Glucose Fuels The Brain
Although glucose so far sounds like a bad thing, you wouldnt be able to survive without it. In fact, one of the amazing facts about your brain is that your noggin runs on glucose. According to Harvard Universitys Neuroscience Institute, the brain uses the most energy out of all the bodys organs, and so requires half of the bodys sugar. In addition, glucose is the primary source of energy used by our bodies, Zuckerbrot says. Once your body has used the energy it needs, glucose is stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles, she says. If your body runs low on glucose, the pancreas will release its other hormone, glucagon. Glucagon induces the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream, Zuckerbrot says.
When To Get Urgent Medical Attention
Contact your diabetes care team immediately if you have a high blood sugar level and experience the following symptoms:
- feeling or being sick
- a fever for more than 24 hours
- signs of dehydration, such as a headache, dry skin and a weak, rapid heartbeat
- difficulty staying awake
These symptoms could be a sign of a more serious complication of hyperglycaemia, such as diabetic ketoacidosis or a hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state, and you may need to be looked after in hospital.
Read Also: How Long Do Type 1 Diabetics Live
If Possible Eliminate Long
McIntyre says that too much stress can be a warning that something needs to change. Since long-term stressors affect your long-term blood sugar levels and can cause damage to your overall health, theyre even more worthy of a reevaluation. Is it your job thats tipping you over the edge? If so, he suggests that you have a conversation with your boss on how to improve your work environment, apply for a transfer, or even start the hunt for a new job.
Recommended Reading: Hyperglycemic Diet Plan
How Stress Affects Blood Sugar Levels
Two types of stress can change blood sugar levels:
- Physical stress
- Mental or emotional stress
Each type of stress affects blood sugar levels differently. Physical stress generally causes blood sugar levels to increase. Physical stress includes:
- Illness
Mental or emotional stress has mixed effects, depending on the type of diabetes you have:
- Type 1 diabetes: Mental stress can increase or decrease blood sugar levels.
- Type 2 diabetes: Mental stress generally increases blood sugar levels.
Stress also can affect your blood sugar levels indirectly by causing you to forget about your regular diabetes care routine. When you’re stressed out, you might:
- Exercise more or less
- Not test your blood sugar level as often
- Forget or delay a dose of medication and/or insulin
Your Diet And Anxiety

Many health professionals have said that contemporary Western diets are often overloaded with unhealthy sugars and fats. But anxiety disorders are not likely to be caused by diet alone. Rather, it is believed that a poor diet can trigger or make anxiety symptoms worse by changing the bodys functioning and making it harder for the body and mind to cope with stress.
Thats why those that genuinely want to fight their anxiety may need to look beyond mere dietary changes in order to effectively reduce their anxiety.
Read Also: Is There Sugar In Pedialyte
Your Diabetes Health Care Team
Your diabetes health care team is there to help you with all aspects of your diabetes, including how you feel about it. Share your feelings with them if you feel comfortable to so dothey will give you non-judgemental support and advice. You may want to talk with your:
- GP
- dietitian
- counsellor or psychologist.
Bring this fact sheet to your appointment to help get the conversation started. You will probably feel relieved after sharing your feelings, and it will help your health professional to understand how you are feeling.
Together, you can make plans to manage your anxiety.
What Has Anxiety Got To Do With Diabetes
Anxiety is the most common mental health issue that Australians experience. Among people with diabetes, some have anxiety before a diagnosis of diabetes, while for others, specific fears associated with managing diabetes may trigger anxiety.
The link between anxiety and diabetes is not yet fully understood, and research is ongoing.
What is clear is that anxiety can affect the way people manage their diabetes and, in turn, their physical health. Some examples include:
- checking blood glucose levels continuously due to intense fears of hypos or developing complications
- avoiding injecting in public, or not injecting at all, due to worry about what others might think.
A few years ago I was really anxious, but it wasnt just the diabetes. Diabetes was just one factor, but it was a focal point.
