How Long After Eating Should You Check Your Blood Sugar
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
The Effects Of Protein And Fat
The rate at which food leaves your stomach, called gastric emptying, affects the amount of sugar in your blood after you eat. Protein and fat both slow down gastric emptying, which helps keep blood sugar lower shortly after a meal. In a study published in 2016 in the journal Diabetologica, people who ate high protein-foods before eating carbohydrates , experienced a rise in glucagon, which is thought to play a role in slowing down gastric emptying.
Read more:What Is a Healthy Blood Sugar Reading in the Morning?
Plus, says Palinski-Wade, “if you’re eating a meal that has a large amount of fat or protein, the fat, the protein or the fiber will slow down the absorption and conversion of the sugar, so the peak might be a bit delayed.” She suggests eating carbs with at least one good source of fiber, protein or fat. “Not only is it going to help with the release of blood sugar,” she says, “but it’s also going to help keep you more satisfied.”
Diagnosing Prediabetes Type 2 And Type 1 Diabetes
Depending on which country or medical organization you ask, the qualifying numbers for normal versus prediabetes versus diagnosed type 1 or type 2 diabetes can vary slightly. The following blood sugar and A1c the general results are used to diagnosed prediabetes and diabetes according to sources including the American Diabetes Association and Diabetes UK:
Prediabetes
- HbA1c: 5.7 to 6.4 percent
- Fasting: 100 to 125 mg/dL
- 2 hours after a meal: 140 mg/dL to 199 mg/dL
Type 1 or 2 diabetes
- HbA1c: 6.5 percent or higher
- Fasting: 126 mg/dL or higher
- 2 hours after a meal: 200 mg/dL or higher
Please note: Type 1 diabetes tends to develop very quickly which means that by the time symptoms are felt, blood sugar levels are generally well above 200 mg/dL all the time. For many, symptoms come on so quickly they are dismissed as the lingering flu or another seemingly ordinary virus.
By the time blood sugar levels are tested, many newly diagnosed type 1 patients will see levels above 400 mg/dL or higher. If you do suspect that you or a loved-one has type 1 diabetes, visit your primary care or urgent care immediately and ask for a urine test to measure ketones in addition to testing blood sugar levels and A1c.
Read more about ketones at diagnosis in Diabetes StrongsDiabetic Ketoacidosis Guide.
You May Like: Is There Sugar In Pedialyte
Hours After Eating A Meal
Checking your blood sugar approximately 1 to 2 hours after eating is hugely important, because it tells you if your body has the tools it needs in order to handle your meals. Being consistently higher or lower than your goal range after eating can tell you some very important and clear things about your current diabetes management regimen.
A high blood sugar level 1 to 2 hours after eating could suggest:
- What you ate or drank at your last meal was more than your body could handle on your current diabetes management regimen.
- Your body may need some extra help from a diabetes medication.
- Your current diabetes medications may need a change in dosage.
- Your current diabetes medication may not be the right fit for you.
- Its time to try a different type of diabetes medication.
A low blood sugar level in the hours after eating could suggest:
- Youre getting too much of a certain diabetes medication .
- Your insulin sensitivity or insulin production has improved, which means your medication dosages need to be adjusted by your healthcare team.
Talk to your healthcare team about making any adjustments to your diabetes regimen to help you achieve your blood sugar goals.
Normal Hba1c For Person Without Diabetes

For someone who does not have diabetes, a normal HbA1C level is below 5.7%. An A1C between 5.7% to 6.4% is indicative of prediabetes.
Its recommended that adults over the age of 45 or adults under 45 who are overweight and have one or more risk factors for diabetes have a baseline A1C checked. If the result is normal, the A1C should be checked every 3 years. If the result indicates prediabetes, the A1C should be checked every 1 to 2 years.
Read Also: How To Reduce Blood Sugar Level Immediately
How To Improve Blood Test Results
Identifying the foods or meals that regularly spike your blood sugar too high, too fast, or too long can help you to individualize your diet for longevity.
