Symptoms Signs Causes Of Levels Of High Blood Sugar In The Blood
High blood sugar or hyperglycemia is an abnormally high blood sugar level in the blood. Hyperglycemia is a hallmark sign of diabetes and prediabetes.
Signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia include blurred vision, headaches, hunger, and …
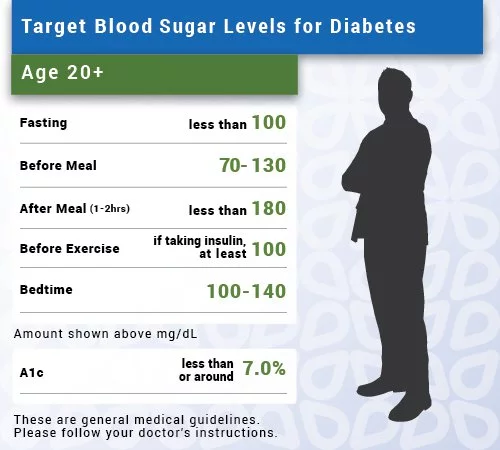
The normal ranges for blood sugar levels in adults who do not have diabetes while fasting are 72-99 mg/dL. These ranges may increase to 80-130 mg/dL for those being treated for diabetes.
According to the American Diabetes Association, people with diabetes should have
- blood sugar levels of 80-130 mg/dL before eating a meal , and
- less than 180 mg/dL about 1-2 hours after eating a meal
High blood sugar ranges for people who dont have diabetes begin at 140 mg/dL, while those being treated for diabetes have a high range beginning at 180 mg/dL.
What Is High Blood Sugar
The is the amount of glucose in the blood. Glucose is a sugar that comes from the foods we eat, and its also formed and stored inside the body. Its the main source of energy for the cells of our body, and its carried to each cell through the bloodstream.
Hyperglycemia is the medical word for high blood sugar levels. High blood sugar levels happen when the body either cant make insulin or cant respond to insulin properly . The body needs insulin so glucose in the blood can enter the cells of the body where it can be used for energy. In people who have developed diabetes, glucose builds up in the blood, resulting in hyperglycemia.
Having too much sugar in the blood for long periods of time can cause serious health problems if its not treated. Hyperglycemia can damage the vessels that supply blood to vital organs, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke, kidney disease, vision problems, and nerve problems. These problems dont usually show up in kids or teens who have had the disease for only a few years. But they can happen in adulthood in some people with diabetes, particularly if they havent managed or controlled their diabetes well.
Blood sugar levels are considered high when theyre above your target range. Your diabetes health care team will let you know what your target blood sugar levels are.
page 1
Preventing A Low Blood Sugar Level
If you have diabetes, you can reduce your chance of getting a low blood sugar level if you:
- Check your blood sugar level regularly and be aware of the symptoms of a low blood sugar level so you can treat it quickly.
- Use a continuous glucose monitor or flash monitor to see how your blood sugar levels are changing. Ask your diabetes care team about getting a monitor if you do not already have one.
- Always carry a sugary snack or drink with you, such as glucose tablets, a carton of fruit juice or some sweets. If you have a glucagon injection kit, always keep it with you.
- Do not skip meals.
- Be careful when drinking alcohol. Do not drink large amounts, check your blood sugar level regularly, and eat a carbohydrate snack afterwards.
- Be careful when exercising eating a carbohydrate snack before exercise can help to reduce the risk of a hypo. If you take some types of diabetes medicine, your doctor may recommend you take a lower dose before or after doing intense exercise.
- Have a carbohydrate snack, such as toast, if your blood sugar level drops too low while youre asleep .
If you keep getting a low blood sugar level, talk to your diabetes care team about things you can do to help prevent it.
