How Do Carbs Affect Blood Sugar
Carbs in food make your blood sugar levels go higher after you eat them than when you eat proteins or fats. You can still eat carbs if you have diabetes. The amount you can have and stay in your target blood sugar range depends on your age, weight, activity level, and other factors. Counting carbs in foods and drinks is an important tool for managing blood sugar levels. Make sure to talk to your health care team about the best carb goals for you.
Postprandial Blood Sugar Few Of Those With Diabetes Know Why It Is So Important
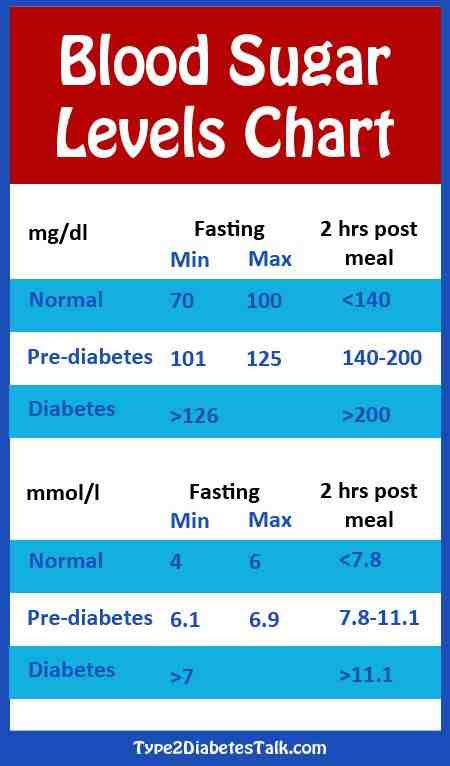
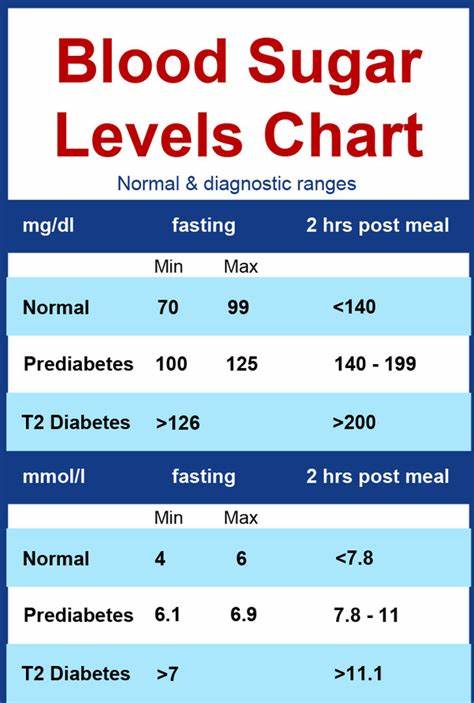
Blood sugar after a meal is referred to as postprandial blood sugar. So the opposite, namely before a meal, is called preprandial. The American Diabetes Association advises keeping your blood sugar levels before meals between 80130 mg/dl and your levels 12 hours after meals under 180.
Usually, blood sugar begins to rise 10-15 minutes after a meal and reaches its peak after an hour. However, it is important to note that these are just approximate guidelines as postprandial glucose depends on several factors, such as the type of food consumed.
Influence on HbA1c
Research has shown that postprandial blood sugar levels are significant for HbA1c. Even if glucose spikes after eating are only brief, they still have the potential to raise HbA1c over the course of the day. Most people with diabetes check their blood sugar before a meal but not afterwards or they leave it until the next mealtime. This can lead to glucose spikes being undetected and remaining high for a long period of time.
How to deal with high postprandial blood sugar levels
Be sure to check your levels at least 90 minutes after a meal. Why? By that time rapid acting analogue insulin has reached its maximum effect .
If its still too high then you should look into the causes such as:
-
what type of food did I eat?
-
did I correctly estimate my carbs?
-
is my insulin-to-carb ratio correct?
-
and is the injection-meal interval correct?
Featured Posts
Animation: Blood Sugar Regulation In Diabetics
View the animation below, then complete the quiz to test your knowledge of the concept. 1 After eating a meal, blood sugar levels 2 Insulin, released after a meal is eaten by a person who does not have diabetes, will cause blood sugar levels to A) increase far above normal. B) return to about normal. C) decrease far below normal. 3 In Type I diabetes blood sugar levels remain high after a meal because A) too much insulin is released. B) protein is converted to glucose. D) muscle and liver cells do not receive a signal. 5 The treatment for Type I diabetes always includes A) oral thiazolidinedione.Continue reading >>
Don’t Miss: How To Lower Sugar Levels Fast
If You Start Stop Or Change Any Medications
Different medications can have an effect on your blood sugar, for example, steroids and anti-psychotic medications increase your blood sugar levels according to the American Diabetes Association. Several medications, such as beta-blockers, bactrim, MAO inhibitors, and metformin can cause low blood sugar according to MedLinePlus. Whenever you start, stop or change medication, it is a good idea to frequently test your blood sugar until you understand how the medication affects your glucose levels.
