How Can I Treat Low Blood Sugar
If youve had low blood sugar without feeling or noticing symptoms , you may need to check your blood sugar more often to see if its low and treat it. Driving with low blood sugar can be dangerous, so be sure to check your blood sugar before you get behind the wheel.
Carry supplies for treating low blood sugar with you. If you feel shaky, sweaty, or very hungry or have other symptoms, check your blood sugar. Even if you dont have symptoms but think you may have low blood sugar, check it. If your blood sugar is lower than 70 mg/dL, do one of the following immediately:
- Take four glucose tablets.
- Drink four ounces of fruit juice.
- Drink four ounces of regular soda, not diet soda.
- Eat four pieces of hard candy.
Wait for 15 minutes and then check your blood sugar again. Do one of the above treatments again until your blood sugar is 70 mg/dL or above and eat a snack if your next meal is an hour or more away. If you have problems with low blood sugar, ask your doctor if your treatment plan needs to be changed.
Americans Rationing Insulin As Prices Skyrocket
More than half of the people testing their blood sugar at home didn’t need to do this, accounting for 14 percent of the total study population, researchers reported Monday in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“Many Type 2 diabetes patients not using insulin or other medications at risk of rapid changes in blood sugar levels are testing far more often than they need to be,” said the lead study author, Dr. Kevin Platt of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor.
“This needless behavior causes unnecessary pokes, worry and costs,” Platt said by email. “More is not always better when it comes to medical care.”
Type 2 diabetes, the most common form of the disease, is linked to obesity and aging and develops when the body can’t properly use or make enough of the hormone insulin to convert blood sugar into energy. Left untreated, it can lead to complications like blindness, kidney failure, nerve damage and amputations.
Many patients can keep their blood sugar in a healthy range with oral medications and don’t need insulin. Unlike insulin, which immediately affects blood sugar and requires regular testing to ensure that blood sugar is in a healthy range, those on oral medication for diabetes don’t require regular testing because the pills don’t cause rapid shifts in blood sugar, Platt said.
Causes Of Type 1 Diabetes
The bodys immune system is responsible for fighting off foreign invaders, such as harmful viruses and bacteria.
In people with type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakes the bodys own healthy cells for foreign invaders. The immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. After these beta cells are destroyed, the body is unable to produce insulin.
Researchers dont know why the immune system sometimes attacks the bodys own cells. It may have something to do with genetic and environmental factors, such as exposure to viruses. Research into autoimmune diseases is ongoing.
Recommended Reading: Why Is Sugar Level Low
One Last Question: How Much Sugar Can People With Diabetes Have
Grieger adds that there isn’t a set recommendation for the amount of sugar people with diabetes should or should not consume, as sugar is a subgroup of carbs and carbs are important to monitor on a daily basis because they can have a direct effect on blood sugar.
But the 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines recommend keeping added sugar below 10 percent of your overall daily caloric intake. And the American Heart Association suggests consuming no more than 9 teaspoons equal to 36 grams or 150 calories of added sugar if you’re a man, and 6 tsp equal to 25 g or 100 calories if you’re a woman. “Naturally occurring sugars don’t count in these recommendations,” notes Grieger, which means you should worry less about those sugars in fruits and veggies, for instance, than you should about those in processed fare.
To help cut down on added sugar in your diet, keep it simple by avoiding packaged, processed foods, and opting instead for whole foods. Try eating an apple instead of applesauce, an apple pastry, or apple juice, Grieger suggests.
Additional reporting by Melinda Carstensen
If you’re aiming to lower the amount of sugar in your diet, check out Diabetes Daily’s article “10 Ways to Reduce the Sugar in Your Diet!”
What Is Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome

Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome develops more slowly than diabetic ketoacidosis. It occurs in patients with Type 2 diabetes, especially the elderly and usually occurs when patients are ill or stressed.If you have HHNS, you blood glucose level is typically greater than 600 mg/dL. Symptoms include frequent urination, drowsiness, lack of energy and dehydration. HHNS is not associated with ketones in the blood. It can cause coma or death. Youll need to be treated in the hospital.