Also Check: How Do You Make Sugar Wax At Home
How Do You Treat Hypoglycemia
Low blood sugar levels happen when theres too little glucose left in the bloodstream to continue supplying fuel to your organs, muscles, and tissues. It most often occurs when you dont eat enough food, especially carb-containing foods, given your blood-sugar-lowering medications and physical activity levels, ONeill says. Levels can decrease gradually or suddenly.
When the amount of glucose in the bloodstream drops to too-low levels, the body reacts by releasing epinephrine, also called adrenaline or the fight or flight hormone. Epinephrine revs your heart rate and can cause sweating, shaking, anxiety, and irritability. If not enough glucose is able to reach the brain, the result may be difficulty concentrating, confused thinking, and slurred speech. In extreme cases, a lack of glucose within the brain can lead to seizures, coma, and even death, she says.
People with low glucose levels can use the ADAs 15-15 Rule, which advises people consume 15 g of carbs, wait 15 minutes, and check their levels again. If the number is still low, repeat until reaching at least 70 mg/dL.
You can find 15 g of carbs in:
- 1 slice of bread
- 1 small piece of fresh fruit
- cup of yogurt
- Three to four hard candies
- Glucose tablets as indicated on the label
- Glucose gel as indicated on the label
Once your glucose levels are back to normal, the ADA suggests going ahead and eating your next scheduled meal or snack, which will help prevent levels from dropping again.
Manage Blood Sugar Levels
One of the most important skills to learn is how to manage your blood sugar level. This is true whether you have type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, or gestational diabetes.
Follow your doctor’s instructions on the use of insulin or diabetes medicines, diet, and exercise. They will help you avoid blood sugar problems. You’ll learn to recognize the symptoms and know if they’re from high or low blood sugar levels. Then you can take the right steps to bring your blood sugar back to your target levels.
People who keep their blood sugar levels under control with diet, exercise, or oral diabetes medicines are less likely to have problems with high or low blood sugar levels. Do not drink alcohol if you have problems noticing the early signs of low blood sugar.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Signs And Symptoms Of High Blood Sugar
What Is The A1c Test
The A1C test is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2 or 3 months. The test is done at a lab or your doctors office in addition tonot instead ofregular blood sugar testing you do yourself.
A1C testing is part of the ABCs of diabetesimportant steps you can take to prevent or delay health complications down the road:
- A: Get a regular A1C test.
- B: Try to keep your blood pressure below 140/90 mm Hg .
- C: Manage your cholesterol levels.
- s: Stop smoking or dont start.
The A1C goal for most adults with diabetes is between 7% and 8%, but your goal may be different depending on your age, other health conditions, medicines youre taking, and other factors. Work with your doctor to establish a personal A1C goal for you.
Nighttime Low Blood Sugar
While low blood sugar can happen at any time during the day, some people may experience low blood sugar while they sleep. Reasons this may happen include:
- Having an active day.
- Being physically active close to bedtime.
- Taking too much insulin.
- Drinking alcohol at night.
Eating regular meals and not skipping them can help you avoid nighttime low blood sugar. Eating when you drink alcohol can also help. If you think youre at risk for low blood sugar overnight, have a snack before bed.
You may wake up when you have low blood sugar, but you shouldnt rely on that. A continuous glucose monitor can alert you with an alarm if your blood sugar gets low while youre sleeping.
Don’t Miss: Does Vodka Have Sugar In It
Why The Test Is Performed
Your doctor may order this test if you have signs of diabetes . More than likely, the doctor will order a fasting blood sugar test.
The blood glucose test is also used to monitor people who already have diabetes.
The test may also be done if you have:
- An increase in how often you need to urinate
- Recently gained a lot of weight
SCREENING FOR DIABETES
This test may also be used to screen a person for diabetes.
High blood sugar and diabetes may not cause symptoms in the early stages. A fasting blood sugar test is almost always done to screen for diabetes.
If you are over age 45, you should be tested every 3 years.