Louise, 27, person with diabetes
Also Check: What Causes High Glucose
Why Your Blood Sugar Drops
The goal of diabetes treatment is to lower your blood sugar. But sometimes, it drops too low. Most people feel symptoms if it goes below 70 milligrams per deciliter . It can happen when you:
- Take too much diabetes medicine
- Skip meals
- Eat less
- Exercise more than normal
People who donât have diabetes can get low blood sugar, too. Some medicines and diseases can cause it. It can also happen if you:
- Drink too much alcohol
- Eat lots of sugary, high-carb foods
Orthopaedic Trauma And Non
Karunakar et al., did a study to analyze the effect of stress hyperglycemia on infectious complications in orthopaedic trauma patients. They divided them into two subgroups based on mean serum glucose greater than 220 mg/dl 3.0 or greater) and concluded that mean perioperative glucose levels greater than 220 mg/dl were associated with a seven times higher risk of infection in orthopaedic trauma patients with no known history of diabetes mellitus .
Chen et al., carried out a prospective observational analysis of 1,257 consecutive patients with no history of diabetes who suffered hip fractures. They measured fasting blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin. They divided all the patients into stress hyperglycemia and non-hyperglycemia groups according to their FBG, and recorded incidence of acute myocardial infarction . Among the patients enrolled, the frequency of stress hyperglycemia was 47.89% and that of AMI was 9.31% and the occurrence of AMI in the SIH group was higher than in the non-hyperglycemia group. The authors concluded that SIH after hip fracture increased the risk of AMI .
Richards et al., studied the relationship of SIH and surgical site infections. They studied 790 patients with orthopaedics injuries who required operative intervention. They found that hyperglycemia with blood glucose levels 200mg/dl and HGI 1.76 was an independent risk factor for 30 day surgical-site infection in orthopaedic trauma patients without a history of diabetes .
Recommended Reading: How To Decrease Sugar Level Immediately
Can High Blood Sugar Cause Anxiety
If you have a chronic disease such as diabetes, do you often get anxious and stressed out? Have you ever pondered over can high blood sugar cause anxiety?
Diabetes is typically a manageable metabolic disorder, however, it can result in anxiety. For some people, concerns related to daily blood glucose level monitoring, long term health effects can create added stress.
Read on to find out more about the association between high blood sugar and anxiety and if anxiety can result in high blood sugar levels as well.
What The Research Says
40% of people with diabetes. This prevalence is much higher than that in the general U.S. population, where the condition affects 18.1% of people.
People with diabetes are at risk of developing low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia. Some of the symptoms of hypoglycemia are identical to those of anxiety.
Additionally, the results of a 2015 animal study suggest that experiencing several episodes of hypoglycemia can increase the likelihood of anxiety. The reason for this may be that hypoglycemic episodes trigger chemical and metabolic changes that physically affect the part of the brain that plays a role in processing anxiety.
Diabetes and anxiety share several symptoms. The American Diabetes Association and the National Institute of Mental Health both list the following symptoms for hypoglycemia and anxiety, respectively:
- feeling on edge or irritable
- difficulty focusing thoughts
The procedures that healthcare professionals use to diagnose diabetes and anxiety are quite different.
Also Check: Vitamins To Stop Sugar Cravings
What Is High Blood Sugar
Hyperglycemia is the medical term describing an abnormally high blood glucose level. Blood sugar is measured in a sample of blood taken from a vein or from a small finger stick sample of blood. It can be measured in a laboratory either alone or with other blood tests, or it can be measured using a handheld glucometer, a small device that allows frequent monitoring of blood glucose levels without the need for a doctors office or laboratory.
Hyperglycemia or high blood sugar is a hallmark sign of diabetes and prediabetes. Normal ranges for blood glucose measurements can vary slightly among different laboratories, but in general a fasting glucose level is considered normal if it is between 70-100 mg/dL. Glucose levels may rise slightly above this range following a meal. Random blood glucose measurements are usually lower than 125 mg/dL.
