symptoms, except in people with insulinomas in whom hyperinsulemia can cause low blood sugar . Treatment of hyperinsulinemia is directed at the underlying problem.Continue reading > >
When Is Blood Sugar Considered To Be Too High Or Too Low
Slight fluctuations in blood sugar levels are completely normal, and also happen every day in people who dont have diabetes, in response to the food they eat. Between around 60 and 140 milligrams of sugar per deciliter of blood is considered to be healthy. This is equivalent to a blood sugar concentration of between 3.3 and 7.8 mmol/l. Millimoles per liter is the unit that blood sugar is measured in. It describes the amount of a certain substance per liter.
If someone has readings over 7.8 mmol/l , they are considered to have hyperglycemia. These high blood sugar levels mainly occur if there isn’t enough insulin or the insulin doesn’t work properly. Without the effect of insulin, the organs can’t make good use of the sugar in the blood, so the sugar builds up. If type 1 diabetes is left untreated, blood sugar levels can increase to over 27.8 mmol/l . Such high levels tend to be uncommon in type 2 diabetes.
Blood sugar levels below 3.3 mmol/l are considered to be too low. But, as you can see in the illustration below, there are no clear-cut borders between normal blood sugar levels and too high or too low blood sugar levels.
Blood sugar: Normal range between hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia
Recommended Reading: Is Pure Cane Sugar Good For You