How Are High Blood Sugar Levels Treated
To treat high blood sugar, it helps to know what is causing it. You might need to take more insulin or diabetes pills because youre growing and eating more food, or you might need to get more exercise each day.
Having high blood sugar levels every once in a while isnt a big deal. It happens to everyone with diabetes from time to time. But if your blood sugar levels are high a lot, your diabetes health care team will have to help you figure out how to get them back to a healthy level.
How To Check Your Blood Sugar Levels
As Dr. Emanuele says, glucose monitoring can be an important tool to help you get your blood sugar under control. Typically, you would do it yourself using a glucose meter or glucometer, which analyzes a drop of blood that you draw by sticking your finger with a lancet and placing the blood on a disposable test strip that you insert into the meter. Your blood sugar goals are set by you and your doctor, but blood glucose for an adult without diabetes is below 100 mg/dl before meals and at fasting and less than 140 mg/dl two hours after a meal, notes the ADA.
Some people will check their blood sugar daily or multiple times a day, sometimes using a continuous monitor that is worn on the body particularly those who have type 1 diabetes or who have type 2 but take insulin. Yet how frequently a person should monitor their blood sugar is based on a number of factors, including but not limited to whether theyre on insulin, whether they’re taking oral medication, and how well their blood sugar is controlled and how old they are.
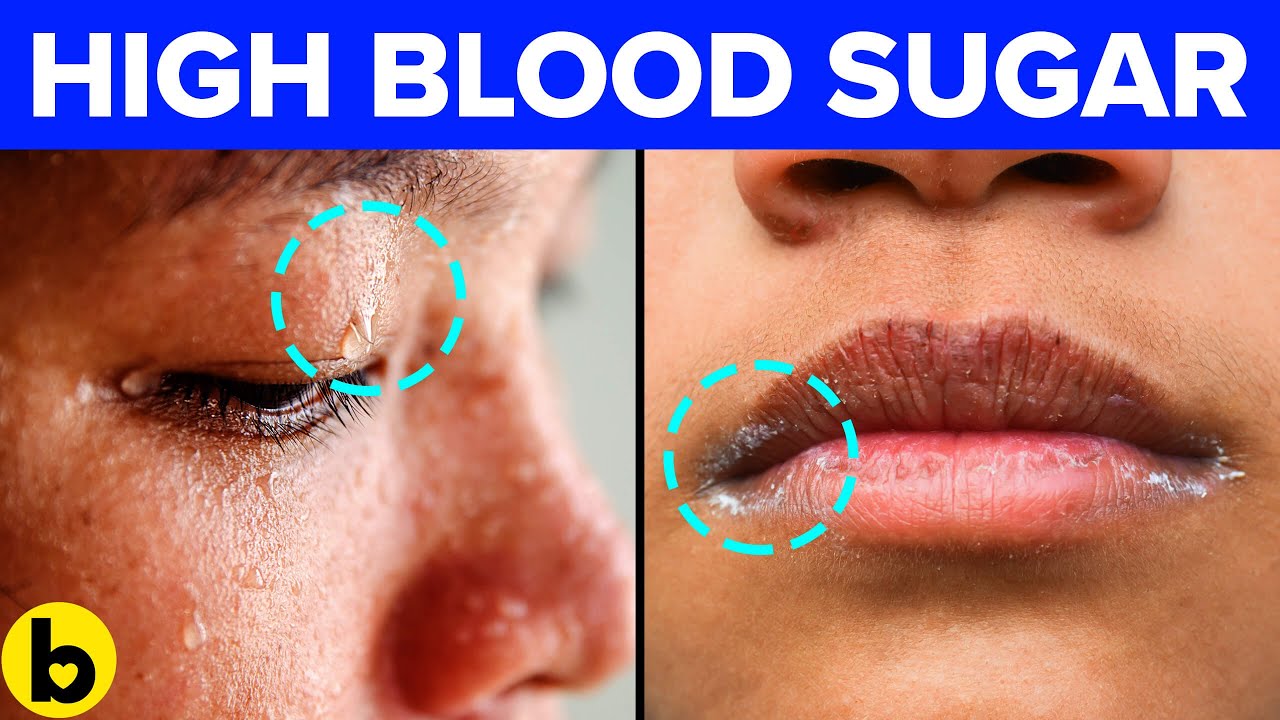
Meanwhile, keep an eye out for these nine key warning signs and symptoms that blood sugar is too high and talk to your doctor about whether you need to adjust your management plan.