Knowing Blood Sugar Levels
If you have diabetes, the frequency of testing your blood glucose level depends on your treatment plan, so follow your doctors advice on the appropriate times for you.
Common times to check are in the morning, before and after meals, before and after exercise, at bedtime, and if you feel sick. Some people may not need to check their blood sugar daily.
What you eat and what you do for physical activity affect your blood sugar. But theres no way to know what effect they have unless you test your blood sugar.
Blood glucose meters are used to test blood sugar levels so you can see if your levels are within the target range. Your doctor will also work with you on your individualized range.
Recommended Reading: Is 200 Blood Sugar High
What Are The Target Ranges
Blood glucose targets are individualized based on:
- duration of diabetes
- conditions a person may have
- cardiovascular disease or diabetes complications
- hypoglycemia unawareness
- individual patient considerations
The American Diabetes Association suggests the following targets for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes.;A1C targets;differ based on age and health. Also, more or less stringent glycemic goals may be appropriate for each individual.;
- A1C:;Less than 7%A1C may also be reported as eAG:;Less than 154;mg/dL
- Before a meal :;80130 mg/dL
- 1-2 hours after beginning of the meal *:;Less than 180 mg/dL
Before And After Meals And Snacks
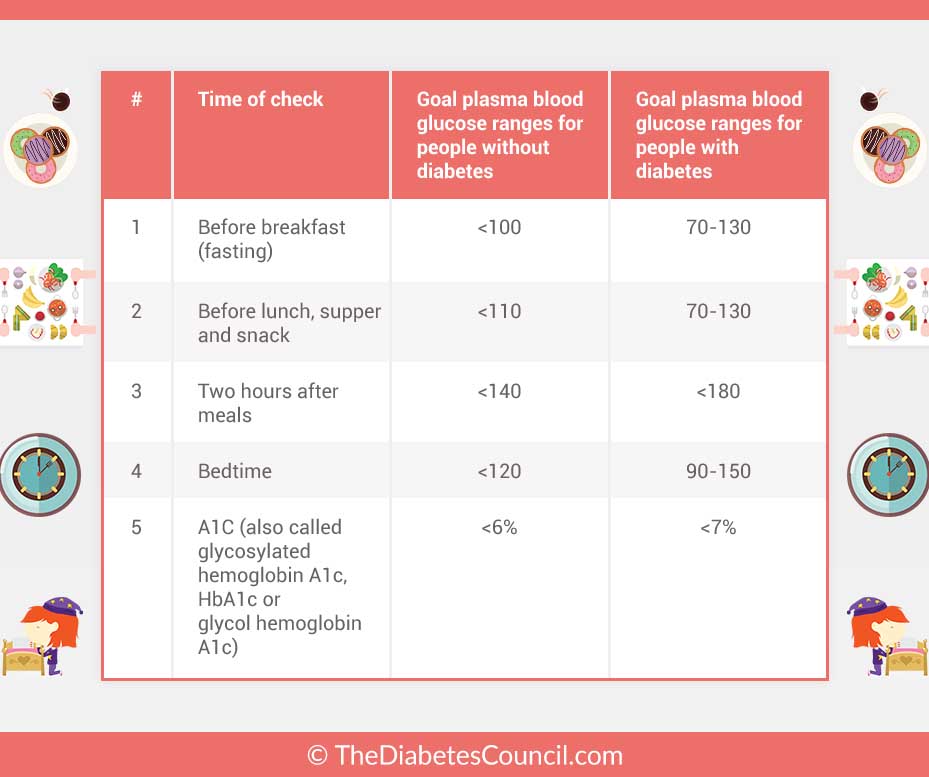
If you eat first thing in the morning, your first blood sugar check of the day can also count as your pre-meal check, but if you dont, youll need to check again before breakfast.;
This can inform you as to how much insulin youll need for your meal . If youre running a little high, youll need to bolus extra, but if your blood sugar is on the lower end, you can take a little less insulin for any carbohydrates eaten.;
Checking before every meal and snack can help curb postprandial glucose excursions, otherwise known as the stubborn high blood sugars you sometimes can experience after eating a meal and not adequately bolusing for said meal.;
Ideally, you should also be checking 2 hours after all meals as well, to determine if your meal bolus was adequate, if you took too much insulin, or if you need to adjust and take more insulin.;
Two hours is the recommended time frame, because by then most carbohydrates have been absorbed into the body and most fast-acting insulin has already peaked.;
When checking before snacks , make sure youre calculating any active insulin on board so you dont overtreat a high and end up going low.;
Don’t Miss: What Is High Blood Sugar Levels Chart
When Should You Test Your Blood Sugar
Blood sugar testing is important for controlling type 2 diabetes. Find out what goes into determining the best testing schedule for you.