After a few weeks of testing your blood sugar levels after eating various types of food, you should have a clear record of how your body responds.
A balanced blood sugar results in a greater sense of wellbeing, having more energy, preventing the afternoon crash and feeling hangry , and getting a better nights rest.
Heres what It feels like to have normal blood sugar:
- No extreme hunger between meals
- No sleepiness after meals or mid-day
- Balanced mood
Four Hours After Eating
If you’re generally healthy or are properly managing your diabetes, your blood glucose should fall between 90 and 130 milligrams per deciliter four hours after eating. If you’re not diabetic, your sugar could even go as high as 140 milligrams per deciliter after meals. Of course, if you are a diabetic, your blood glucose could rise even higher — 180 milligrams per deciliter or above, even several hours after eating.
Also Check: Is There Sugar In Pedialyte
Why Do People Get Blood Sugar Spikes After Meals
When people eat a meal, especially when it contains carbohydrates, it is normal for them to have a temporary spike in their sugar level before the insulin their body produces immediately starts working to lower the spike. For someone with type 1 diabetes, who cant produce their own insulin, these spikes can be higher and last longer.
This is because it can take longer for the type of insulin they inject to start working, in comparison to the insulin that is produced naturally by the body of someone who does not have diabetes, to reduce these post-meal spikes.
Furthermore, it is important to know that people living with type 1 diabetes may have alterations in different digestive enzymes which will cause faster digestion of our meals . This can obviously impact on the size of the spike too.
How To Measure Your Spikes
The American Diabetes Association recommends you check your blood sugar levels right before mealtime with a blood sample from a finger stick. Then do it again 1 to 2 hours after that first bite of food.
Keep this up for a week or so. Write down the time and the blood sugar number. Make a note about anything you think might affect your levels, like medicine or exercise. And donât forget to log exactly what you ate, along with portion sizes and the amount of carbs.What levels are too high after a meal? Experts vary on what the number should be, but the ADA says a general goal is a blood sugar level under 180 mg/dL, 1 to 2 hours after a meal. Talk to your doctor about what you should aim for, and donât adjust your medicine without speaking to them first.
Don’t Miss: Are Bananas Bad For Blood Sugar
Which Is Right For You
Finding the best glucose monitoring system that is right for you is about finding the choice that best suits your needs. By considering the benefits and limitations between the different systems that are available in Canada, you can find a system that meets your individual requirements while improving the efficiency and effectiveness of your diabetes care routine.
Our glucose monitoring comparison chart provides a summary of CGM, Flash glucose monitoring devices and test strips and meters.
Planning For Sick Days
Your body releases stress hormones when you are sick, which can cause hyperglycemia. Keep taking your insulin and other diabetes medications, even if you are throwing up. If you have ketones and your blood sugar is above 240 mg/dL, call your doctor. They might also want you to call if:
- You have diarrhea that lasts more than 6 hours
- You are throwing up
- You have a high fever or trouble breathing
- You feel very sleepy or confused
Continue checking your blood sugar levels and keep track of the results.
Don’t Miss: What Fruit Contains The Most Sugar
How Do I Check Blood Sugar Level
Checking blood sugar level is very simple thanks to the availability of easy-to-use handheld glucometers. These consumer glucometers have made it very easy to always keep an eye on your blood sugar level. They are an absolute essential for diabetics and also for people trying to maintain their blood glucose level.
- Check out Here how to choose the best diabetic blood sugar meter.
They operate by taking pin-pricks of blood onto a small electrode slip, which when inserted into the device gives a digital readout of the amount of glucose content in the blood. These devices have become extremely popular for their convenience, reliability and accuracy.