For People With Type 1 Diabetes
Contact your doctor or go to hospital if:
- Vomiting stops you from drinking and makes eating difficult
- Blood glucose levels remain high
- Moderate to large ketones are present in the urine.
In type 1 diabetes, high blood glucose levels can progress to a serious condition called Ketoacidosis.
Also Check: How Much Sugar Does Vanilla Ice Cream Have
When To Seek Medical Care
I would say that anybody with type 1 diabetes, first of all, they should always carry ketone sticks with them, says Dr. Hong. So, if blood sugars were to run high or they were to feel sickly, they should test their urine for ketones and if that is positive, they should seek care from a doctor or an emergency room. She says anyone should seek care if they feel very sick, have nausea, vomiting, severe abdominal pain, confusion, or trouble thinking clearly. And then, if they are checking blood glucoses and they notice that their sugars are running significantly higher than what they’re used to and it’s not responding to any of their usual care such as drinking water or taking their insulin, they should absolutely seek care and speak to the doctor as well, Dr. Hong adds.
What If It Goes Untreated

Hyperglycemia can be a serious problem if you don’t treat it, so it’s important to treat as soon as you detect it. If you fail to treat hyperglycemia, a condition called ketoacidosis could occur. Ketoacidosis develops when your body doesn’t have enough insulin. Without insulin, your body can’t use glucose for fuel, so your body breaks down fats to use for energy.
When your body breaks down fats, waste products called ketones are produced. Your body cannot tolerate large amounts of ketones and will try to get rid of them through the urine. Unfortunately, the body cannot release all the ketones and they build up in your blood, which can lead to ketoacidosis.
Ketoacidosis is life-threatening and needs immediate treatment. Symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath
Talk to your doctor about how to handle this condition.
Don’t Miss: Can Sugar Cause Afib
Problems Associated With High Blood Sugar
Frequent high blood pressure puts patients at risk of diabetes complications that can be potentially serious. Even when blood sugar does not reach acutely dangerous levels, complications can develop over time if blood sugar is consistently above a patients target range. Serious conditions and complications associated with high blood glucose include:
- Damage to the blood vessels of the eyes
- Nerve damage in the feet and hands
- Increased risk of kidney disease
- Increased risk of heart problems like heart disease
Depending on the type of diabetes a patient has, there are two different extreme forms of hyperglycemia as well. Ketoacidosis is severe hyperglycemia that impacts people with type 1 diabetes. Ketoacidosis occurs when the body runs out of glucose and begins to use ketones, a type of toxic acid, for energy. Ketoacidosis can lead to diabetic coma or even death, and it is extremely serious. Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome is a severe form of hyperglycemia that impacts people with Type 2 diabetes. It occurs when the blood glucose level goes too high and the body tries to rid itself of the excess glucose through frequent urination. If the body becomes dehydrated enough, it can go into a coma.
How Is High Blood Sugar Diagnosed
There are different kinds of blood tests that can diagnose hyperglycemia. These include:
Random blood glucose: this test reflects the blood sugar level at a given point in time. Normal values are generally between 70 and 125 mg/dL, as discussed earlier.
Fasting blood glucose: this is a measurement of blood sugar level taken in the early morning prior to eating or drinking anything since the night before. Normal fasting blood glucose levels are less than 100 mg/dL. Levels above 100 mg/dL up to 125 mg/dL suggest prediabetes, while levels of 126 mg/dL or above are diagnostic of diabetes.
Oral glucose tolerance test: this is a test that measures blood glucose levels at given time points after a dose of sugar is consumed. This test is most commonly used to diagnose gestational diabetes.
Glycohemoglobin A1c: is a measurement of glucose that is bound to red blood cells and provides an indication about blood sugar levels over the past 2 to 3 months.
Don’t Miss: Can Too Much Sugar Cause Seizures
Is Hyperglycaemia Serious
The aim of diabetes treatment is to keep blood sugar levels as near to normal as possible.
But if you have diabetes, no matter how careful you are, you’re likely to experience hyperglycaemia at some point.
It’s important to be able to recognise and treat hyperglycaemia, as it can lead to serious health problems if left untreated.
Occasional mild episodes are not usually a cause for concern and can be treated quite easily or may return to normal on their own.
But hyperglycaemia can be potentially dangerous if blood sugar levels become very high or stay high for long periods.