If you’re overweight and have any of the risk factors below, ask your health care provider about getting tested at an earlier age and more often:
- High blood sugar level on a previous test
- Blood pressure of 140/90 mm Hg or higher, or unhealthy cholesterol levels
- History of heart disease
- Member of a high-risk ethnic group
- Woman who has been diagnosed with gestational diabetes
- Polycystic ovary disease
- Close relative with diabetes
- Not physically active
Children age 10 and older who are overweight and have at least two of the risk factors listed above should be tested for type 2 diabetes every 3 years, even if they have no symptoms.
How Are High Blood Sugar Levels Treated
Treating high blood sugar levels involves fixing what caused them in the first place. Your diabetes health care team will give you specific advice on how to keep your blood sugar levels in a healthy range. But here are some ways to manage the common causes of high blood sugar levels:
| Reason for High Blood Sugar Level | What to Do |
|---|---|
| Not getting enough insulin or other diabetes medicine |
|
| Not following the meal plan |
|
| Not getting enough exercise | |
|
|
| Use of other medicines that can increase blood sugar |
|
page 3
Also Check: How To Stop My Sugar Addiction
You May Like: How To Treat Low Blood Sugar On Keto Diet
A Few Final Notes On Keeping Blood Sugar Stable
Taking an active, intentional approach to your blood sugar levels is crucial to your quality of life and overall health, ONeill says. Avoiding too-high or too-low blood sugar levels will help you avoid adverse symptoms and health complications, and staying within your target range can enable you to feel your best and do whatever you want to do in life, she says.
Test your blood sugar regularly, listen to your body, and dont ever hesitate to reach out to your doctor.
Additional reporting by Karen Appold.
Symptoms Of Blood Blood Sugar Levels
Symptoms of blood sugar levels differ depending on if it is high or low. To determine which way the blood sugar have moved, the symptoms for each are typically:
| High Blood Sugar Symptoms | |
| Slow healing wounds | Turning pale |
If symptoms are left untreated, more extreme circumstances can happen such as fainting, weakness, disorientation, vomiting and dehydration. When you notice symptoms, usually more than one at one time, it is advised to see a doctor right away.
It is important to get the right treatment so that you can return to a healthy normal blood sugar level and inhibit it from occurring again.
Treatment methods vary from the severity of the blood sugar level, whether it is high or low and if the patient has existing medical conditions, such as diabetes. Here are ways in which blood sugar levels can be treated:
Read Also: What Are Symptoms Of Sugar Being Too High
What Abnormal Results Mean
If you had a fasting blood glucose test:
- A level of 100 to 125 mg/dL means you have impaired fasting glucose, a type of prediabetes. This increases your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- A level of 126 mg/dL or higher usually means you have diabetes.
If you had a random blood glucose test:
- A level of 200 mg/dL or higher often means you have diabetes.
- Your provider will order a fasting blood glucose, A1C test glucose tolerance test , depending on your random blood glucose test result.
- In someone who has diabetes, an abnormal result on the random blood glucose test may mean that the diabetes is not well controlled.
Other medical problems can also cause a higher-than-normal blood glucose level, including:
- Overactive thyroid gland
- Swelling and inflammation of the pancreas ( pancreatitis
- Stress due to trauma, stroke, heart attack, or surgery
- Rare tumors, including
- Weight loss after weight loss surgery
- Vigorous exercise
Some medicines can raise or lower your blood glucose level. Before having the test, tell your provider about all the medicines you are taking.
For some thin young women, a fasting blood sugar level below 70 mg/dL may be normal.
What Are Risk Factors For Hyperglycemia

Major risk factors for hyperglycemia are:
- You have a family history of type 2 diabetes.
- You are African American, Native American, Hispanic or Asian American.
- You are overweight.
- You have high blood pressure or cholesterol.
- You have polycystic ovarian syndrome .
- You have a history of gestational diabetes.