An essential laboratory test of blood glucose level is the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test or OGTT. It is a diagnostic test for DM or any glucose intolerance. Here, a blood sugar reading is taken after a 10-12 hour fast. Then another reading is taken after 2 hours after ingesting a measured amount of glucose. This test shows the bodys ability to absorb glucose, thus is a confirmatory test for DM.
The Insulin Injection Technique Is As Follows:
Insulin comes in an airtight bottle that is labeled with the insulin type and the concentration. Before using, mix the contents. It says on the label to roll it gently, not shake it. The reason for this is to prevent foam formation which will make accurate measuring difficult. Some of the types of insulin used in dogs have a strong tendency to settle out of suspension. If it is not shaken properly, it will not mix well, and dosing will not be accurate. Therefore, the trick is to shake it vigorously enough to mix it without creating foam. Since bubbles can be removed , it is more important to mix it well than to worry about foam formation. When you have finished shaking it, turn the bottle upside down to see if any white powder adheres to the bottle. If so, more shaking is needed.
Insulin is a hormone that will lose its effectiveness if exposed to direct sunlight or high temperatures. It should be kept in the refrigerator, but it should not be frozen. It is not ruined if left out of the refrigerator for a day or two and not exposed to direct sunlight, although this is not advisable. Insulin is safe as long as it is used as directed, but it should be kept out of the reach of children.
Don’t Miss: Yogurt With The Least Sugar
Blood Sugar Levels Before And After Eating
Blood sugar levels in our bodies will fluctuate depending on various conditions and circumstances. Here are the different levels:
1. Normal Blood Sugar Levels After Eating
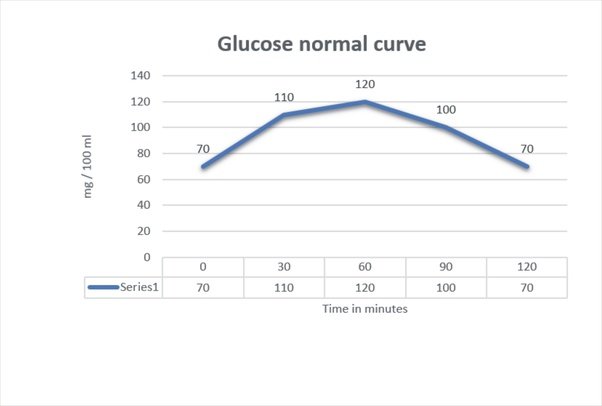
According to the American Diabetics Association, normal blood sugar levels after meals should be 70 mg/dl 140mg/dl.This should be the reading 2 hours after a meal. If the levels are lower than 70mg/dl, it might mean that you have hypoglycemia. If your blood sugar is slightly higher than 140mg/dl, it does not necessarily mean that you have diabetes. However, you might need to have an oral glucose tolerance test later on to determine the severity of your elevated post-meal blood sugar.
2. Normal Levels of Fasting Blood Sugar
This blood sugar level is taken first thing when you wake up before your first meal. A normal level of fasting blood sugar lies from 70mg/dl to 92mg/dl. This is also the blood sugar level for a normal person who has not eaten for the past few hours.
3. Normal Blood Sugar Level for Type 1 Diabetics
American Diabetes Association recommends that blood sugar targets should lie between the following:
Before eating your blood sugar should be:
- Adults: 90-130mg/dl
After 1 to 2 hours after meals, your blood sugar should be:
- Adults: less than 180mg/dl
When going to bed, your blood sugar should be:
- Adults: 90-150mg/dl
4. Normal Blood Sugar Level for Type 2 Diabetics
American Diabetes Association recommends the following blood sugar targets for people with type 2 diabetes:
- Adults: 70-130mg/dl
Whats A Blood Sugar Spike And Why Do They Happen
Postprandial spikes are temporary high blood sugars that occur soon after eating. It is normal for the blood sugar to rise a small amount after eating, even in people who do not have diabetes. However, if the spike is too high, it can affect your quality of life today and contribute to serious health problems down the road.