You May Like: Where Should My Blood Sugar Level Be
What You Eat And Drink
The calories in, calories out philosophy is being drowned out with research on other factors that may be just as important. Don’t get me wrong, limiting calories, carbohydrates or fat can certainly help you lose weight but that’s simply not the only factor for long-term weight loss and maximum energy .
I do, however, support calorie labelling as a tool to help people make informed decisions – the amount and type of calories matter.
Ideally, you need a varied diet full of minimally-processed foods . This simple concept is paramount for diabetes and weight management, energy, and overall health and wellness.
Every day this is what you should strive for:
How Type 1 Diabetes Develops
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease, which means it results from the immune system mistakenly attacking parts of the body. In the case of type 1 diabetes, the immune system incorrectly targets insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
Nobody knows why this occurs, or how to stop it. The immune systems of people with type 1 diabetes continue to attack beta cells until the pancreas is incapable of producing insulin.
People with type 1 diabetes need to inject themselves with insulin to compensate for the death of their beta cells. Everyone with type 1 diabetes is insulin-dependent.
Read Also: Is There Sugar In Pedialyte
What Causes Low Blood Sugar
Low blood sugar has many causes, including missing a meal, taking too much insulin, taking other diabetes medicines, exercising more than normal, and drinking alcohol. Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL is considered low.
Signs of low blood sugar are different for everyone. Common symptoms include:
- Shaking.
- Dizziness.
- Hunger.
Know what your individual symptoms are so you can catch low blood sugar early and treat it. If you think you may have low blood sugar, check it even if you dont have symptoms. Low blood sugar can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible.
Type 1 Diabetes And Low
Carbohydrates are often made out to be the bad guy in managing type 1 diabetes, but it would be a mistake to think you should avoid them entirely. “That’s a misconception because the main source of energy for humans is carbohydrates,” says Arevalo.
Carbohydrates provide most of the sugar in your bloodstream, which is why the quantity and quality of the carbs you take in matter.
RELATED: The Zero Carb Diet May Be a Simple Way to Lose WeightBut Is It Safe?
“We advise our patients with type 1 diabetes to carb count, which means learning to calculate the total number of carbohydrates in their meal and providing themselves insulin based on this carb amount,” says Dr. Adimoolam.
“The less simple sugars a person living with type 1 diabetes has in their meal, the more stable their blood sugar values will be,” she adds. “In general, we encourage our patients with type 1 diabetes to not restrict or limit carbohydrates, but to follow a healthy, balanced diet.”
Don’t Miss: Does Rice Spike Blood Sugar
Whats The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that impacts 1.25 million American children and adults. For type 1, the immune system destroys the cells that release insulin, eventually leading to the complete inability to produce insulin in the body. Type 1 generally manifests at a young age and lasts a lifetime.
Type 2 diabetes has multiple contributing factors including genetics and lifestyle factors such as obesity and inactivity. The disease generally arises during adulthood and oftentimes can be reversed or controlled through diet and exercise. 90-95% of those diagnosed with diabetes have type 2.
What Are The Complications Of Diabetes
If your blood glucose level remains high over a long period of time, your bodys tissues and organs can be seriously damaged. Some complications can be life-threatening over time.
Complications include:
- Dental problems.
Complications of gestational diabetes:
In the mother:Preeclampsia , risk of gestational diabetes during future pregnancies and risk of diabetes later in life.
In the newborn: Higher-than-normal birth weight, low blood sugar , higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes over time and death shortly after birth.
You May Like: Can You Have Sugar On The Keto Diet
The Difference Between Type 1 And Type 2
30.3 million people have diabetes , in one type or another. 84.1 million adults aged 18 years or older have prediabetes (33.9% of the adult US population. But what exactly is Diabetes? There are a lot of myths and misunderstandings surrounding the disease, particularly when it comes to type 1 versus type 2.
So lets start with the basics.