Very high blood sugar levels can cause life-threatening complications, such as:
- diabetic ketoacidosis a condition caused by the body needing to break down fat as a source of energy, which can lead to a diabetic coma this tends to affect people with type 1 diabetes
- hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state severe dehydration caused by the body trying to get rid of excess sugar this tends to affect people with type 2 diabetes
Regularly having high blood sugar levels for long periods of time can result in permanent damage to parts of the body such as the eyes, nerves, kidneys and blood vessels.
If you experience hyperglycaemia regularly, speak to your doctor or diabetes care team.
You may need to change your treatment or lifestyle to keep your blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
How Are Ketones Tested
Testing your blood or urine to measure your ketone levels can all be done at home. At-home testing kits are available for both types of tests, although urine testing continues to be more common. Urine tests are available without a prescription at most drugstores, or you can buy them online.
You should test your urine or blood for ketones when any of the following occurs:
- Your blood sugar is higher than 240 mg/dL.
- You have symptoms of DKA.
- You feel sick or nauseated, regardless of your blood sugar reading.
To perform a urine test, you urinate into a clean container and dip the test strip into the urine. For a child who isnt potty-trained, a parent can usually press the stick to their childs wet diaper to test for ketones.
Urine testing strips contain special chemicals that change colors when they react with ketones. You can interpret the test results by comparing the test strip to the color chart on the package. When you have ketones present in your urine, its called ketonuria.
An at-home meter is available to test for blood ketones. This is performed in a similar way to a finger-stick glucose test. You prick your finger with a needle and place a small drop of blood onto the testing area.
Doctors often recommend that people whove just received a diabetes diagnosis test their ketones twice daily.
While individual testing may vary, in general, results for ketone testing are labeled in the following way:
| normal/negative |
Read Also: What Is A Normal A1c For A Non Diabetic
You May Like: Can Sugar Trigger Afib
Low Blood Sugar Symptoms
Hypoglycemia happens when blood glucose levels drop too low. Low blood sugar can be caused by many things including the two different types of diabetes, certain medications, alcohol, endocrine disorders, eating disorders, pregnancy , and disorders of the liver, kidneys, or heart.
Here are some of the most common symptoms that someone with low blood sugar might experience:
- Lightheadedness
- Fainting
- Tingling lips
If your blood sugar is low you might start to feel some of the first signs of hypoglycemia like dizziness, lightheadedness, or sweating. The only way to know for sure if your blood sugar is low is to test it with a glucose meter or other glucose monitoring device.
If you dont have access to these tools and start to feel the symptoms of low blood sugar, consume 15 grams of carbs or take a quick dissolve glucose tablet to raise your blood sugar levels and avoid further symptoms, according to the American Diabetes Association . Once your blood sugar is back in its target range, you can have a snack or meal to make sure it doesnt drop again.
Here are some other lifestyle and medicinal treatments that can help treat hypoglycemia:
- Eat a healthy diet full of whole foods that are minimally processed.
- Take prediabetes or diabetes medications as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Use a glucagon kit in emergencies. Glucagon is a hormone that raises blood sugar levels quickly.
Why Is High Blood Sugar So Dangerous
We know that hyperglycemia can cause cardiovascular problems and many others, but have you ever wondered why? Studies point to inflammation and other mechanisms of action mentioned above, but we also need to address glycation.
Glycation is defined as a natural process wherein the sugar in a persons bloodstream attaches to proteins and forms harmful new molecules named advanced glycation end products.
Higher glycation occurs with elevated blood sugar concentration, which can explain why hyperglycemia can cause problems such as heart attack and stroke. At the same time, glycated particles such as LDL or bad type of cholesterol are more susceptible to oxidation. As a result, oxidized LDL induces the atherosclerosis process.
What makes excess glycation so harmful? Well, glycated particles arent able to perform their functions adequately anymore. This also leads to apoptosis or cell death eventually.
In other words, high blood sugar leads to an increase in the process of glycation and leads to the production of potentially harmful particles. These particles affect blood flow and impair LDL functionality, HDL, and other proteins and lipids in our bodies. This causes a chain of reactions that lead to cardiovascular diseases, heart attack, stroke, but also induces nerve damage and slows down wound healing.
Glycated plasma proteins also trigger pro-inflammatory responses and prosclerotic cytokines, which lead to the development and progression of diabetic complications.
You May Like: Which Cells Produce Hormones To Regulate Blood Sugar
Controlled Means Different Things To Different People
Theres no one-size-fits-all recommendation for blood sugar control.