Blood sugar testing is a fundamental part of treating type 2 diabetes. By obtaining regular blood sugar readings, people with diabetes can, among other things, help their doctor make more informed decisions regarding the type and dosage of medication they need. Blood sugar testing also can help you see what foods, events, and activities trigger highs and lows in your blood sugar levels.
So how often should you test your blood sugar? The answer depends mostly on the status of your health and the demands of your daily life.
People with type 2 diabetes should take a blood sugar reading at least once a day. Some may need to test as frequently as seven times a day. Whether you need to or are able to perform more frequent testing depends on a number of factors:
You should talk with your doctor about these factors to devise the right blood glucose monitoring schedule for you.
Creating a Blood Sugar Testing Schedule
In general, type 2 diabetes patients should schedule blood sugar testing to coincide with specific daily events. That makes it easier to remember when to test. Regular testing times include:
- Before all three meals
Not Understanding Your Meter
Today’s glucose meters are more sophisticated in their accuracy yet easier to use than ever before. Still, you need to check your meter’s accuracy periodically and you should follow the manufacturer’s instructions for doing this correctly. You also need to know the fine points on how to use it and care for it, and what the error messages mean.
The solution for better diabetes control: If you’re confused about the ins and outs of your meter, ask for help from your doctor, diabetes educator, or pharmacist.
You May Like: How To Reduce Blood Sugar With Food
Normal Blood Sugar Levels In Children
Younger than 6 years old mg/dL
| Bedtime; | 100-140 |
Adults who are 20 years or older will have blood sugar levels that range between less than 100-180 mg/dL over the course of a day. When you wake up in the morning, your fasting blood sugar should be at its lowest because you havent consumed food for about eight hours. If youre an adult and struggling with glucose control, your healthcare provider can help you develop a treatment plan to manage your blood sugar better.;;;
Blood glucose levels outside the ranges listed above are categorized as either high or low blood sugar. Blood sugar levels are considered high if theyre over 130 mg/dL before a meal or 180 mg/dL within one to two hours after a meal. Many people wont start to experience symptoms from high blood sugar until their levels are at 250 mg/dL or higher. The highest blood sugar level thats considered safe will depend on the person and whether they have diabetes, but will typically be between 160 to 240 mg/dL.;
What Is The A1c Test
The A1C test; is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2 or 3 months. The test is done at a lab or your doctors office in addition tonot instead ofregular blood sugar testing you do yourself.
A1C testing is part of the ABCs of diabetesimportant steps you can take to prevent or delay health complications down the road:
- A: Get a regular A1C test.
- B: Try to keep your blood pressure;below 140/90 mm Hg .
- C: Manage your cholesterol;levels.
- s: Stop smoking;or dont start.
The A1C goal for most adults with diabetes is between 7% and 8%, but your goal may be different depending on your age, other health conditions, medicines youre taking, and other factors. Work with your doctor to establish a personal A1C goal for you.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Sugar Substitute For Baking
What If I Have Trouble Getting To My Blood Sugar Goals
There may be times when you have trouble reaching your blood sugar goals. This does not mean that you have failed. It means that you and your health care team should see if changes are needed. Call your health care team if your blood sugar is often too high or too low. Taking action will help you be healthy today and in the future.
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis
If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms.
When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up in your body and cause diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA. DKA is very serious and can cause a coma or even death. Common symptoms of DKA include:
- Fast, deep breathing.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Stomach pain.
If you think you may have DKA, test your urine for ketones. Follow the test kit directions, checking the color of the test strip against the color chart in the kit to see your ketone level. If your ketones are high, . DKA requires treatment in a hospital.
DKA happens most in people with type 1 diabetes and is sometimes the first sign of type 1 in people who havent yet been diagnosed. People with type 2 diabetes can also develop DKA, but its less common.
Also Check: Is There Sugar In Smirnoff Ice
Recommended Target Blood Glucose Level Ranges
The NICE recommended target blood glucose levels are stated below for adults with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and children with type 1 diabetes.
In addition, the International Diabetes Federations target ranges for people without diabetes is stated.
The table provides general guidance. An individual target set by your healthcare team is the one you should aim for.
| Target Levels |
|---|
*The non-diabetic figures are provided for information but are not part of NICE guidelines.