Dont Miss: Is Milk Bad For Type 2 Diabetes
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of High Blood Sugar Levels
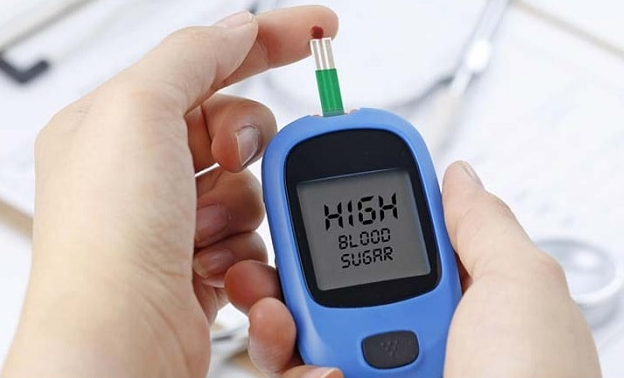
Signs of high blood sugar levels include:
- Peeing a lot: The kidneys respond by flushing out the extra glucose in urine. People with high blood sugar need to pee more often and in larger amounts.
- Drinking a lot: Someone losing so much fluid from peeing that often can get very thirsty.
- Losing weight even though your appetite has stayed the same: If there isnt enough insulin to help the body use glucose, the body breaks down muscle and stored fat instead in an attempt to provide fuel to hungry cells.
- Feeling tired: Because the body cant use glucose for energy properly, a person may feel unusually tired.
page 2
Read Also: What Is Signs Of High Blood Sugar
What Happens To My Blood Sugar Levels When Im Stressed
During stressful situations, epinephrine , glucagon, growth hormone and cortisol play a role in blood sugar levels. Stressful situations include infections, serious illness or significant emotion stress.
When stressed, the body prepares itself by ensuring that enough sugar or energy is readily available. Insulin levels fall, glucagon and epinephrine levels rise and more glucose is released from the liver. At the same time, growth hormone and cortisol levels rise, which causes body tissues to be less sensitive to insulin. As a result, more glucose is available in the blood stream.
When you have type 2 diabetes, low blood sugars from too much medication or insulin are a common cause of stress. The hormonal response to a low blood sugar includes a rapid release of epinephrine and glucagon, followed by a slower release of cortisol and growth hormone. These hormonal responses to the low blood sugar may last for 6-8 hours during that time the blood sugar may be difficult to control. The phenomena of a low blood sugar followed by a high blood sugar is called a rebound or Somogyi reaction.
When you have type 2 diabetes, stress may make your blood sugar go up and become more difficult to control and you may need to take higher doses of your diabetes medications or insulin.
During times of stress, individuals with diabetes, may have more difficulty controlling their blood sugars.
How Are You Sweetening Your Coffee What You Add To Your Cup May Affect Your Blood Sugar Levels
Whether you were recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes or have been living with the condition for several years, you know how fickle blood sugar levels can be, and how important it is that they stay controlled.
Proper blood sugar control is key for warding off potential diabetes complications, such as kidney disease, nerve damage, vision problems, stroke, and heart disease, according to the National Institutes of Health . Plus, keeping your levels in check on a daily basis can help you stay energized, focused, and in a good mood, explains Lisa McDermott, RD, CDCES, a diabetes specialist with the Pittsburgh-based Allegheny Health Network.
According to the American Diabetes Association , proper medication, effective meal planning, regular exercise, and regular blood sugar checks can all help you keep your levels within a healthy range. The ADA recommends blood glucose stay within 80 to 130 milligrams per deciliter before meals and below 180 mg/dL two hours after the start of a meal. Furthermore, the organization recommends getting an A1C test, which measures your average blood glucose over the past two to three months, at least twice per year if your levels are stable and you are meeting treatment goals.
Dont Miss: Insulin Effect On Phosphate
You May Like: What Is Signs Of High Blood Sugar
Anxiety Over Low Blood Sugar
A low blood sugar episode, which can include anything from confusion and shakiness to nausea, loss of consciousness, and seizures, can be very scary. It therefore makes sense that some people with diabetes also experience anxiety related to possibly having a low blood sugar episodeand not just as a physiological reaction to low blood sugar levels.
This anxiety is so common that the term “fear of hypoglycemia” is commonly used among physicians and researchers. Research has found that a history of experiencing mild hypoglycemia increases FoH in people who have diabetes.