The reason blood sugar spikes is a simple matter of timing. In a non-diabetic, consumption of carbohydrate results in two important reactions: the immediate release of insulin into the bloodstream, and production of a hormone called amylin which keeps food from reaching the intestines too quickly. In most cases, the after-meal blood sugar rise is barely noticeable.
However, in people with diabetes, the situation is like a baseball player with very slow reflexes batting against a pitcher who throws 98 mph fastballs: the timing is not good. Rapid-acting insulin that is injected at mealtimes takes approximately 15 minutes to start working, 60-90 minutes to peak, and four hours or more to finish working. And dont forget about the amylin hormone effect. In people with diabetes, amylin is either produced in insufficient amounts or not at all. As a result, food digests even faster than usual. The combination of slower insulin and faster food can cause blood sugar to rise absurdly high soon after eating. This is followed by a sharp drop once the mealtime insulin finally kicks in.
Recommended Reading: Which Cells Produce Hormones To Regulate Blood Sugar
Blood Sugar Level After 2 Hours:
Another crucial time to check blood glucose level is about an hour and a half after a meal. Generally, around this time the process of digestion and absorption is near its end. So, high blood sugar during this time generally means that the body cant process sugar properly.
In case of a normal individual, blood glucose level at this time is below 7.8 mmol/L. If the sugar level is 11.1 mmol/L or more, then the individual is considered to be diabetic.
Risks Of High Readings
If you experience spikes in blood glucose after you eat high-carbohydrate meals, your levels will be higher than normal for as much as six to nine hours out of each day. High blood glucose damages blood vessels, which leads to complications such as diabetic retinopathy and neuropathy, or nerve damage. High blood glucose levels after meals also increases your risk of developing atherosclerosis, a build-up of plaque in the arteries that can cause heart attack or stroke.
References
Donât Miss: Why Does Blood Sugar Go Up At Night
Recommended Reading: How To Drop Sugar Level
Right Before Lunch Or Dinner
Checking your blood sugar before your next meal can tell you two things:
- How well your body and/or medication dosages handled your last meal
- How well your body and/or medication dosages handled your blood sugar in the last few hours without food being digested.
Keep in mind that some meals take longer to digest than others. High-fat meals that are also high in carbohydrates can take many hours to digest, affecting your blood sugar for many hours, too.
A high blood sugar level before lunch or dinner could suggest:
- What you ate or drank at your last meal was more than your body could handle on your current diabetes management regimen.
- Your body may need some extra help from a diabetes medication.
- Your current diabetes medications may need a change in dosage.
- Your current diabetes medication may not be the right fit for you.
- Its time to try a different type of diabetes medication.
- Your overall insulin production or insulin resistance level has changed and your body needs more support from a new or current medication.
A low blood sugar level before your next meal could suggest:
- Youre getting too much of a certain diabetes medication .
- Your insulin sensitivity or insulin production has improved, which means your medication dosages need to be adjusted by your healthcare team.
Talk to your healthcare team about making any adjustments to your diabetes regimen to help you achieve your blood sugar goals.
What You Can Drink With Meals
Add a low-calorie, low-sugar drink or choose water. Proper hydration is essential to helping your body remove excess sugar.
Some drinks that are good for keeping your blood sugar level low include:
- Unsweetened tea
- Unsweetened coffee
- Sparkling water or club soda
- Flavored water or sparkling water without added sugar
- Diet soda or other diet drinks
You May Like: How Much Sugar To Add To Hard Cider
What Is A Dangerous Level Of A1c
When levels rise to 9.0, the risk of kidney and eye damage and neuropathy increases. Some people who are newly diagnosed could have levels over 9.0. Lifestyle changes and possibly medication can lower levels quickly. For someone who has long-standing diabetes, levels rise above 9.0 could signal the need for a change in their treatment plan.
Some labs estimate average blood glucose , which corresponds to home glucose meter readings , allowing patients to understand the results better.