The ADA says that a reasonable goal for many nonpregnant adults is to aim for an A1C level of less than 7. Yet some patients may be given a more stringent goal by their healthcare providers, such as 6.5, if thats reachable without harmful side effects, including hypoglycemia.
On the other hand, if you are elderly, managing other health complications, or reliant on insulin, you may be given less stringent goals. It really becomes more important to just keep in the same place, says Rahil Bandukwala, DO, an endocrinologist at MemorialCare Saddleback Medical Center in Laguna Hills, California. Keeping A1C between 7.5 and 8.5 may be very reasonable for such a patient, Dr. Bandukwala adds, echoing the ADAs recommendations.
Because elderly people are more likely to have blood sugar that swings too far downward, with fewer warning signs, managing their glucose too tightly can put them at greater risk for hypoglycemia, says Bandukwala. When you have low blood sugar, youre at a higher risk for becoming dizzy and falling or passing out, notes the ADA.
RELATED: 10 Warning Signs of Low Blood Sugar
What Causes Hyperglycemia
A number of things can cause hyperglycemia:
- If you have type 1, you may not have given yourself enough insulin.
- If you have type 2, your body may have enough insulin, but it is not as effective as it should be.
- You ate more than planned or exercised less than planned.
- You have stress from an illness, such as a cold or flu.
- You have other stress, such as family conflicts or school or dating problems.
- You may have experienced the dawn phenomenon .
Recommended Reading: How To Get Off Sugar And Carbs
What Is High Blood Sugar
Elevated blood sugar levels are known as hyperglycemia. Blood sugar levels are measured using a small sample of blood that is tested in a lab. Blood sugar can also be tested using at home devices such as a handheld glucometer. Levels that indicate hyperglycemia are indicative of prediabetes and both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Normal ranges of blood sugar will vary depending on the test being done. In general, a normal fasting glucose level will be between 70-100 mg/dL. After a meal, these levels are expected to rise slightly around 1 to 2 hours after the beginning of a meal, but should be less than 180 ml/dL.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is important not only for metabolic health, but heart health too. Over time, high blood sugar can damage blood vessels and the nerves that control your heart. People with diabetes are also more likely to have other conditions that raise the risk for heart disease:
- High blood pressure increases the force of blood through your arteries and can damage artery walls. Having both high blood pressure and diabetes can greatly increase your risk for heart disease.
- Too much LDL cholesterol in your bloodstream can form plaque on damaged artery walls.
Stick To Your Medication And Insulin Regimen
Skipping a dose of medication or insulin can be harmful to your body and increase your blood sugar levels.
Its important to stick to your treatment plan and follow your doctors instructions for taking your medication.
Summary
Healthful lifestyle habits can help people manage their blood sugar levels over the long term, such as eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, staying hydrated, and getting good sleep.
Don’t Miss: Most Sugar Fruit
Are Low Blood Sugar Levels Dangerous
Yes, low blood sugar symptoms can cause problems such as hunger, nervousness, perspiration, dizziness and even confusion if untreated, low blood sugar may result in unconsciousness, seizures, coma, or death. Low blood sugar levels begin at 70 mg/dL or less. People with diabetes who take too much medication or take their usual amount but then eat less or exercise more than usual can develop hypoglycemia. Although much rarer, hypoglycemia may develop in some people without diabetes when they take someone elses medication, have excessive alcohol consumption, develop severe hepatitis, or develop a rare tumor of the pancreas . The treatment for hypoglycemia is oral glucose intake (15. 0 grams of sugar, for example, 1 tablespoon of sugar, honey, corn syrup, or IV fluids containing glucose. Recheck your blood sugar levels in about 15 minutes after treatment is advised.
How Does Hyperglycemia Happen
Insulin is a hormone that lets your body use the sugar in your blood, which comes primarily from carbohydrates in the food that you eat. Hyperglycemia happens when your body has too little insulin to use the sugar in your blood.
People with type 1 diabetes can have episodes of hyperglycemia every day. Although this can be frustrating, it rarely creates a medical emergency. Not taking enough insulin can lead to hyperglycemia .
Other things that can cause hyperglycemia include:
- Caffeine
- Having trouble seeing or concentrating
- Experiencing stomach pain, nausea, or vomiting
- Having sweet-smelling or fruity breath
- Cuts or sores that do not heal, infections, and unexplained weight loss may also be signs of long-term hyperglycemia.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should check your blood sugar. If your blood sugar is very high, you should also test for ketones in either your blood or urine.
You May Like: How To Drop Sugar Level