The two main types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2. In type 1 diabetes , the body completely stops making insulin. People with type 1 diabetes must take daily insulin injections to survive. This form of diabetes usually develops in children or young adults, but can occur at any age.In type 2 diabetes the body produces insulin, but the cells dont respond to insulin the way they should. This is called insulin resistance. In response to this insulin resistance, the pancreas should make more insulin, but in the case of type 2 diabetes, this does not happen. Because of these two problems, insulin resistance and trouble making extra insulin, there is not enough of an insulin effect to move the glucose from the blood into the cells. Type 2 diabetes is more likely to occur in people who are over the age of 40, overweight, and have a family history of diabetes, although more and more younger people, including adolescents, are developing type 2 diabetes.
Its important to know a few things about how your body works before you can take the best care of your diabetes.
Topics featured in this article
Can Prediabetes Type 2 Diabetes And Gestational Diabetes Be Prevented
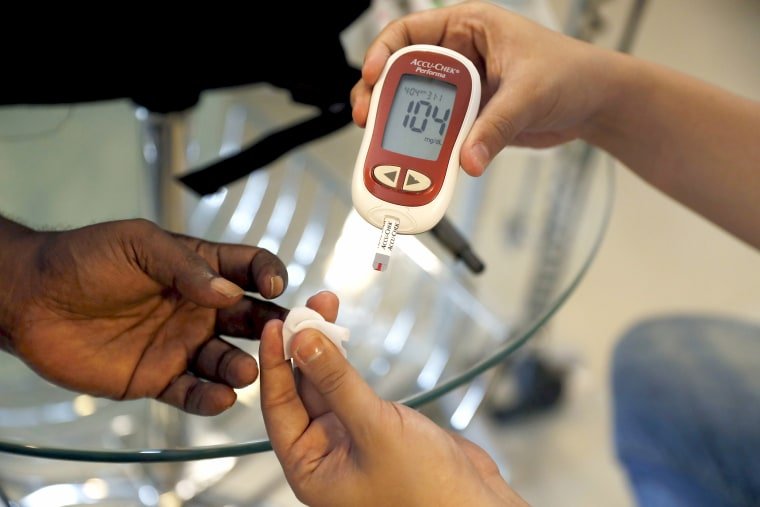
Although diabetes risk factors like family history and race cant be changed, there are other risk factors that you do have some control over. Adopting some of the healthy lifestyle habits listed below can improve these modifiable risk factors and help to decrease your chances of getting diabetes:
- Eat a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean or Dash diet. Keep a food diary and calorie count of everything you eat. Cutting 250 calories per day can help you lose ½ pound per week.
- Get physically active. Aim for 30 minutes a day at least five days a week. Start slow and work up to this amount or break up these minutes into more doable 10 minute segments. Walking is great exercise.
- Lose weight if you are overweight. Dont lose weight if you are pregnant, but check with your obstetrician about healthy weight gain during your pregnancy.
- Lower your stress. Learn relaxation techniques, deep breathing exercises, mindful meditation, yoga and other helpful strategies.
- Limit alcohol intake. Men should drink no more than two alcoholic beverages a day women should drink no more than one.
- Get an adequate amount of sleep .
- Take medications to manage existing risk factors for heart disease or to reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes as directed by your healthcare provider.
- If you think you have symptoms of prediabetes, see your provider.
You May Like: When’s The Best Time To Check Blood Sugar
Why People With Type 2 Diabetes Need Sugar
Refined sugar isn’t the evil carb it once was, but substitutes still have their place.
In the past, sugarwe’re talking about sucrose, or common table sugarwas a “bad guy” to be avoided by people with type 2 diabetes. But research has shown that all carbohydrates can increase blood sugar in roughly the same way.
So if you want to consume sugar in coffee or have a sugar-containing treat, it’s OK as long as it’s in moderation and it’s factored into your meal plan in terms of calories and carbohydrates.