Does Stress Cause Diabetes Symptom Flare
People with diabetes have to deal with the same everyday stresses that everyone experiences. However, they have the added pressure of having to monitor their blood sugar regularly, watch their diets and possibly take daily medication. Furthermore, being diagnosed with a chronic health condition can be extremely stressful in itself.
Some individuals locate this tough to handle as well as might experience one thing called diabetes mellitus suffering. It could possibly trigger all of them to disregard their diabetic issues treatment for instance, certainly not inspecting their blood glucose level, working out on a regular basis, or even consuming the appropriate meals. Enhanced booze and also cigarette make use of can easily likewise possess a damaging influence.
As a result, it is actually important that folks along with diabetes mellitus discover helpful stress-management methods to stay away from elevating their blood sugar level and also running the risk of potential difficulties.
Recommended Reading: Is Pedialyte Safe For Diabetics
Is It Time To Ditch Sugar
Its no secret that sugar can cause issues if youre indulging in a little too much of the sweet stuff. Still, most Americans are eating too much sugar.
The harmful effects it can have on your physical health are well studied, which is why we talk so much about reducing sugar intake to lower the risk of these effects, like chronic disease.
While ditching the sweet stuff can result in a physically healthier you, its the effect sugar has on our mental health thats worth taking a second look.
What Are Symptoms Of Depression
Too much stress sometimes can lead to depression. People with diabetes are more likely to be depressed than the average person. You may be at risk for depression if you have any of the following symptoms for more than a week:
- Feeling sad or irritable
- Having lost interest in activities you enjoy
- Feeling worthless
You May Like: Is There Sugar In Pedialyte
Managing Blood Sugars Increases The Risk Of Anxiety
According to the findings from the 2006 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, people with diabetes had a 20 percent higher prevalence of lifetime diagnosis of anxiety than those without. A complementary 2013 meta-analysis, featuring a total of twelve studies with data for 12,626 people with diabetes, supports that diabetes is associated with an increased likelihood of having anxiety disorders and elevated anxiety symptoms.
Diabetes may provoke anxiety related to:
- Anticipating a diagnosis. Some people have anxiety before a definitive diagnosis.
- Managing the condition itself. Anxiety may be triggered by specific fears associated with managing diabetes, including the risks of hypoglycemia or developing complications, including neuropathy and chronic kidney disease.
- Worrying about judgment from others. Some people may be worried about what others think, which may result to noncompliance to diabetes management i.e. avoiding insulin injections in public or altogether.
Managing Diabetes with Confidence
If feeling anxious about managing diabetes, seek out the support from family members and friends and consult with a primary care provider, dietitian, diabetes educator, and other interdisciplinary team members as needed.
Their provision of care can not only help identify methods to control blood sugars, but instill confidence to do so and disseminate the risk of anxiousness surrounding the condition.
A Psychologist Or Psychiatrist
You might also like to talk with a psychologist or psychiatrist. These professionals are best placed to make a diagnosis and provide treatment for anxiety. Treatment may involve the following:
- One-on-one counselling
- Medication
- A combination of psychological therapy and medication.
Ask your diabetes health professional if they know a psychologist or psychiatrist in your area who is familiar with diabetes, or try the following options:
- Find a psychologist near you by going to the Australian Psychological Society website at psychology.org.au/FaP.
- Find a psychiatrist near you by going to the Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists at yourhealthinmind.org/mental-illnesses-disorders/anxiety-disorders.
You will need a referral from your GP to see a psychiatrist, but not to see a psychologist.
Your GP can tell you if you are eligible for a Mental Health Treatment Plan to reduce the costs of seeing a psychologist or psychiatrist.
Read Also: Most Sugar Fruit
Why Low Blood Sugar Makes You Anxious
When your blood sugar drops, your body tries to bring it up. It pumps out , a âfight or flightâ? hormone that, among other things, tells your to make more glucose .
Adrenaline also makes your race and your palms sweat. And it can make you feel cranky and anxious. These are warning signs that your blood sugar is too low. If it stays there, your body puts out more hormones, including one called , also known as the hormone, partially because it helps control things like your mood and fear.
Put adrenaline and cortisol together, and youve got a recipe for .