You May Like: What Can Raise Blood Sugar Levels
How Does Hyperglycemia Happen
Insulin is a hormone that lets your body use the sugar in your blood, which comes primarily from carbohydrates in the food that you eat. Hyperglycemia happens when your body has too little insulin to use the sugar in your blood.
People with type 1 diabetes can have episodes of hyperglycemia every day. Although this can be frustrating, it rarely creates a medical emergency. Not taking enough insulin can lead to hyperglycemia .
Other things that can cause hyperglycemia include:
- Having trouble seeing or concentrating
- Experiencing stomach pain, nausea, or vomiting
- Having sweet-smelling or fruity breath
- Cuts or sores that do not heal, infections, and unexplained weight loss may also be signs of long-term hyperglycemia.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should check your blood sugar. If your blood sugar is very high, you should also test for ketones in either your blood or urine.
What Are The Symptoms
While it can sometimes be easy to recognize signs and tell the difference between hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia, at other times it can be hard to tell them apart because of some overlap. For example, confusion and headaches can occur in both cases. Try to be aware of any symptoms you experience that can help you differentiate between the two conditions. And talk to your care team to see if getting a CGM is something that could benefit you. CGM is a great tool to help you know when you are too high or too low.
Though not everyone experiences all of these symptoms every time, and it may take time to learn to recognize these symptoms quickly, here is what can occur with hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia:
|
Hyperglycemia |
You May Like: What Is The Danger Zone For High Blood Sugar
How Is Hypoglycemia Diagnosed
Your doctor will diagnose hypoglycemia based on a physical exam, your health history, your symptoms, and testing of blood glucose. A first step in diagnosis can be to document blood glucose values of less than 70 mg/dL at home when symptoms occur. This may be confirmed with a blood draw.
Timing of hypoglycemia can be important in the diagnosis. Some causes of hypoglycemia are more likely to result in low blood glucose when fasting, while other causes can induce hypoglycemia after meals.
Recommended Reading: Why Do Diabetics Legs Swell
Signs And Symptoms Of Hypoglycemia
The good news is that you can use test strips or a continuous glucose monitor to measure your blood sugar levels, past research establishes. Its important to know that some people can feel symptoms of low blood glucose even if the blood sugar is normal, called pseudohypoglycemia. On the flip side, some mild cases of low blood sugar may not cause any symptoms at all. This is where regular at-home testing becomes important if you have diabetes, especially if you have type 1 diabetes, as established by previous research.
One of the first physical symptoms of hypoglycemia is hunger. At first, you might pass this off as being hangry if you have other symptoms like irritability from not eating in a while. But aside from hunger and irritability, the Mayo Clinic outlines other early signs of hypoglycemia, such as:
- Shakiness, which is especially noticeable in your hands
Dont Miss: Whats The Normal Diabetes Level
You May Like: Which Vodka Has The Least Amount Of Sugar
Sugar And Cholesterol: Whats The Link
On average, Americans take in 22 teaspoons of added sugars a day that can add up to 350 extra calories.
Added sugars are different from the ones naturally found in things like fruits or milk. Added sugars includes sweeteners you add to your food, like:
- Artificial sweeteners made from high fructose corn syrup.
Added sugars contain calories but not nutrients. These additional empty calories, besides affecting your weight and raising your chances for diabetes, also impact your cholesterol levels. And sugary foods affect your liver, which makes cholesterol.
Itâs important to understand that your body needs cholesterol to work well. Itâs a key ingredient your body needs to build new cells.
There are two types of cholesterol:
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol . When you have high levels of this “bad” cholesterol, the waxy, fat-like substance can build up in the walls of your arteries and can clog it. This raises your chances for a heart attack or a stroke.
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol . This is the “good” cholesterol. It picks up all the extra LDL in your bloodstream, takes it back to the liver, which then removes it from your body. HDL also lowers your chances of heart disease.
When you eat too much sugar, your liver makes more LDL while lowering the amount of HDL in your body.
Triglycerides are stored in your fat cells and released between meals when your body needs more energy.