Yellow, blue, or pink: Sugar substitutes in packetsHowever, low-calorie or no-calorie sugar substitutes can be an easy way to cut carbohydrate and caloric intake. And food companies have introduced low-sugar desserts such as ice cream and candy bars, aimed straight at the waistlines and wallets of people with diabetes.
“Sugar-free foods let me give my husband a treat, so he doesn’t feel like he’s denied all the things he liked to eat before,” says Harriet Kritz, who looks after her husband, Karl, 78, who was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes more than 20 years ago.
You have to read the labels even on sugar-free or low-sugar options to be sure you know how many calories and grams of fat and carbohydrates you’re getting along with the sweet taste.
Although some sweeteners don’t contain calories or carbohydrates themselves, the prepared foods that contain themsuch as some yogurtsstill have carbohydrates from other sources.
Next Page: Safe in moderation
They include:
Sugars Diabetes And The Food Environment
Reducing intake of sugars is a healthy choice from many perspectives. From the societal perspective, it would have many health benefits, including preventing and reducing dental caries, reducing obesity, and preventing weight gain, with a favourable impact on other illnesses, such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. From a diabetes perspective alone, reduction of free sugars, specifically SSBs, may have an independent influence on type 2 diabetes risk and gestational diabetes risk. All this said, dietary changes must occur within a societal context.
Read Also: How To Take Your Blood Sugar
How Much Sugar Can A Person With Diabetes Have
If you have diabetes, you may have been told to watch your sugar intake or even eliminate sugar altogether. But does that truly mean you can never ever eat any sugar? Or is there a way for you to enjoy a sweet treat every now and then?
Here we look at how sugar impacts your blood sugar. Read on to learn tips to identify hidden sugars, choose better carbs, and work with your doctor to stick to a diabetes-friendly diet.
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Type 1 Diabetes
People can have diabetes without knowing it because the symptoms aren’t always obvious and they can take a long time to develop. Type 1 diabetes may come on gradually or suddenly.
When a person first has type 1 diabetes, he or she may:
- pee a lot because the body tries to get rid of the extra blood sugar by passing it out of the body in the urine
- drink a lot to make up for all that peeing
- eat a lot because the body is hungry for the energy it can’t get from sugar
- lose weight because the body starts to use fat and muscle for fuel
- feel tired all the time
Also, girls who have developed diabetes are more likely to get vaginal yeast infections before they’re diagnosed and treated.
If these early symptoms of diabetes aren’t recognized and treatment isn’t started, chemicals can build up in the blood and cause stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, breathing problems, and even loss of consciousness. Doctors call this diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA.
There’s good news, though getting treatment can control or stop these diabetes symptoms from happening and reduce the risk of long-term problems.
You May Like: What Happens To Your Body When You Cut Out Sugar
Where Can I Find Help Acquiring Or Paying For Insulin
The ADA has a dedicated page for helping people who need insulin get it, regardless of finances: .
JRDF has a page with a variety of links to organizations who also supply insulin assistance:
The Sugar And Type 2 Diabetes Story: Not So Sweet
After the suspicion that sugar was the cause of diabetes, the scientific community pointed its finger at carbohydrates. That makes sense, notes Grieger, explaining that simple and complex carbohydrates are both metabolized as sugar, leading blood sugar levels to fluctuate.
Yet carbs are processed differently in the body based on their type: While simple carbs are digested and metabolized quickly, complex carbs take longer to go through this system, resulting in more stable blood sugar. It comes down to their chemical forms: A simple carbohydrate has a simpler chemical makeup, so it doesnt take as much for it to be digested, whereas the complex ones take a little longer, Grieger explains.
Sources of complex carbohydrates include whole-wheat bread and brown rice, legumes like black beans, and quinoa. These foods contain fiber, vitamins, and minerals that are appropriate for any eating plan, regardless of whether you have prediabetes, have diabetes, or are perfectly healthy. In fact, experts know including complex carbs in your daily diet can help you maintain a healthy weight, among other health benefits.
You May Like: What Helps To Curb Sugar Cravings