Recommended Blood Sugar Targets For Most People With Diabetes*
Your targets may not be the same as the examples in this chart. Your targets are important and should be specific to you.
| A1C** | |
| 4.0 to 7.0 | 5.0 to 10.0 |
* This information is based on the Diabetes Canada 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines;for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Canada and is a guide.** A1C is a measurement of your average blood sugar control for the last two to three months and approximately 50 per cent of the value comes from the last 30 days.
You May Like: What Vitamin Stops Sugar Cravings
Blood Sugar Levels During Pregnancy
The NIDDK states that gestational diabetes is high blood sugar that occurs during pregnancy if you were not diabetic before getting pregnant. Healthy blood sugar during pregnancy can help lower your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later. It can also lower the risk of your baby being born prematurely, at a high birth weight, and having respiratory problems.
Blood sugar and insulin levels during the first trimester of pregnancy tend to be lower than usual, but they rise during the late second and early third trimesters. You can be diagnosed with an oral glucose tolerance test .;
These are the steps for the 2-step strategy.
- Drink a solution with 50 grams of glucose about the amount in 1 16-oz. bottle of a soft drink
- Get your blood drawn after 1 hour. IF the value is high, retest
- Fast overnight
- Drink a solution with 100 grams of glucose about the amount in 12 peanut butter cups
- Get your blood drawn immediately and after 1, 2, and 3 hours
Or, your doctor might use the 1-step strategy with a 2-hour OGTT:
- Fast overnight
- Drink a solution with 75 grams of glucose
- Get your blood drawn immediately and after 1 and 2 hours
These are some values to know from NIDKK related to gestational diabetes and healthy blood sugar in pregnancy.
| Time or Situation |
|---|
| Baseline: at least 105 mg/dl1 hour: at least 190 mg/dl2 hours: at least 165 mg/dl3 hours: at least 145 mg/dl |
Blood Sugar Monitoring: When To Check And Why
Managing diabetes is one part investigation and two parts action. Unlike some other diseases that rely primarily on professional medical treatment, diabetes treatment requires active participation by the person who has it. Monitoring your blood sugar level on a regular basis and analyzing the results is believed by many to be a crucial part of the treatment equation.
When someone is first diagnosedwith diabetes, he is usually given a blood sugar meter and told how and when to use it, as well as what numbers to shoot for. However, the advice a person receives on when to monitor and what the results should be generally depend on his type of diabetes, age and state of overall health. It can also depend on a health-care providers philosophy of care and which set of diabetes care guidelines he follows. At least three major health organizations have published slightly different recommendations regarding goals for blood sugar levels.
There is some common ground when it comes to blood sugar monitoring practices. For example, most people take a fasting reading before breakfast every morning. Some people also monitor before lunch, dinner and bedtime; some monitor after each meal; and some monitor both before and after all meals. However, when monitoring after meals, some people do it two hours after the first bite of the meal, while others prefer to check one hour after the start of a meal.
Also Check: What Are The Effects Of High Sugar Levels
What Is The Normal Range For Blood Sugar
In general, the American Diabetes Association’s recommended blood sugar levels are9:
- Between 70 and 130 mg/dL before meals
- Less than 180 mg/dL after meals
Your range is yours alonebased on your health, age, level of activity and other factors. And remember that your target is a range you’d like to stay within, not a single number.
Dont Inject The Insulin Too Deep
Insulin is supposed to be injected into the fat layer under the skin using a short needle. This is referred to as a subcutaneous injection.
If you inject the insulin too deep and it enters your muscle, your body may absorb it too quickly. The insulin might not last very long and the injection could be very painful.
Also Check: When Testing Blood Sugar Levels What Is Normal
When Blood Sugar Is Too Low
Glucose is a sugar that comes from the foods we eat, and it’s also formed and stored inside the body. It’s the main source of energy for the cells of our body, and is carried to each cell through the bloodstream. Our brains depend on glucose to function, even when we’re sleeping.
The is the amount of glucose in the blood. When these levels drop too low, it’s called hypoglycemia . Very low blood sugar levels can cause serious symptoms that need to be treated right away.
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Low Blood Sugar
Different people may feel low blood sugar levels differently. People with low blood sugar may:
- feel hungry or have “hunger pains” in their stomach
- feel shaky or like they’re trembling
- have a rapid heart rate
- feel sweaty or have cold, clammy skin
- have pale, gray skin color
- have a headache
- have seizures or convulsions
- lose consciousness
If you have diabetes, try to remember how your body reacts when your blood sugar levels are low. It may help you figure out when you’re having a low blood sugar level more quickly the next time.
Recommended Reading: Can Too Much Sugar Cause Afib